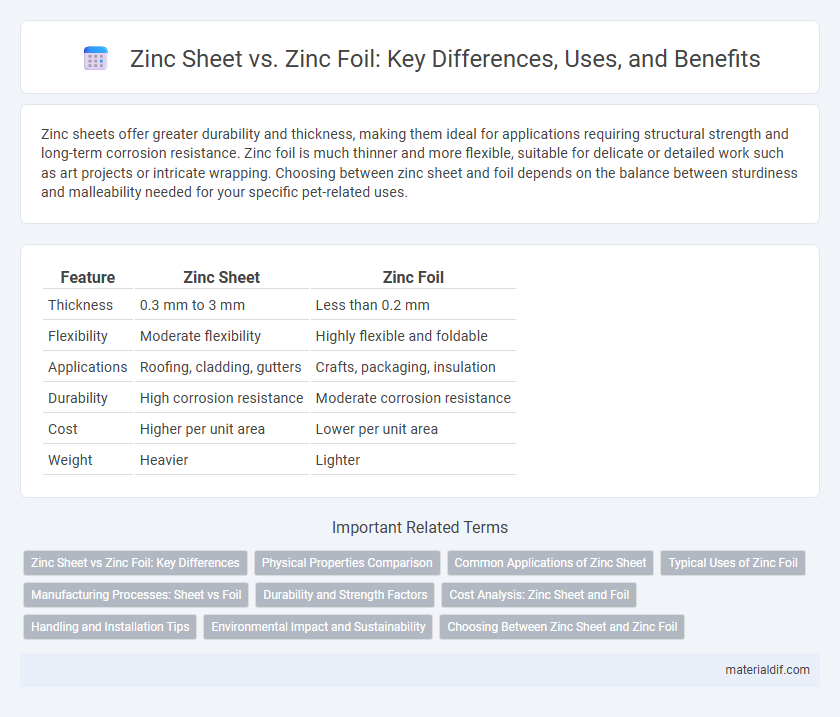
Zinc sheets offer greater durability and thickness, making them ideal for applications requiring structural strength and long-term corrosion resistance. Zinc foil is much thinner and more flexible, suitable for delicate or detailed work such as art projects or intricate wrapping. Choosing between zinc sheet and foil depends on the balance between sturdiness and malleability needed for your specific pet-related uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Sheet | Zinc Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.3 mm to 3 mm | Less than 0.2 mm |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Highly flexible and foldable |
| Applications | Roofing, cladding, gutters | Crafts, packaging, insulation |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance |
| Cost | Higher per unit area | Lower per unit area |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
Zinc Sheet vs Zinc Foil: Key Differences
Zinc sheet is thicker, typically ranging from 0.2mm to several millimeters, providing greater durability and structural support compared to zinc foil, which is extremely thin, often less than 0.2mm, and designed for lightweight applications. Zinc foil offers more flexibility and ease of cutting, making it ideal for detailed work, while zinc sheets are preferred for roofing, cladding, and industrial uses due to their strength and weather resistance. The distinct thickness and mechanical properties of zinc sheets versus zinc foil determine their specific applications in construction and manufacturing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Zinc sheets typically measure between 0.2 to 6 millimeters in thickness, offering greater structural strength and durability, while zinc foils are ultra-thin, usually less than 0.2 millimeters, and provide flexibility and malleability for delicate applications. The density of both forms remains consistent at approximately 7.14 g/cm3, but zinc sheets exhibit higher tensile strength ranging from 110 to 150 MPa compared to zinc foil, which has lower mechanical resistance due to its reduced thickness. Thermal conductivity for zinc sheets and foils is similar, around 116 W/m*K, making both suitable for heat dissipation, though zinc sheets are preferred for environments requiring mechanical robustness.
Common Applications of Zinc Sheet
Zinc sheets are commonly used in architectural cladding, roofing, and gutter systems due to their durability and corrosion resistance. They are favored for manufacturing custom flashings and decorative panels, providing long-lasting protection in outdoor environments. Zinc sheets also play a key role in industrial applications such as chemical processing equipment and roofing membranes.
Typical Uses of Zinc Foil
Zinc foil is commonly used in applications requiring thin, flexible metal layers such as protective barriers in batteries, corrosion-resistant wraps for electronics, and shielding in construction materials. Its malleability and ability to form tight seals make it ideal for pharmaceutical packaging and food preservation to prevent contamination. Compared to zinc sheets, zinc foil provides enhanced adaptability for delicate and precise uses where minimal thickness and flexibility are critical.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheet vs Foil
Zinc sheets are typically manufactured through hot rolling or cold rolling processes, which produce thicker, more rigid metal suitable for structural applications. Zinc foil is created by further processing zinc sheets through extensive cold rolling to achieve extremely thin, flexible layers commonly used in electronics and decorative purposes. The key difference lies in the thickness and flexibility, with sheets offering durability and foils delivering precision in thinness for specialized uses.
Durability and Strength Factors
Zinc sheets typically offer greater durability and strength compared to zinc foil due to their thicker gauge and robust composition, making them ideal for structural and external applications. Zinc foil, being thinner and more flexible, is better suited for decorative or lightweight uses where less mechanical stress is expected. The enhanced tensile strength and corrosion resistance of zinc sheets contribute significantly to their superior performance in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Sheet and Foil
Zinc sheets typically cost more per unit area than zinc foil due to their greater thickness and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications like roofing and architectural cladding. Zinc foil offers a more economical solution for lightweight uses such as decorative elements and small-scale electronics shielding, benefiting from lower material volume and easier handling. Choosing between zinc sheet and foil depends on balancing project requirements against budget constraints, with sheets favored for longevity and foils for cost efficiency.
Handling and Installation Tips
Zinc sheet offers greater rigidity, making it easier to cut and shape without tearing, while zinc foil requires careful handling due to its thinness and flexibility. Use gloves to prevent fingerprints and oxidation during installation of both materials, and employ specialized tools like zinc snips for sheets and fine scissors for foil to ensure precision. Proper surface preparation and secure fastening are crucial to avoid warping and ensure long-lasting adhesion in roofing, cladding, or artistic applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc sheets offer greater durability and longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and overall material waste compared to thinner zinc foil. The production of zinc sheets typically involves less energy-intensive processes per unit area, lowering the carbon footprint relative to zinc foil manufacturing. Furthermore, both zinc sheets and foil are fully recyclable, but zinc sheets' structural integrity enhances the efficiency of recycling streams, improving sustainability outcomes in zinc applications.
Choosing Between Zinc Sheet and Zinc Foil
Choosing between zinc sheet and zinc foil depends on the application requirements, with zinc sheets offering greater durability and structural support for roofing, cladding, or industrial use, while zinc foil excels in flexibility and thinness, ideal for packaging, insulation, or decorative purposes. Zinc sheets typically range in thickness from 0.7mm to 3mm, providing robustness suitable for exterior exposures, whereas zinc foil is usually below 0.2mm, allowing for easy molding and layering. Selecting the appropriate zinc form ensures optimal corrosion resistance and performance based on mechanical strength and application environment.
Zinc Sheet vs Zinc Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com