Sheet zinc forming involves shaping thin, flat zinc materials through bending, cutting, and pressing techniques to create precise, lightweight components suitable for roofing and decorative applications. Extrusion forming pushes heated zinc through a die to produce uniform profiles with consistent cross-sections, ideal for structural parts and custom trims. Comparing these methods, sheet forming offers greater flexibility in surface finishes and design detail, while extrusion provides superior strength and dimensional accuracy for complex shapes.
Table of Comparison
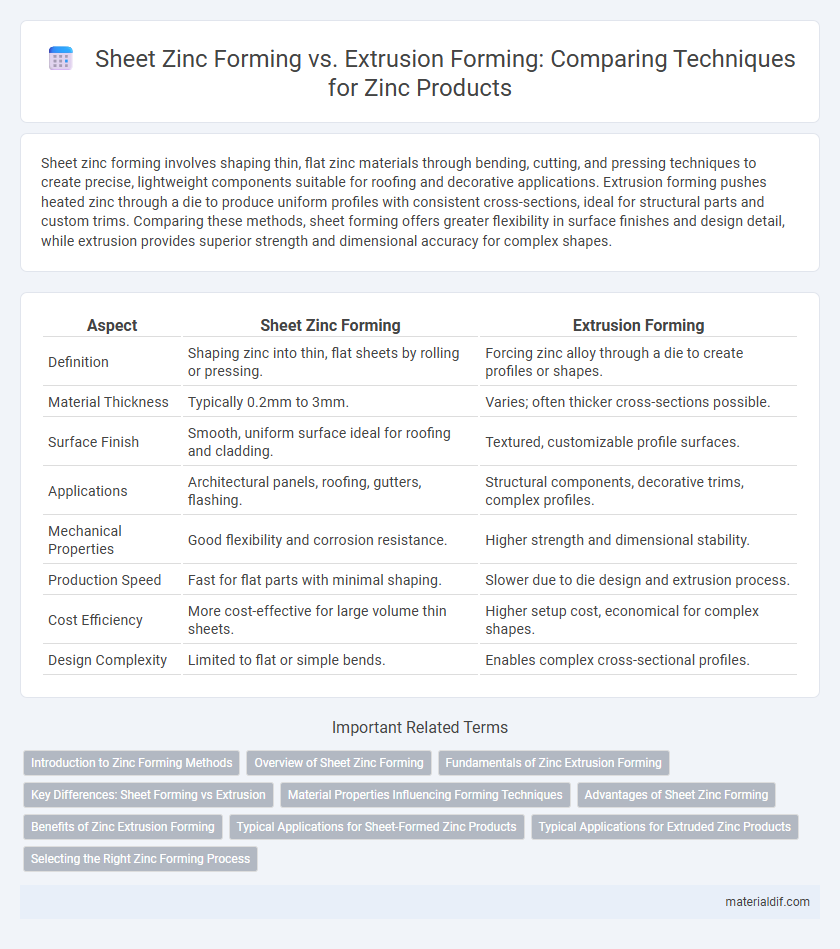
| Aspect | Sheet Zinc Forming | Extrusion Forming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shaping zinc into thin, flat sheets by rolling or pressing. | Forcing zinc alloy through a die to create profiles or shapes. |
| Material Thickness | Typically 0.2mm to 3mm. | Varies; often thicker cross-sections possible. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform surface ideal for roofing and cladding. | Textured, customizable profile surfaces. |
| Applications | Architectural panels, roofing, gutters, flashing. | Structural components, decorative trims, complex profiles. |
| Mechanical Properties | Good flexibility and corrosion resistance. | Higher strength and dimensional stability. |
| Production Speed | Fast for flat parts with minimal shaping. | Slower due to die design and extrusion process. |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective for large volume thin sheets. | Higher setup cost, economical for complex shapes. |
| Design Complexity | Limited to flat or simple bends. | Enables complex cross-sectional profiles. |
Introduction to Zinc Forming Methods
Sheet zinc forming involves processing zinc into thin, flat sheets through rolling, ideal for applications like roofing and cladding due to its flexibility and corrosion resistance. Extrusion forming shapes zinc by forcing it through a die, producing complex profiles used in architectural trims and industrial components that require precise cross-sections. Both methods optimize zinc's malleability and durability, enabling diverse product designs tailored to specific construction and manufacturing needs.
Overview of Sheet Zinc Forming
Sheet zinc forming involves shaping zinc into thin, flat sheets using processes such as rolling and pressing, offering high precision and uniform thickness for applications like roofing and cladding. This method enhances zinc's corrosion resistance and malleability, making it ideal for architectural and industrial uses where surface finish and material performance are critical. Compared to extrusion forming, sheet zinc forming provides superior dimensional control and surface quality essential for creating durable zinc products.
Fundamentals of Zinc Extrusion Forming
Zinc extrusion forming involves forcing heated zinc billets through a die to create complex cross-sectional shapes with precise dimensions, enhancing material strength and surface finish. This process enables the production of high-quality zinc products with intricate profiles that are difficult to achieve through sheet zinc forming, which primarily involves bending and cutting flat zinc sheets. Extrusion forming also offers superior mechanical properties and reduced waste compared to sheet forming methods.
Key Differences: Sheet Forming vs Extrusion
Sheet zinc forming involves rolling zinc into thin, flat sheets ideal for roofing, cladding, and decorative applications, emphasizing surface finish and flexibility. Extrusion forming pushes heated zinc through a die to create complex cross-sectional profiles used in architectural trims, window frames, and structural components, prioritizing strength and detailed shapes. The key difference lies in sheet forming's flat, uniform thickness output versus extrusion's capability to produce intricate, three-dimensional profiles.
Material Properties Influencing Forming Techniques
Sheet zinc forming leverages the metal's excellent malleability and moderate tensile strength, enabling precise shaping through rolling and stamping processes ideal for thin, flat products. Extrusion forming capitalizes on zinc's good ductility and relatively low melting point, facilitating the production of complex cross-sectional profiles with uniform mechanical properties. Material properties such as grain structure, hardness, and thermal conductivity directly influence the choice between sheet forming and extrusion, affecting product performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Advantages of Sheet Zinc Forming
Sheet zinc forming offers superior surface quality and precise dimensional control, making it ideal for architectural and decorative applications. Enhanced workability allows for intricate shapes and fine detailing without compromising material strength. This process provides better corrosion resistance due to the controlled thickness and uniform structure of sheet zinc products.
Benefits of Zinc Extrusion Forming
Zinc extrusion forming offers precise dimensional control and enhanced structural integrity, making it ideal for complex profiles and custom designs in zinc products. This process enables superior mechanical properties and improved surface finish compared to sheet zinc forming. Extrusion forming also allows for greater material efficiency and reduced waste, contributing to cost-effectiveness in zinc component manufacturing.
Typical Applications for Sheet-Formed Zinc Products
Sheet-formed zinc products are widely used in roofing systems, cladding, and rainwater goods due to their excellent corrosion resistance and malleability, enabling precise shaping for architectural designs. These applications benefit from zinc's natural patina formation, which provides long-term durability without frequent maintenance. Typical uses include gutters, downspouts, flashing, and decorative facades that require thin, flat metal sections tailored through sheet forming processes.
Typical Applications for Extruded Zinc Products
Extruded zinc products are commonly utilized in architectural components, including window frames, door frames, and decorative trim, due to their excellent structural integrity and malleability. These forms are also favored in automotive parts and electronic housings where precision and durability are critical. Furthermore, extruded zinc is prominent in manufacturing heat exchangers and battery casings, benefiting from zinc's superior corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
Selecting the Right Zinc Forming Process
Sheet zinc forming offers precise thickness control and is ideal for applications requiring flat, uniform surfaces such as roofing and cladding panels. Extrusion forming enables the production of complex cross-sectional profiles with enhanced mechanical strength, suitable for architectural components and structural elements. Selecting the right zinc forming process depends on the desired shape complexity, surface finish, and mechanical performance requirements of the final zinc product.
Sheet Zinc Forming vs Extrusion Forming (Zinc Products) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com