Zinc plated surfaces feature a thin layer of zinc applied through electroplating, providing moderate corrosion resistance and a smooth, uniform finish ideal for indoor applications. Zinc coated materials, often produced by hot-dip galvanizing, have a thicker zinc layer that offers superior protection against rust and environmental damage, making them suitable for outdoor and industrial use. Choosing between zinc plated and zinc coated depends on the specific durability requirements and exposure conditions of the pet products.
Table of Comparison
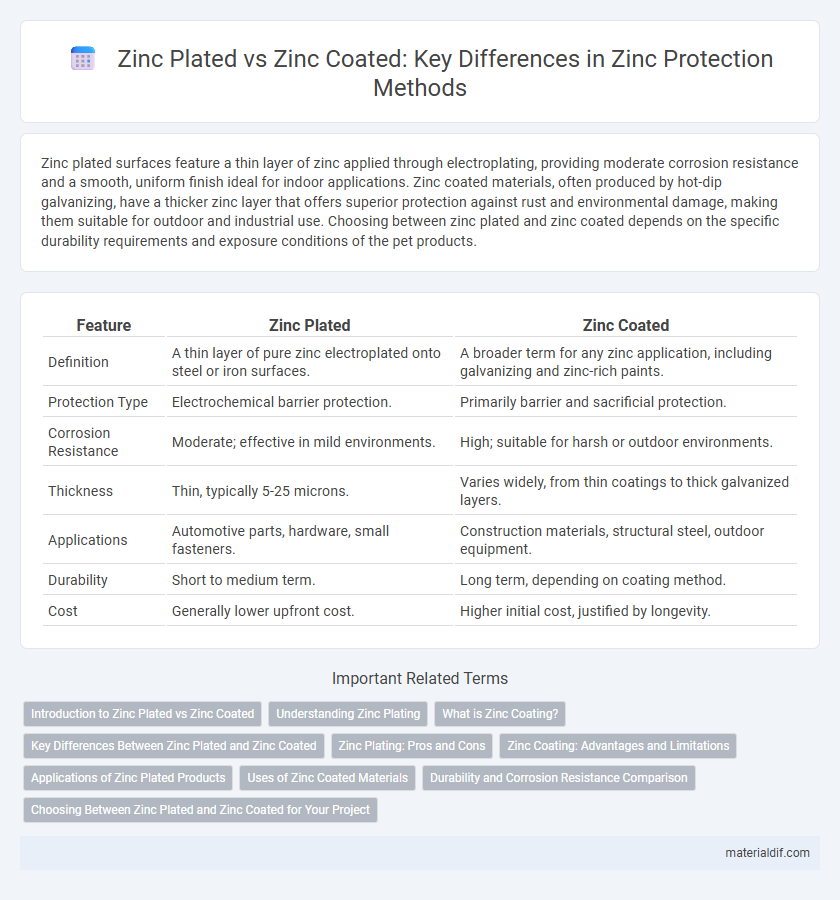
| Feature | Zinc Plated | Zinc Coated |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A thin layer of pure zinc electroplated onto steel or iron surfaces. | A broader term for any zinc application, including galvanizing and zinc-rich paints. |
| Protection Type | Electrochemical barrier protection. | Primarily barrier and sacrificial protection. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; effective in mild environments. | High; suitable for harsh or outdoor environments. |
| Thickness | Thin, typically 5-25 microns. | Varies widely, from thin coatings to thick galvanized layers. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, hardware, small fasteners. | Construction materials, structural steel, outdoor equipment. |
| Durability | Short to medium term. | Long term, depending on coating method. |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost. | Higher initial cost, justified by longevity. |
Introduction to Zinc Plated vs Zinc Coated
Zinc plated and zinc coated refer to surface treatments that protect metal from corrosion by applying a layer of zinc. Zinc plating involves electroplating a thin, uniform zinc layer onto the metal surface, providing enhanced corrosion resistance and a shiny finish. Zinc coating, often achieved through hot-dip galvanizing, applies a thicker zinc layer that offers superior durability in harsher environments.
Understanding Zinc Plating
Zinc plating involves applying a thin layer of zinc onto metal surfaces through electroplating, providing corrosion resistance and enhancing durability. This method creates a uniform, tightly bonded coating that prevents rust and extends the lifespan of steel and iron components. Understanding zinc plating is crucial for selecting appropriate protective finishes in automotive, construction, and industrial applications.
What is Zinc Coating?
Zinc coating is a protective layer of zinc applied to metal surfaces, primarily steel or iron, to prevent corrosion and enhance durability. This coating is typically achieved through processes like galvanization, where molten zinc bonds to the metal, creating a robust barrier against rust. Zinc-plated finishes involve a thinner zinc layer applied through electroplating, while zinc coating generally refers to thicker, more durable layers created by hot-dip galvanizing or mechanical plating.
Key Differences Between Zinc Plated and Zinc Coated
Zinc plated refers to a thin layer of zinc electroplated onto a metal surface to provide corrosion resistance, typically ranging from 5 to 25 microns in thickness. Zinc coated often implies a thicker, more robust layer of zinc applied through hot-dip galvanizing, offering superior durability and protection against rust. The key difference lies in the application process and coating thickness, where zinc coating provides enhanced longevity suitable for outdoor or harsh environments compared to the more decorative and lighter zinc plating.
Zinc Plating: Pros and Cons
Zinc plating offers superior corrosion resistance by creating a thin, uniform layer of zinc on metal surfaces, extending the lifespan of components in moderate environments. The process is cost-effective and enhances aesthetic appeal with its bright, smooth finish but can be prone to wear and less durable in harsh, outdoor conditions compared to thicker coatings. Maintenance involves periodic inspection and potential re-plating to ensure continued protection against rust and oxidation.
Zinc Coating: Advantages and Limitations
Zinc coating provides a robust layer of corrosion resistance by forming a protective barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the underlying metal, extending the lifespan of steel components significantly. It offers advantages such as enhanced durability, cost-effectiveness, and excellent adhesion to the substrate, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications where exposure to harsh environments is common. However, zinc coating has limitations including potential susceptibility to mechanical damage and the gradual thinning of the protective layer over time, which can reduce its effectiveness if not properly maintained.
Applications of Zinc Plated Products
Zinc plated products are primarily used in automotive parts, fasteners, and electrical components due to their corrosion resistance and enhanced aesthetic appeal. These items benefit from a thin, uniform zinc layer that provides effective protection against rust while maintaining electrical conductivity. The application of zinc plating is ideal for indoor environments or areas with minimal exposure to harsh weather conditions.
Uses of Zinc Coated Materials
Zinc coated materials, commonly used in construction, automotive, and electrical industries, provide superior corrosion resistance to steel and iron components, extending the lifespan of structures and machinery. These materials are ideal for outdoor applications such as roofing, fencing, and piping, where exposure to moisture and harsh environmental conditions is frequent. Their protective zinc layer not only prevents rust but also offers excellent adhesion for paint and other finishes, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zinc plated steel offers a thin layer of zinc applied through electroplating, providing moderate corrosion resistance suitable for indoor or low-exposure environments. Zinc coated materials, often galvanized through hot-dip galvanizing, have a thicker zinc layer that significantly enhances durability and corrosion resistance in harsh outdoor or industrial conditions. The thicker zinc coating in galvanized products creates a robust barrier against moisture and oxidation, resulting in longer-lasting protection compared to zinc plated alternatives.
Choosing Between Zinc Plated and Zinc Coated for Your Project
Choosing between zinc plated and zinc coated finishes depends on the specific requirements of corrosion resistance and durability in your project environment. Zinc plated components offer a thin, sacrificial layer ideal for indoor use and light protection, while zinc coated materials provide a thicker, more robust barrier suitable for outdoor and harsh conditions. Understanding the performance characteristics of each finish ensures optimal protection and longevity of your metal parts.
Zinc Plated vs Zinc Coated Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com