Zinc injection molding offers precise dimensional control and faster production cycles, making it ideal for complex, high-volume pet components. In contrast, zinc gravity casting provides superior mechanical strength and surface finish, suitable for larger or structurally demanding parts in pet products. Choosing between the two depends on the specific requirements for detail, strength, and production efficiency in zinc pet manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
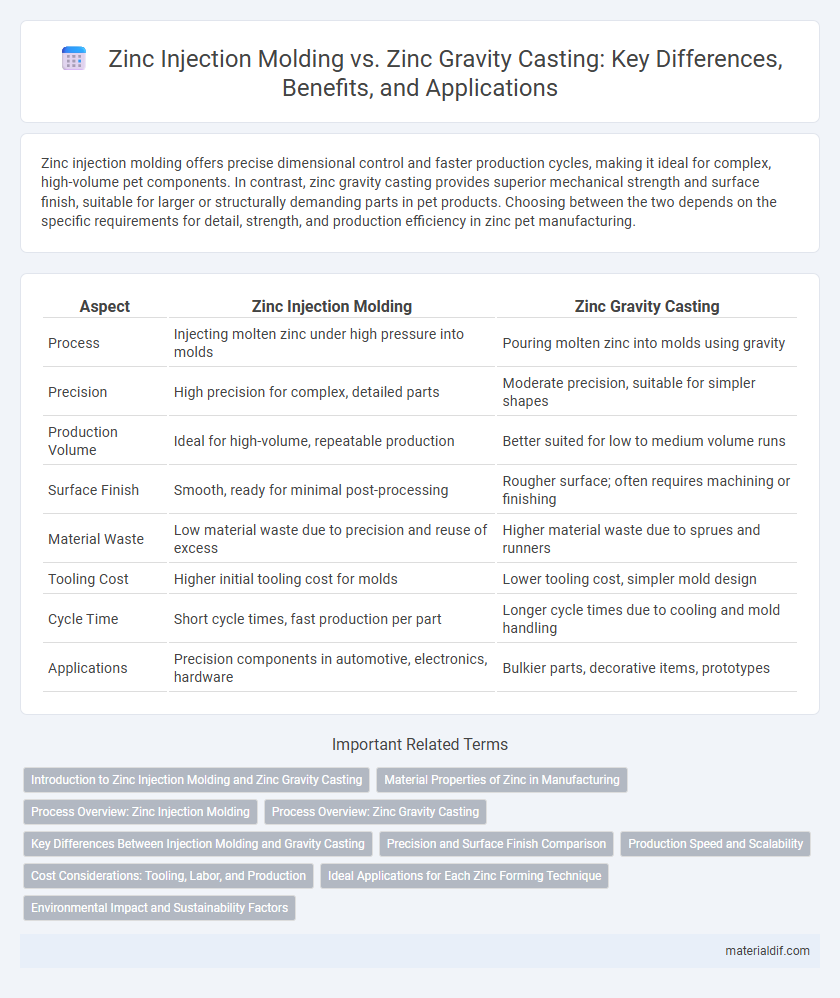
| Aspect | Zinc Injection Molding | Zinc Gravity Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Injecting molten zinc under high pressure into molds | Pouring molten zinc into molds using gravity |
| Precision | High precision for complex, detailed parts | Moderate precision, suitable for simpler shapes |
| Production Volume | Ideal for high-volume, repeatable production | Better suited for low to medium volume runs |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ready for minimal post-processing | Rougher surface; often requires machining or finishing |
| Material Waste | Low material waste due to precision and reuse of excess | Higher material waste due to sprues and runners |
| Tooling Cost | Higher initial tooling cost for molds | Lower tooling cost, simpler mold design |
| Cycle Time | Short cycle times, fast production per part | Longer cycle times due to cooling and mold handling |
| Applications | Precision components in automotive, electronics, hardware | Bulkier parts, decorative items, prototypes |
Introduction to Zinc Injection Molding and Zinc Gravity Casting
Zinc injection molding involves injecting molten zinc alloy into precision-engineered steel molds under high pressure, enabling the production of intricate and dimensionally accurate components with smooth surface finishes. Zinc gravity casting relies on pouring molten zinc into molds using gravity alone, which suits larger parts with less intricate details and offers a cost-effective solution for moderate production volumes. Both manufacturing methods leverage zinc's excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity to produce durable components in automotive, hardware, and electronics industries.
Material Properties of Zinc in Manufacturing
Zinc injection molding offers superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy compared to zinc gravity casting, making it ideal for intricate and high-precision components in manufacturing. The alloy composition in zinc injection molding enhances tensile strength and corrosion resistance, while gravity casting typically results in higher porosity and lower mechanical strength due to slower cooling rates. Material properties like improved density and uniform microstructure in zinc injection molding contribute to better wear resistance and durability in end-use applications.
Process Overview: Zinc Injection Molding
Zinc injection molding involves heating zinc alloy until molten and injecting it at high pressure into a steel mold cavity, producing complex shapes with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. The process enables rapid cooling, resulting in superior strength and fine grain structures compared to gravity casting. Ideal for high-volume production, zinc injection molding offers excellent dimensional accuracy and reduced post-processing requirements.
Process Overview: Zinc Gravity Casting
Zinc gravity casting is a manufacturing process where molten zinc is poured into a mold under the influence of gravity, allowing the metal to fill the cavities slowly and uniformly. This technique produces parts with good dimensional accuracy and a smooth surface finish, suitable for components requiring moderate strength and intricate shapes. The process is cost-effective for medium to large production runs and offers better control over metal flow compared to pressure-based methods like zinc injection molding.
Key Differences Between Injection Molding and Gravity Casting
Zinc injection molding uses high pressure to force molten zinc into precise molds, enabling complex shapes with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. In contrast, zinc gravity casting relies on gravity to fill molds, producing thicker walls and larger parts with less dimensional accuracy and surface detail. Injection molding offers faster production cycles and higher repeatability, while gravity casting is better suited for larger, simpler designs and lower initial tooling costs.
Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
Zinc injection molding offers superior precision and intricate detailing compared to zinc gravity casting due to its ability to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances, often within +-0.05 mm. The surface finish of injection-molded zinc parts typically exhibits a smoother, more uniform texture, minimizing the need for secondary machining or polishing. In contrast, zinc gravity casting results in a coarser surface and less dimensional accuracy, making it less suitable for components requiring high precision and fine surface quality.
Production Speed and Scalability
Zinc Injection Molding offers faster production speeds due to its automated process, enabling high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality. In contrast, Zinc Gravity Casting has slower cycle times, making it less efficient for large-scale production but suitable for complex shapes and lower volumes. Scalability is more favorable in Injection Molding, allowing rapid expansion without compromising precision or throughput.
Cost Considerations: Tooling, Labor, and Production
Zinc injection molding typically incurs higher initial tooling costs due to the complexity of mold design, but offers lower labor expenses and faster production cycles, making it cost-effective for high-volume runs. Zinc gravity casting involves lower upfront tooling costs and simpler molds but demands more manual labor and longer production times, increasing per-unit costs for large batches. Evaluating the balance between tooling investment, labor intensity, and production volume is crucial for optimizing cost efficiency in zinc component manufacturing.
Ideal Applications for Each Zinc Forming Technique
Zinc injection molding is ideal for producing complex, high-precision components with excellent surface finishes, commonly used in electronics, automotive parts, and consumer goods requiring tight tolerances. Zinc gravity casting is better suited for larger, less intricate parts where strength and durability are priorities, such as hardware fittings, plumbing components, and industrial machinery. Selecting between zinc injection molding and gravity casting depends on the desired production volume, part complexity, and mechanical performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Zinc injection molding generates less waste and consumes lower energy compared to zinc gravity casting, enhancing sustainability through efficient material use. Injection molding enables precise control over alloy composition, reducing environmental impact by minimizing scrap and emissions during production. Gravity casting, while versatile, typically involves higher energy consumption and more extensive post-processing, contributing to increased carbon footprint and resource depletion.
Zinc Injection Molding vs Zinc Gravity Casting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com