Zinc alloy casting offers greater design flexibility and is ideal for producing complex, custom shapes with detailed features. Die-cast zinc provides high precision and superior surface finish, making it suitable for large-scale production with consistent quality. Both methods deliver strong, corrosion-resistant components but differ in cost efficiency and production volume suitability.
Table of Comparison
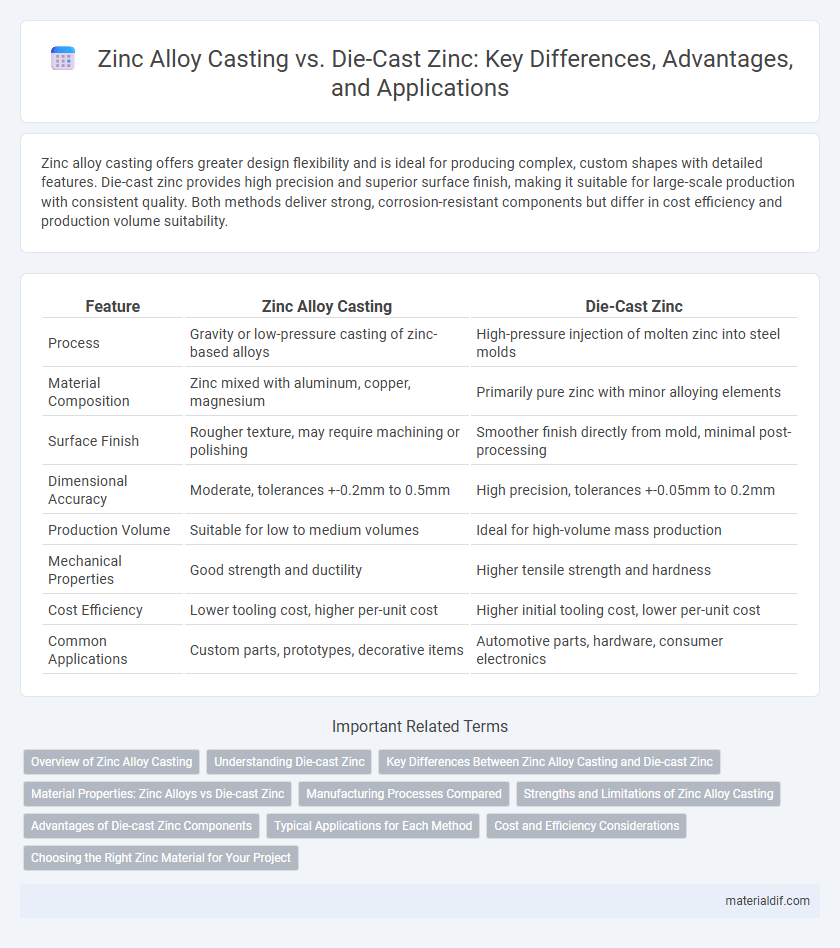
| Feature | Zinc Alloy Casting | Die-Cast Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Gravity or low-pressure casting of zinc-based alloys | High-pressure injection of molten zinc into steel molds |
| Material Composition | Zinc mixed with aluminum, copper, magnesium | Primarily pure zinc with minor alloying elements |
| Surface Finish | Rougher texture, may require machining or polishing | Smoother finish directly from mold, minimal post-processing |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Moderate, tolerances +-0.2mm to 0.5mm | High precision, tolerances +-0.05mm to 0.2mm |
| Production Volume | Suitable for low to medium volumes | Ideal for high-volume mass production |
| Mechanical Properties | Good strength and ductility | Higher tensile strength and hardness |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower tooling cost, higher per-unit cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower per-unit cost |
| Common Applications | Custom parts, prototypes, decorative items | Automotive parts, hardware, consumer electronics |
Overview of Zinc Alloy Casting
Zinc alloy casting involves melting zinc and combining it with other metals like aluminum, copper, or magnesium to create versatile alloys known for strength and corrosion resistance. This process allows for precise molding of complex shapes with fine details, making it ideal for applications in automotive parts, hardware, and electronics. Zinc alloy casting offers excellent dimensional stability and surface finish, outperforming standard die-cast zinc in durability and mechanical properties.
Understanding Die-cast Zinc
Die-cast zinc offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to zinc alloy casting due to the high-pressure injection process that fills intricate mold details efficiently. This method produces components with enhanced mechanical properties, including greater strength and corrosion resistance, making die-cast zinc ideal for precision applications in automotive and electronics industries. Understanding die-cast zinc involves recognizing its advantages in production speed, mold longevity, and the ability to create complex shapes with thin walls.
Key Differences Between Zinc Alloy Casting and Die-cast Zinc
Zinc alloy casting involves pouring molten zinc mixed with other metals into molds to form complex shapes, offering versatility and lower tooling costs, while die-cast zinc uses high-pressure injection of molten zinc into precise steel molds, resulting in high-volume production with superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Zinc alloy casting typically suits intricate, low-to-medium volume parts with varied thickness, whereas die-cast zinc excels in producing consistent, high-strength components at mass scale. Differences in cooling rates and pressure in die casting yield finer grain structures and enhanced mechanical properties compared to gravity-based zinc alloy casting.
Material Properties: Zinc Alloys vs Die-cast Zinc
Zinc alloys used in casting offer enhanced mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and improved corrosion resistance compared to standard die-cast zinc, which typically contains a higher proportion of zinc with limited alloying elements. Die-cast zinc provides excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish but may exhibit lower fatigue resistance and impact strength relative to specialized zinc alloys. The selection between zinc alloy casting and die-cast zinc depends on the required balance between strength, durability, and precision for specific industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Zinc alloy casting involves melting a mixture of zinc and other metals, then pouring it into molds to form complex shapes with moderate production speed and cost. Die-cast zinc uses high-pressure injection of molten zinc into steel dies, resulting in highly precise, consistent parts with superior surface finish and faster production cycles. The manufacturing differences impact product quality, dimensional accuracy, and scalability for industrial applications.
Strengths and Limitations of Zinc Alloy Casting
Zinc alloy casting offers excellent corrosion resistance, good dimensional stability, and affordability, making it ideal for complex shapes and moderate production runs. However, it has limitations in mechanical strength and surface finish compared to die-cast zinc, which provides superior precision and higher tensile strength for high-volume manufacturing. Selecting zinc alloy casting depends on balancing cost-effectiveness with the desired physical properties and production scale.
Advantages of Die-cast Zinc Components
Die-cast zinc components offer superior dimensional accuracy and intricate detail compared to zinc alloy casting, enabling the production of complex shapes with tight tolerances. The die-casting process results in higher strength and better surface finish, reducing the need for secondary machining and finishing operations. Die-cast zinc also provides enhanced corrosion resistance and consistent mechanical properties, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing and durable industrial applications.
Typical Applications for Each Method
Zinc alloy casting is commonly used for producing complex, high-strength components such as automotive parts, electrical connectors, and hardware fittings due to its durability and versatility. Die-cast zinc is preferred for applications requiring high precision and smooth surface finishes, including consumer electronics casings, intricate machinery components, and decorative items. Both methods leverage zinc's excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties but cater to different industry needs based on production volume and detail requirements.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
Zinc alloy casting typically reduces tooling costs due to simpler molds, making it ideal for low to medium production volumes, whereas die-cast zinc offers higher efficiency with faster cycle times suited for high-volume manufacturing. Die-cast zinc parts achieve finer detail and superior surface finish, minimizing post-processing expenses despite higher initial investment in durable dies. The choice between zinc alloy casting and die-cast zinc hinges on balancing upfront tooling expenditure against production speed and part complexity to optimize overall cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Zinc Material for Your Project
Zinc alloy casting offers superior fluidity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for complex shapes and outdoor applications. Die-cast zinc provides high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish, perfect for mass production and detailed components. Evaluating project requirements such as strength, detail, and environmental exposure ensures the optimal choice between zinc alloy casting and die-cast zinc.
Zinc Alloy Casting vs Die-cast Zinc Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com