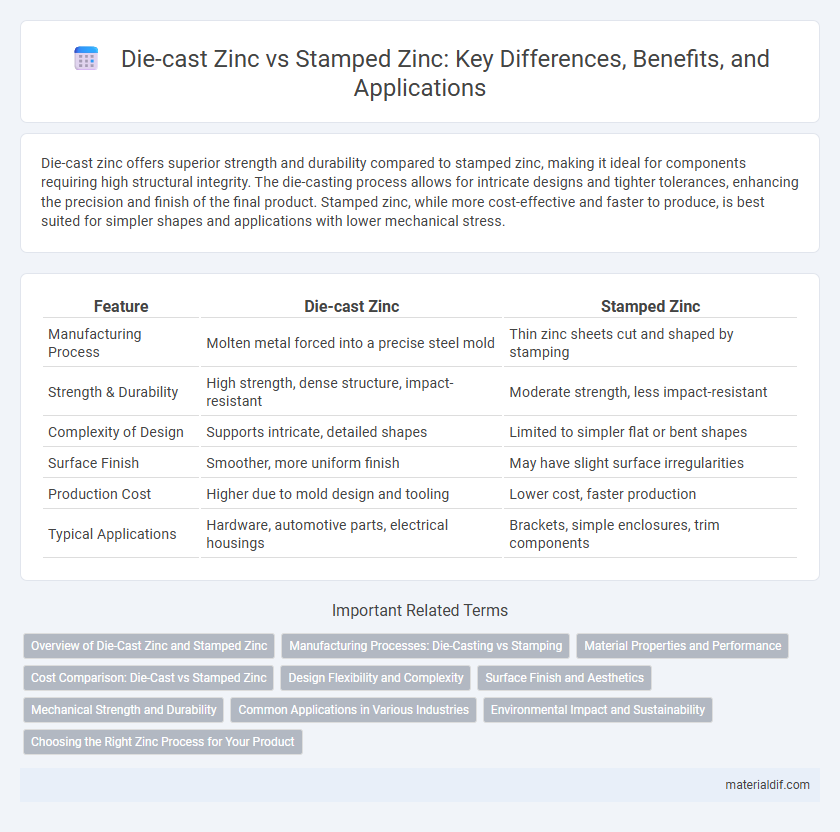
Die-cast zinc offers superior strength and durability compared to stamped zinc, making it ideal for components requiring high structural integrity. The die-casting process allows for intricate designs and tighter tolerances, enhancing the precision and finish of the final product. Stamped zinc, while more cost-effective and faster to produce, is best suited for simpler shapes and applications with lower mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Die-cast Zinc | Stamped Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Molten metal forced into a precise steel mold | Thin zinc sheets cut and shaped by stamping |
| Strength & Durability | High strength, dense structure, impact-resistant | Moderate strength, less impact-resistant |
| Complexity of Design | Supports intricate, detailed shapes | Limited to simpler flat or bent shapes |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, more uniform finish | May have slight surface irregularities |
| Production Cost | Higher due to mold design and tooling | Lower cost, faster production |
| Typical Applications | Hardware, automotive parts, electrical housings | Brackets, simple enclosures, trim components |
Overview of Die-Cast Zinc and Stamped Zinc
Die-cast zinc involves pouring molten zinc into molds to create complex, precise shapes with excellent strength and corrosion resistance, ideal for intricate components. Stamped zinc consists of shaping zinc sheets through high-pressure stamping, offering cost-effective production suited for simple, flat parts with high volume output. Both methods deliver distinct mechanical properties and surface finishes, influencing their application in automotive, hardware, and electronics industries.
Manufacturing Processes: Die-Casting vs Stamping
Die-cast zinc involves injecting molten zinc into a precisely engineered mold under high pressure, enabling the production of complex shapes with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Stamped zinc is created by pressing zinc sheets into desired forms using a die, offering faster production rates but less geometric complexity and lower structural integrity. The choice between die-casting and stamping depends on design requirements, with die-casting favoring intricate designs and stamping suited for simpler, high-volume parts.
Material Properties and Performance
Die-cast zinc exhibits superior strength and dimensional stability compared to stamped zinc due to its dense microstructure and controlled cooling process during casting. The material properties of die-cast zinc offer enhanced corrosion resistance and improved load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability. In contrast, stamped zinc is thinner, more prone to deformation, and generally used for components where weight savings and cost efficiency are prioritized over mechanical performance.
Cost Comparison: Die-Cast vs Stamped Zinc
Die-cast zinc typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex mold production and longer cycle times compared to stamped zinc, which benefits from faster, high-volume sheet metal processing. Stamped zinc parts generally offer cost advantages in large production runs by minimizing material waste and reducing labor expenses. The choice between die-cast and stamped zinc depends on budget constraints, production volume, and the precision requirements of the final product.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
Die-cast zinc offers superior design flexibility and can accommodate complex geometries and intricate details due to its molten metal casting process, enabling precise and consistent shapes. In contrast, stamped zinc is limited to simpler, flatter designs because it involves pressing zinc sheets into shape, which restricts the complexity and dimensional variety. This makes die-casting the preferred choice for applications requiring detailed, robust, and highly customizable zinc components.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Die-cast zinc offers superior surface finish and aesthetics due to its ability to create intricate, smooth, and detailed designs with minimal tooling marks. Stamped zinc typically exhibits rougher edges and less uniformity in appearance, limiting its appeal for high-quality visual applications. The die-casting process also allows for better control of surface textures and coatings, enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic longevity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Die-cast zinc offers superior mechanical strength and durability compared to stamped zinc due to its dense, uniform microstructure formed during the casting process. Stamped zinc, created by compressing sheets, typically exhibits lower tensile strength and is more prone to deformation under stress. This makes die-cast zinc ideal for applications requiring robust load-bearing components and long-term wear resistance.
Common Applications in Various Industries
Die-cast zinc is widely used in automotive components, electrical housings, and hardware due to its high strength and dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for complex shapes and structural parts. Stamped zinc finds common applications in battery terminals, connectors, and decorative trims across electronics and appliance industries, favored for its cost-effectiveness and thin, lightweight properties. Both manufacturing methods serve critical roles in construction, consumer electronics, and automotive sectors, leveraging zinc's corrosion resistance and conductive qualities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Die-cast zinc typically has a higher environmental impact compared to stamped zinc due to its energy-intensive melting and casting processes, which result in greater carbon emissions. Stamped zinc, produced by cutting and shaping sheet metal, offers enhanced sustainability by generating less waste and consuming less energy during manufacturing. Both methods benefit from zinc's recyclability, but stamped zinc generally supports a lower ecological footprint in sustainable production cycles.
Choosing the Right Zinc Process for Your Product
Die-cast zinc offers superior strength, dimensional accuracy, and intricate detail reproduction compared to stamped zinc, making it ideal for complex and high-precision products. Stamped zinc is more cost-effective for high-volume production with simpler shapes but may lack the durability and fine detailing required for premium applications. Selecting the right zinc process depends on factors such as product complexity, production volume, mechanical properties required, and budget constraints.
Die-cast Zinc vs Stamped Zinc Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com