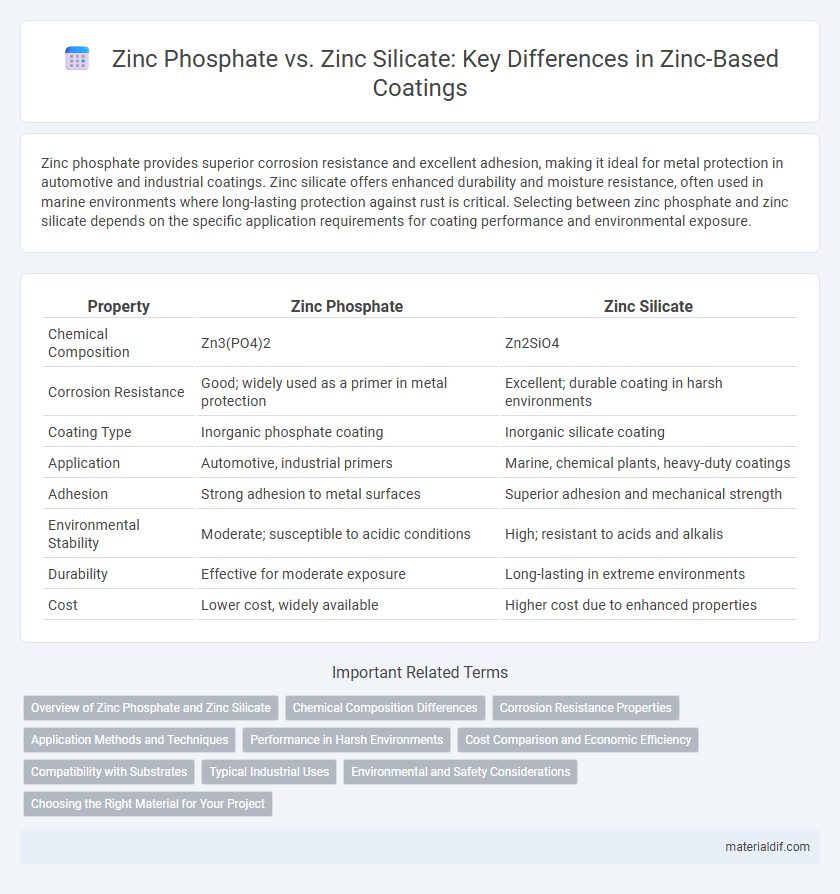
Zinc phosphate provides superior corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion, making it ideal for metal protection in automotive and industrial coatings. Zinc silicate offers enhanced durability and moisture resistance, often used in marine environments where long-lasting protection against rust is critical. Selecting between zinc phosphate and zinc silicate depends on the specific application requirements for coating performance and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc Phosphate | Zinc Silicate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Zn3(PO4)2 | Zn2SiO4 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good; widely used as a primer in metal protection | Excellent; durable coating in harsh environments |
| Coating Type | Inorganic phosphate coating | Inorganic silicate coating |
| Application | Automotive, industrial primers | Marine, chemical plants, heavy-duty coatings |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion to metal surfaces | Superior adhesion and mechanical strength |
| Environmental Stability | Moderate; susceptible to acidic conditions | High; resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Durability | Effective for moderate exposure | Long-lasting in extreme environments |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Overview of Zinc Phosphate and Zinc Silicate
Zinc phosphate is a widely used corrosion-resistant coating primarily applied in automotive and industrial metal surfaces, valued for its strong adhesion and excellent protection against rust. Zinc silicate, known for its inorganic composition, offers superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical exposure, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as coatings for steel structures and machinery. Both compounds serve as essential protective coatings but differ in chemical properties, durability, and specific industrial uses.
Chemical Composition Differences
Zinc phosphate consists primarily of zinc ions combined with phosphate anions (Zn3(PO4)2), forming an inorganic compound known for its corrosion-resistant properties on metal surfaces. Zinc silicate, in contrast, contains zinc ions bonded to silicate anions (Zn2SiO4), offering superior chemical durability and enhanced barrier protection against environmental factors. These distinct chemical compositions influence their applications, with zinc phosphate favored in primer coatings and zinc silicate preferred in high-performance industrial coatings.
Corrosion Resistance Properties
Zinc phosphate coatings provide superior corrosion resistance through their crystalline structure that enhances adhesion and forms a protective barrier against rust on metal surfaces. Zinc silicate coatings offer exceptional durability and chemical resistance, often used in high-temperature or marine environments where long-term protection against corrosion is critical. Comparing both, zinc silicate exhibits better resistance to harsh chemicals and mechanical wear, while zinc phosphate excels in improving paint adhesion and providing effective rust prevention on ferrous metals.
Application Methods and Techniques
Zinc phosphate coatings are primarily applied through immersion, spray, or dip methods, offering excellent corrosion resistance and adhesion for metal surfaces in automotive and industrial painting. Zinc silicate coatings utilize brush, spray, or trowel application techniques, forming a chemically bonded, moisture-resistant layer ideal for protecting steel structures in marine and industrial environments. The choice between zinc phosphate and zinc silicate depends on the substrate, desired durability, and exposure conditions.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Zinc phosphate coatings offer superior corrosion resistance by forming a dense crystalline layer that enhances adhesion and durability in harsh environments. Zinc silicate provides exceptional chemical stability and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive industrial conditions. Both coatings improve metal protection, but zinc phosphate excels in moisture-rich settings while zinc silicate performs better against chemical exposure and heat.
Cost Comparison and Economic Efficiency
Zinc phosphate coatings generally offer a more cost-effective solution due to lower raw material and application expenses compared to zinc silicate, which requires higher purity chemicals and more complex processing. While zinc silicate provides superior corrosion resistance and longevity, its higher initial cost can impact economic efficiency in projects with tight budgets. For large-scale applications prioritizing upfront savings, zinc phosphate remains the preferred choice, whereas zinc silicate suits long-term investments where durability justifies the added cost.
Compatibility with Substrates
Zinc phosphate coatings exhibit superior compatibility with ferrous substrates due to their excellent corrosion resistance and strong adhesion, making them ideal for steel surfaces in industrial applications. Zinc silicate coatings, known for their chemical inertness and high-temperature stability, show enhanced compatibility with both metal and concrete substrates, providing robust protection in harsh environments. The choice between zinc phosphate and zinc silicate depends on substrate material, environmental exposure, and required durability.
Typical Industrial Uses
Zinc phosphate is widely used as an anti-corrosive primer in automotive and marine coatings due to its excellent adhesion and rust-prevention properties. Zinc silicate is favored in heavy industrial settings such as steel plants and offshore platforms because of its long-lasting durability and resistance to high temperatures and chemical exposure. Both compounds serve as protective coatings but zinc silicate outperforms zinc phosphate in harsh, corrosive environments requiring extended service life.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Zinc phosphate coatings offer effective corrosion resistance with lower heavy metal toxicity, making them more environmentally friendly than zinc silicate, which contains higher levels of hazardous silicates and requires solvent-based applications that emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Zinc phosphate is water-based, reducing harmful emissions, while zinc silicate's dependence on organic solvents presents greater fire hazards and environmental pollution. Safety protocols for zinc phosphate involve standard handling procedures, whereas zinc silicate demands stricter ventilation and protective equipment due to its flammability and respiratory risks.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Zinc phosphate offers excellent corrosion resistance and strong adhesion, making it ideal for metal priming in industrial coatings. Zinc silicate provides superior durability and chemical resistance, especially in harsh environments, due to its high zinc content and silicate binder. Selecting the right material depends on environmental exposure, substrate type, and desired longevity for optimal project performance.
Zinc phosphate vs Zinc silicate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com