Zinc sheet metal offers superior flexibility and is ideal for applications requiring precise bending and shaping, making it well-suited for architectural cladding and roofing. Zinc extrusion provides enhanced structural strength and complex cross-sectional designs, often used in construction frameworks and decorative trims. Choosing between zinc sheet metal and zinc extrusion depends on the specific project demands for durability, formability, and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
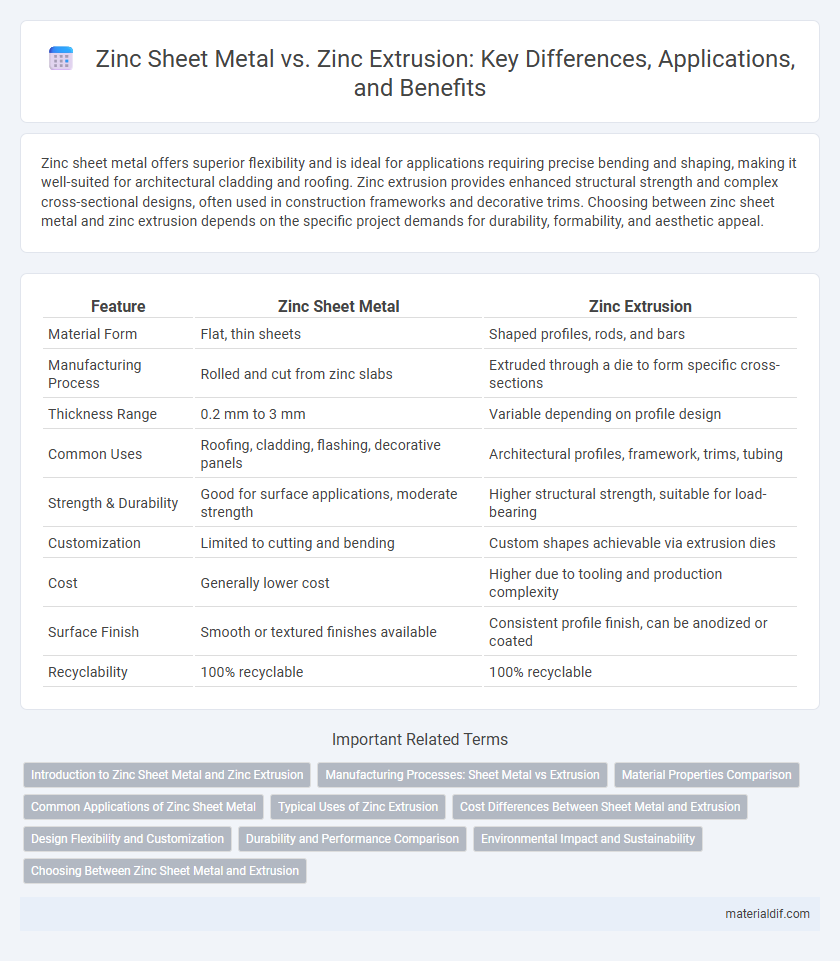
| Feature | Zinc Sheet Metal | Zinc Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Form | Flat, thin sheets | Shaped profiles, rods, and bars |
| Manufacturing Process | Rolled and cut from zinc slabs | Extruded through a die to form specific cross-sections |
| Thickness Range | 0.2 mm to 3 mm | Variable depending on profile design |
| Common Uses | Roofing, cladding, flashing, decorative panels | Architectural profiles, framework, trims, tubing |
| Strength & Durability | Good for surface applications, moderate strength | Higher structural strength, suitable for load-bearing |
| Customization | Limited to cutting and bending | Custom shapes achievable via extrusion dies |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher due to tooling and production complexity |
| Surface Finish | Smooth or textured finishes available | Consistent profile finish, can be anodized or coated |
| Recyclability | 100% recyclable | 100% recyclable |
Introduction to Zinc Sheet Metal and Zinc Extrusion
Zinc sheet metal is a flat, rolled product commonly used in roofing, cladding, and architectural applications due to its malleability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Zinc extrusion involves forcing molten zinc through a die to create complex cross-sectional profiles, ideal for structural components, window frames, and decorative trims. Both materials benefit from zinc's natural patina formation, enhancing durability and longevity in various construction and industrial uses.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheet Metal vs Extrusion
Zinc sheet metal is produced through rolling processes that create thin, flat sheets with uniform thickness ideal for roofing and cladding applications, while zinc extrusions are formed by forcing heated zinc alloy through a die to achieve complex cross-sectional profiles used in architectural and structural components. The rolling method ensures consistent surface finish and dimensional accuracy, whereas extrusion allows for greater design flexibility and strength in custom shapes. Manufacturing techniques impact material properties and application suitability, with sheet metal favored for large surface coverage and extrusions chosen for intricate designs requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity.
Material Properties Comparison
Zinc sheet metal offers superior corrosion resistance and formability due to its uniform thickness and smooth surface, making it ideal for cladding and roofing applications. Zinc extrusion provides enhanced structural strength and design flexibility, allowing complex profiles with increased mechanical durability in architectural and industrial components. Both materials exhibit excellent resistance to atmospheric conditions, but zinc extrusions typically support heavier loads and custom shapes compared to flat zinc sheets.
Common Applications of Zinc Sheet Metal
Zinc sheet metal is widely used in roofing, cladding, gutters, and architectural panels due to its excellent corrosion resistance and malleability. It is also commonly employed in manufacturing decorative elements and protective coatings for various structures. Unlike zinc extrusion, which is ideal for complex profiles, zinc sheet metal is preferred for flat surfaces and simple bends in construction and industrial applications.
Typical Uses of Zinc Extrusion
Zinc extrusion is commonly used in architectural applications, including window frames, door frames, and decorative trims, due to its ability to create complex cross-sectional shapes with high strength and corrosion resistance. Industrial equipment components and electrical enclosures also benefit from zinc extrusion's durability and excellent thermal conductivity. Unlike zinc sheet metal, which is ideal for flat surfaces and roofing, zinc extrusion offers superior mechanical properties for structural and intricate designs.
Cost Differences Between Sheet Metal and Extrusion
Zinc sheet metal generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to zinc extrusion due to simpler manufacturing processes and reduced material waste. Extrusion involves higher energy consumption and specialized equipment, increasing production expenses and resulting in a higher price per pound. For large-scale projects requiring intricate shapes, zinc extrusion justifies the cost, while sheet metal remains more economical for flat or less complex designs.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Zinc sheet metal offers superior design flexibility due to its ability to be easily cut, bent, and formed into intricate shapes, making it ideal for customized architectural and decorative applications. Zinc extrusion provides consistent cross-sectional profiles with precise dimensional control, suitable for complex, repeatable designs but with less variability in shape changes compared to sheet metal. For projects demanding high customization and complex geometries, zinc sheet metal is preferred, whereas zinc extrusion excels in producing uniform, long structural components.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Zinc sheet metal offers superior corrosion resistance and uniform thickness, making it ideal for roofing and cladding applications requiring long-term durability. Zinc extrusion provides enhanced structural strength and design flexibility, suitable for frameworks and intricate profiles exposed to mechanical stress. Comparing performance, zinc sheet metal excels in weather resistance, while extrusion's robust form supports heavy-duty construction with excellent load-bearing capacity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc sheet metal production typically involves rolling processes that consume less energy compared to the high-temperature extrusion method required for zinc extrusion, leading to a lower carbon footprint. Zinc sheet metal is often more easily recyclable due to its uniform thickness and fewer processing steps, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Conversely, zinc extrusion allows for complex shapes but generates more waste and higher emissions, making sheet metal a greener choice in applications prioritizing eco-efficiency.
Choosing Between Zinc Sheet Metal and Extrusion
Choosing between zinc sheet metal and zinc extrusion depends largely on the project's requirements for form and structural integrity. Zinc sheet metal offers flexibility and ease of fabrication for applications like cladding and roofing, while zinc extrusion provides precise shapes and enhanced mechanical strength ideal for structural components and detailed profiles. Evaluating factors such as design complexity, load-bearing needs, and manufacturing costs will guide the optimal selection between these two zinc materials.
Zinc Sheet Metal vs Zinc Extrusion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com