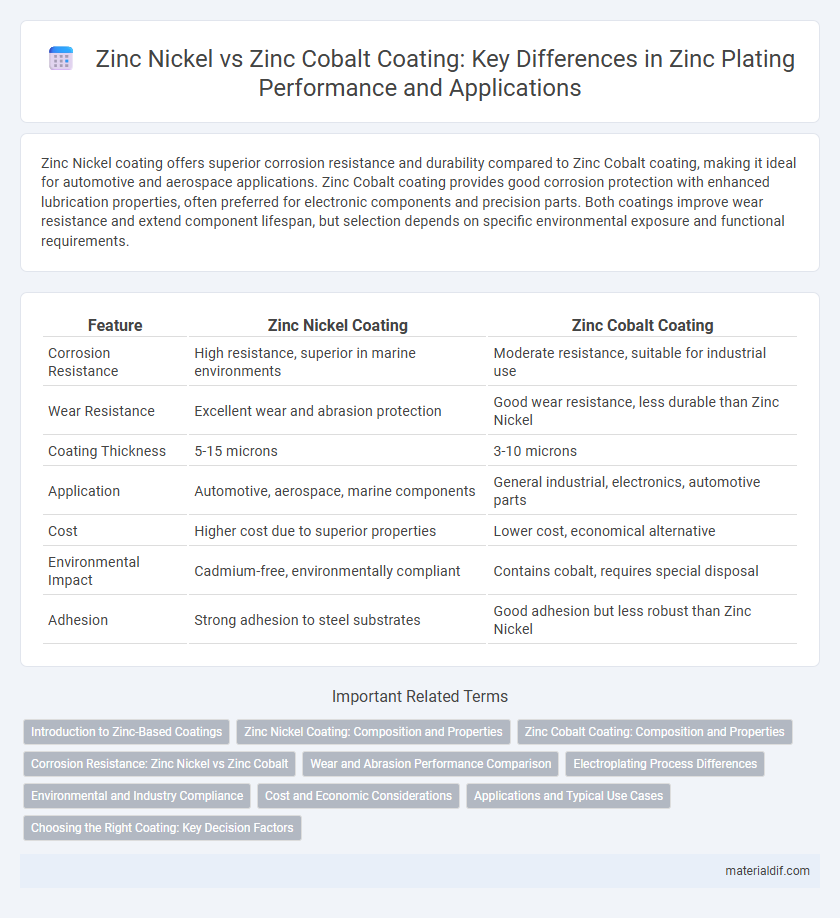
Zinc Nickel coating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to Zinc Cobalt coating, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Zinc Cobalt coating provides good corrosion protection with enhanced lubrication properties, often preferred for electronic components and precision parts. Both coatings improve wear resistance and extend component lifespan, but selection depends on specific environmental exposure and functional requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Nickel Coating | Zinc Cobalt Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance, superior in marine environments | Moderate resistance, suitable for industrial use |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear and abrasion protection | Good wear resistance, less durable than Zinc Nickel |
| Coating Thickness | 5-15 microns | 3-10 microns |
| Application | Automotive, aerospace, marine components | General industrial, electronics, automotive parts |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior properties | Lower cost, economical alternative |
| Environmental Impact | Cadmium-free, environmentally compliant | Contains cobalt, requires special disposal |
| Adhesion | Strong adhesion to steel substrates | Good adhesion but less robust than Zinc Nickel |
Introduction to Zinc-Based Coatings
Zinc-based coatings provide essential corrosion resistance by forming a protective barrier on metal surfaces, with zinc nickel coatings offering enhanced hardness and improved wear resistance compared to conventional zinc cobalt coatings. The zinc nickel layer combines zinc's sacrificial protection with nickel's durability, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications requiring long-lasting performance. Zinc cobalt coatings, while effective for basic corrosion protection, typically exhibit lower mechanical strength and shorter service life under harsh environmental conditions.
Zinc Nickel Coating: Composition and Properties
Zinc nickel coating, composed primarily of a zinc and nickel alloy with typical nickel content ranging from 10% to 15%, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc cobalt coatings. Its unique microstructure enhances hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications where durability is critical. The coating's self-passivating nature provides long-lasting protection against oxidation and salt spray, outperforming zinc cobalt in harsh environments.
Zinc Cobalt Coating: Composition and Properties
Zinc cobalt coating typically consists of a zinc matrix alloyed with cobalt at concentrations ranging from 2% to 5%, enhancing corrosion resistance and mechanical durability compared to pure zinc coatings. The presence of cobalt improves passivation properties, resulting in superior resistance to salt spray corrosion, often exceeding 1,000 hours in neutral salt spray tests. This coating is widely used in automotive and industrial applications where prolonged protection against oxidation and wear is critical.
Corrosion Resistance: Zinc Nickel vs Zinc Cobalt
Zinc nickel coatings provide superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc cobalt coatings due to the formation of a dense, adherent passivation layer that effectively protects steel substrates. Zinc cobalt coatings exhibit moderate corrosion protection but tend to degrade faster in harsh environments, making zinc nickel the preferred choice for automotive and aerospace applications. Studies indicate zinc nickel coatings can extend service life by up to 50% more under salt spray testing than zinc cobalt alternatives.
Wear and Abrasion Performance Comparison
Zinc nickel coatings exhibit superior wear and abrasion resistance compared to zinc cobalt coatings due to their denser microstructure and higher hardness values, often exceeding 500 HV. The enhanced durability of zinc nickel plating makes it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring robust surface protection under mechanical stress. Zinc cobalt coatings, while providing corrosion resistance, typically show lower abrasion resistance and wear performance, limiting their effectiveness in high-friction environments.
Electroplating Process Differences
Zinc nickel coating typically utilizes a highly alkaline electroplating bath with precise pH control between 8.0 and 11.5, enabling uniform alloy deposition and enhanced corrosion resistance due to nickel's contribution. Zinc cobalt coating processes often operate in acidic baths with a pH range of 4.5 to 6.5, promoting faster deposition rates and improved adhesion on steel substrates but with comparatively lower corrosion protection. The variation in electrolyte composition, temperature control, and current density between zinc nickel and zinc cobalt electroplating significantly influences coating morphology and functional properties.
Environmental and Industry Compliance
Zinc Nickel Coating exhibits superior corrosion resistance and meets stringent environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH due to its reduced hazardous metal content compared to traditional coatings. Zinc Cobalt Coating, while effective, often contains higher levels of toxic cobalt compounds, raising concerns for industrial compliance in eco-sensitive applications. Industries increasingly prefer Zinc Nickel Coating to balance performance with sustainability and regulatory adherence in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Zinc Nickel Coating typically incurs higher costs due to the price of nickel but offers enhanced corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Zinc Cobalt Coating generally has lower initial costs and is suitable for less demanding environments but may require more frequent recoating, increasing overall expenses over time. Economic considerations often depend on balancing upfront investment with the expected durability and application-specific performance requirements.
Applications and Typical Use Cases
Zinc nickel coating offers enhanced corrosion resistance and is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries for critical components requiring durability under extreme conditions. Zinc cobalt coating, known for its cost-effectiveness and good corrosion protection, is commonly applied in electronics and electrical equipment to prevent oxidation and maintain conductivity. Both coatings serve distinct applications, with zinc nickel favored in high-performance environments and zinc cobalt preferred for moderate protection with budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Coating: Key Decision Factors
Zinc nickel coating offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness compared to zinc cobalt coating, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications where durability is critical. Zinc cobalt coating provides effective sacrificial protection and is often preferred for cost-sensitive projects requiring moderate corrosion resistance. Key decision factors include environmental conditions, budget constraints, and required mechanical properties to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Zinc Nickel Coating vs Zinc Cobalt Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com