Zinc plating offers a thin, corrosion-resistant layer ideal for small components, providing sacrificial protection against rust. Zinc flake coating delivers a thicker, more uniform barrier that enhances durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for automotive and heavy-duty applications. Both methods improve metal longevity but differ in application techniques and performance characteristics depending on environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
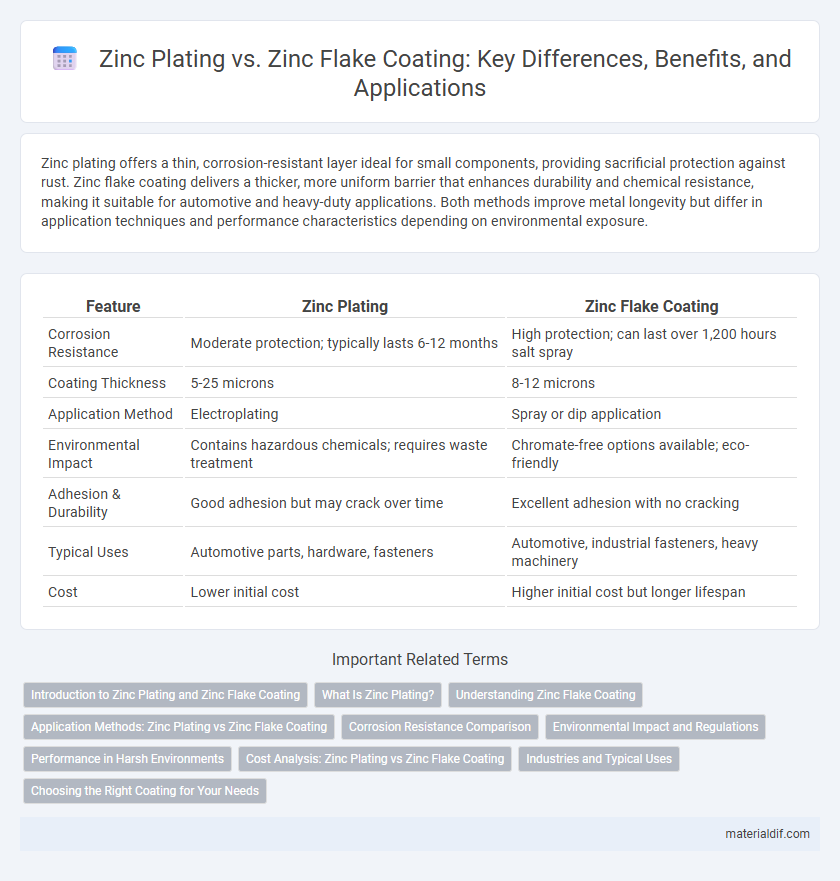
| Feature | Zinc Plating | Zinc Flake Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate protection; typically lasts 6-12 months | High protection; can last over 1,200 hours salt spray |
| Coating Thickness | 5-25 microns | 8-12 microns |
| Application Method | Electroplating | Spray or dip application |
| Environmental Impact | Contains hazardous chemicals; requires waste treatment | Chromate-free options available; eco-friendly |
| Adhesion & Durability | Good adhesion but may crack over time | Excellent adhesion with no cracking |
| Typical Uses | Automotive parts, hardware, fasteners | Automotive, industrial fasteners, heavy machinery |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
Introduction to Zinc Plating and Zinc Flake Coating
Zinc plating involves electroplating a thin layer of zinc onto metal surfaces to provide corrosion resistance and enhance appearance, commonly used in automotive and construction industries. Zinc flake coating is a non-electrolytic, multi-metallic coating that combines zinc and aluminum flakes, offering superior corrosion protection and self-healing properties without requiring heat curing. Both methods improve metal durability, but zinc flake coating typically provides longer-lasting corrosion resistance in harsh environments.
What Is Zinc Plating?
Zinc plating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin layer of zinc onto the surface of metal parts, providing corrosion resistance and enhancing durability. Unlike zinc flake coating, which is a non-electrolytic coating applied by spraying or dipping, zinc plating involves submerging the part in a zinc-rich electrolyte solution where zinc ions bond to the substrate. This method is commonly used for automotive, hardware, and fastener industries to prevent rust and extend the lifespan of steel components.
Understanding Zinc Flake Coating
Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc plating by utilizing a base layer of zinc flakes combined with aluminum flakes, which creates a dense, non-electrolytic barrier. This coating technology eliminates hydrogen embrittlement risks and offers enhanced durability in harsh environments such as automotive and industrial applications. Understanding the chemical composition and application process of zinc flake coatings is essential for selecting the optimal corrosion protection method tailored to specific operational demands.
Application Methods: Zinc Plating vs Zinc Flake Coating
Zinc plating involves electrochemical deposition where zinc ions are reduced and form a thin, uniform metallic layer, typically applied through electroplating or hot-dip processes ideal for smaller parts or components requiring precise thickness control. Zinc flake coating is a non-electrolytic application method combining zinc and aluminum flakes suspended in a binder, applied by spraying or dip-coating, and curing at elevated temperatures to form a robust, corrosion-resistant barrier, often used on fasteners and automotive components. The selection between these methods depends on the part geometry, environmental exposure, and required corrosion protection, with zinc flake coating favored for enhanced durability and zinc plating preferred for conductive coatings or decorative finishes.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zinc plating offers a basic layer of corrosion resistance suitable for indoor or mild environments but tends to degrade faster under harsh conditions. Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion protection by combining thin layers of zinc and aluminum flakes with a special binder, resulting in enhanced resistance to salt spray and chemical exposure. This makes zinc flake coatings ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring long-lasting corrosion defense.
Environmental Impact and Regulations
Zinc plating involves electroplating molten zinc onto metal surfaces, producing hazardous waste and requiring strict disposal protocols under regulations like the EU REACH directive. Zinc flake coating uses a non-electrolytic process that reduces toxic byproducts, aligning with environmental standards by minimizing heavy metal runoff and offering superior corrosion protection. Compliance with global environmental regulations favors zinc flake coatings for sustainable manufacturing and reduced ecological impact.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Zinc plating provides basic corrosion resistance but tends to deteriorate quickly in harsh environments due to its thin, uniform layer. Zinc flake coating offers superior performance, combining a multi-layered structure that enhances resistance to chemicals, salt spray, and abrasion. This advanced coating system significantly extends the lifespan of components exposed to extreme industrial and marine conditions.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Plating vs Zinc Flake Coating
Zinc plating offers a cost-effective solution for corrosion protection with lower upfront expenses and simpler application processes compared to zinc flake coating. Zinc flake coating involves higher initial costs due to advanced materials and multi-layer application but provides superior long-term durability and resistance, potentially reducing maintenance costs over time. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including reapplication frequency and environmental compliance, is essential for an accurate cost analysis between zinc plating and zinc flake coating.
Industries and Typical Uses
Zinc plating is widely used in the automotive and construction industries for corrosion resistance on small to medium-sized steel parts, such as bolts, screws, and fasteners, due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of application. Zinc flake coating is preferred in heavy industries like aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and oil and gas for complex components requiring superior corrosion protection without hydrogen embrittlement. The choice between these coatings depends on the environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and regulatory standards within industries targeting enhanced durability of metal substrates.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
Zinc plating offers excellent corrosion resistance for small parts and provides a bright, smooth finish suitable for aesthetic applications, while zinc flake coating delivers superior protection against harsh environments with a thinner, more uniform layer that resists chipping and cracking. Selecting the right coating depends on factors such as exposure to chemicals, mechanical stress, and environmental conditions, with zinc flake coating favored for automotive and industrial components requiring long-term durability. Cost efficiency, component size, and application method also influence the decision, as zinc plating remains a cost-effective option for simpler protective needs.
Zinc plating vs zinc flake coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com