Zinc strips offer a more flexible and lightweight option for corrosion protection compared to zinc bars, making them ideal for detailed applications and areas with limited space. Zinc bars provide greater durability and longer-lasting performance, suitable for heavy-duty environments where structural integrity is essential. Both forms serve as sacrificial anodes in cathodic protection systems, but the choice depends on the specific requirements of strength and application scale.
Table of Comparison
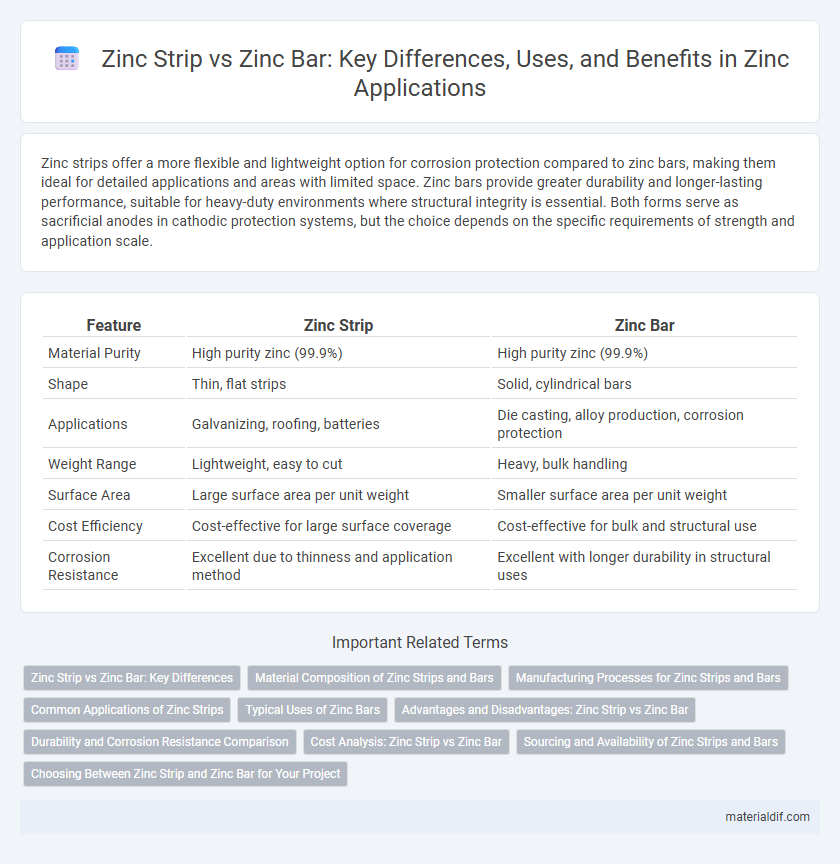
| Feature | Zinc Strip | Zinc Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | High purity zinc (99.9%) | High purity zinc (99.9%) |
| Shape | Thin, flat strips | Solid, cylindrical bars |
| Applications | Galvanizing, roofing, batteries | Die casting, alloy production, corrosion protection |
| Weight Range | Lightweight, easy to cut | Heavy, bulk handling |
| Surface Area | Large surface area per unit weight | Smaller surface area per unit weight |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large surface coverage | Cost-effective for bulk and structural use |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent due to thinness and application method | Excellent with longer durability in structural uses |
Zinc Strip vs Zinc Bar: Key Differences
Zinc strips are thin, flexible pieces of zinc primarily used for corrosion protection and in battery electrodes due to their large surface area, while zinc bars are solid, dense blocks used in construction, galvanizing, and heavy-duty manufacturing. Zinc strips offer better malleability and ease of application in small-scale projects, whereas zinc bars provide structural strength and durability for industrial purposes. The choice between zinc strip and zinc bar depends on the specific requirements of conductivity, surface exposure, and mechanical strength in various applications.
Material Composition of Zinc Strips and Bars
Zinc strips typically consist of high-purity zinc with a composition of 99.9% or higher, ensuring consistent conductivity and corrosion resistance, while zinc bars often contain alloying elements such as aluminum, copper, and magnesium to enhance mechanical strength and durability. The pure zinc material in strips makes them ideal for electrochemical applications and galvanic cells, whereas zinc bars' alloyed composition suits structural and industrial uses requiring added toughness. Understanding the material differences in zinc strips and bars is crucial for selecting the appropriate form for specific electroplating, corrosion protection, or manufacturing projects.
Manufacturing Processes for Zinc Strips and Bars
Zinc strips are typically produced through a rolling process where molten zinc is cast into slabs and then rolled into thin, flat sheets with precise thickness control suitable for applications like galvanizing and battery components. Zinc bars are commonly manufactured by continuous casting or direct chill casting, creating solid bars with uniform cross-sections used in alloy production and metal fabrication. Both methods emphasize controlled cooling rates and surface finishing to ensure material properties meet industrial standards.
Common Applications of Zinc Strips
Zinc strips are widely used in galvanic cells, batteries, and corrosion protection due to their high surface area and ease of fabrication. These strips serve as anodes in electrochemical applications, offering efficient electron transfer and consistent conductivity. Compared to zinc bars, zinc strips provide greater flexibility for shaping and are ideal for coating processes and experimental setups.
Typical Uses of Zinc Bars
Zinc bars are commonly used in galvanization processes to protect steel and iron from corrosion, making them essential in construction and automotive industries. They also serve as raw material for die-casting alloys and battery production, which require high purity zinc for optimal performance. Unlike zinc strips, zinc bars offer greater mass and stability needed for heavy-duty industrial applications and large-scale manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Zinc Strip vs Zinc Bar
Zinc strips offer advantages such as higher surface area for faster galvanic protection and easier installation in small or complex spaces, but they may be less durable and require more frequent replacement compared to zinc bars. Zinc bars provide longer-lasting corrosion protection with greater mechanical strength and are better suited for heavy-duty applications, though they have a lower surface area-to-volume ratio and can be more difficult to install in tight or irregular spaces. Choosing between zinc strip and zinc bar depends on the specific environmental conditions, required longevity, and application surface geometry.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Zinc strips and zinc bars both offer impressive corrosion resistance due to zinc's natural oxide layer, but zinc bars typically provide greater durability because of their thicker, more robust form factor. Zinc bars withstand mechanical stress and environmental wear better, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, while zinc strips are favored in lighter, precision uses where flexibility is needed. The corrosion resistance of both forms is excellent in atmospheric conditions, but zinc bars maintain structural integrity longer under harsh industrial or marine environments.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Strip vs Zinc Bar
Zinc strips generally cost less per unit weight compared to zinc bars, making them a more economical choice for applications requiring frequent replacements or smaller quantities. Zinc bars offer higher purity and structural integrity, which can justify their higher price in industrial or construction settings where durability is critical. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, factors such as project scale, required zinc purity, and handling convenience play a crucial role in determining whether zinc strips or bars provide better value.
Sourcing and Availability of Zinc Strips and Bars
Zinc strips are typically sourced from high-purity zinc sheets and are widely available in standardized thicknesses for laboratory and industrial use. Zinc bars, often produced through casting or extrusion processes, are sourced from bulk raw zinc materials and are commonly available in larger sizes for manufacturing and construction applications. Both zinc strips and bars are readily accessible through metal suppliers and distributors, with availability dependent on regional demand and production capacity.
Choosing Between Zinc Strip and Zinc Bar for Your Project
Selecting between zinc strip and zinc bar depends primarily on your project's requirements for surface area and application method. Zinc strips offer greater flexibility and precise fitting for corrosion protection or galvanic anodes, making them ideal for thin coatings or intricate designs. Zinc bars provide robust structural support and are best suited for heavy-duty applications requiring durability and larger volume of zinc material.
Zinc Strip vs Zinc Bar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com