Zinc plates offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for structural applications where strength and longevity are essential. Zinc foil, being thinner and more flexible, is better suited for delicate wrapping and shielding purposes, providing excellent malleability and ease of application. Choosing between zinc plate and zinc foil depends on the specific requirements for thickness, flexibility, and protective capabilities in your zinc pet project.
Table of Comparison
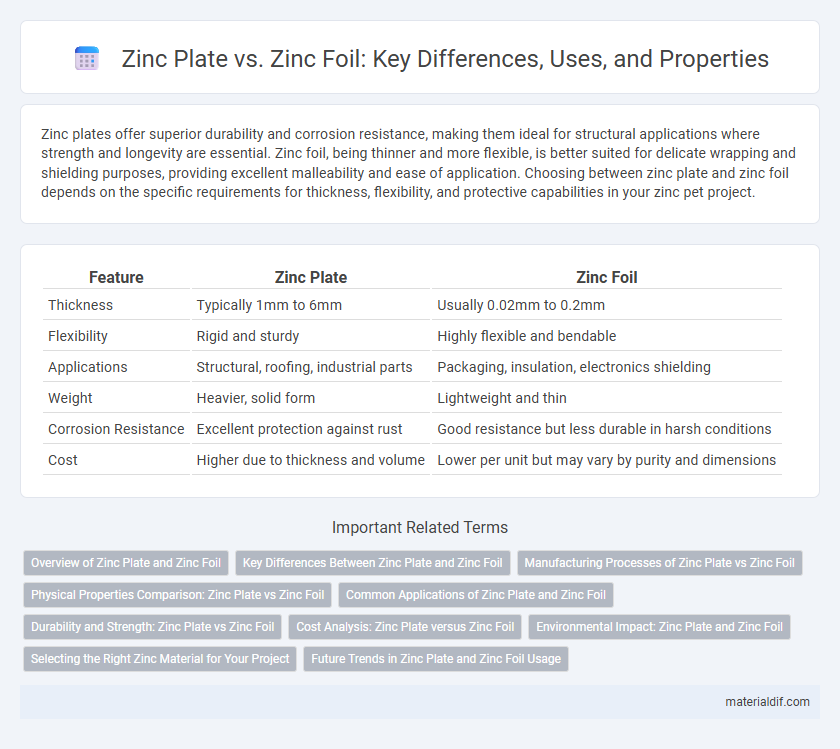
| Feature | Zinc Plate | Zinc Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 1mm to 6mm | Usually 0.02mm to 0.2mm |
| Flexibility | Rigid and sturdy | Highly flexible and bendable |
| Applications | Structural, roofing, industrial parts | Packaging, insulation, electronics shielding |
| Weight | Heavier, solid form | Lightweight and thin |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent protection against rust | Good resistance but less durable in harsh conditions |
| Cost | Higher due to thickness and volume | Lower per unit but may vary by purity and dimensions |
Overview of Zinc Plate and Zinc Foil
Zinc plates are flat, rigid sheets of zinc metal, typically used in construction, corrosion resistance, and industrial applications due to their durability and thickness. Zinc foil, characterized by its thin, flexible, and lightweight nature, is commonly employed in packaging, art, and decorative uses where malleability is essential. Both forms provide corrosion protection but differ significantly in their mechanical properties and application methods.
Key Differences Between Zinc Plate and Zinc Foil
Zinc plate is a thicker, solid sheet primarily used for industrial applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance, while zinc foil is a thinner, more flexible material ideal for delicate or precise work such as laboratory use or packaging. Zinc plates exhibit greater mechanical strength and longer lifespan compared to zinc foil, which is valued for its lightweight and malleability. The manufacturing processes differ, with plates produced through rolling or casting and foils created by rolling zinc into ultra-thin layers.
Manufacturing Processes of Zinc Plate vs Zinc Foil
Zinc plate manufacturing involves a hot-dip galvanizing process where zinc is melted and applied onto steel substrates, producing thicker, durable layers with enhanced corrosion resistance. Zinc foil is created through a cold rolling or rolling mill process that compresses zinc ingots into ultra-thin, flexible sheets suitable for precision applications. The manufacturing differences result in zinc plates offering structural strength, while zinc foils provide versatility in shielding and packaging uses.
Physical Properties Comparison: Zinc Plate vs Zinc Foil
Zinc plate exhibits higher thickness and rigidity compared to zinc foil, providing superior structural strength and durability in industrial applications. Zinc foil, characterized by its thin, flexible nature and lower density, allows for enhanced pliability and ease of wrapping or layering in specialized shielding or decorative uses. The choice between zinc plate and zinc foil depends on the required mechanical strength, flexibility, and application-specific demands such as corrosion resistance or electrical conductivity.
Common Applications of Zinc Plate and Zinc Foil
Zinc plates are commonly used in corrosion protection for steel structures, manufacturing of architectural components, and in battery electrodes due to their durability and thickness. Zinc foil, with its thin and flexible properties, is often utilized in electrical insulation, decorative crafts, and as a barrier material in packaging applications. Both forms provide effective corrosion resistance but serve distinct purposes based on their mechanical properties and application requirements.
Durability and Strength: Zinc Plate vs Zinc Foil
Zinc plates offer superior durability and strength compared to zinc foil, making them ideal for structural applications and environments requiring resistance to wear and impact. Zinc foil, being much thinner and more flexible, provides less mechanical strength but excels in applications where lightweight and malleability are essential, such as shielding and wrapping. The thickness and density of zinc plates contribute significantly to their enhanced longevity and load-bearing capacity.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Plate versus Zinc Foil
Zinc plates generally present a higher upfront cost due to their thickness and durability, which makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications and long-term use. Zinc foil, being thinner and more flexible, tends to be more economical for short-term or lightweight projects, offering cost savings in terms of material consumption and easier handling. When evaluating overall cost efficiency, factors such as application method, lifespan, and material waste should be considered to determine if the initial price difference between zinc plate and zinc foil offsets long-term expenses.
Environmental Impact: Zinc Plate and Zinc Foil
Zinc plate and zinc foil differ significantly in their environmental impact due to production processes and material usage. Zinc plates, being thicker and more durable, often result in higher raw material consumption and energy use during manufacturing compared to the thin, lightweight zinc foil. However, zinc foil's minimal material thickness can lead to increased waste if not properly recycled, while zinc plates generally offer better long-term reuse potential, reducing environmental footprint.
Selecting the Right Zinc Material for Your Project
Selecting the right zinc material depends on the specific requirements of your project, with zinc plate offering durability and thickness suitable for structural applications and heavy-duty shielding. Zinc foil provides flexibility and thinness ideal for intricate designs, wrapping, or corrosion resistance in lightweight assemblies. Consider factors such as strength, malleability, and exposure conditions to determine whether zinc plate or zinc foil best meets your functional and aesthetic needs.
Future Trends in Zinc Plate and Zinc Foil Usage
Rising demand for corrosion-resistant materials is driving increased adoption of zinc plate in automotive and construction industries, while zinc foil is gaining popularity in electronics and medical applications due to its superior flexibility and conductivity. Advancements in eco-friendly and energy-efficient production methods are expected to enhance the sustainability and performance of both zinc plate and foil. Integration of nanotechnology and coating innovations will likely expand the functional properties and application scope of zinc materials in the coming years.
Zinc Plate vs Zinc Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com