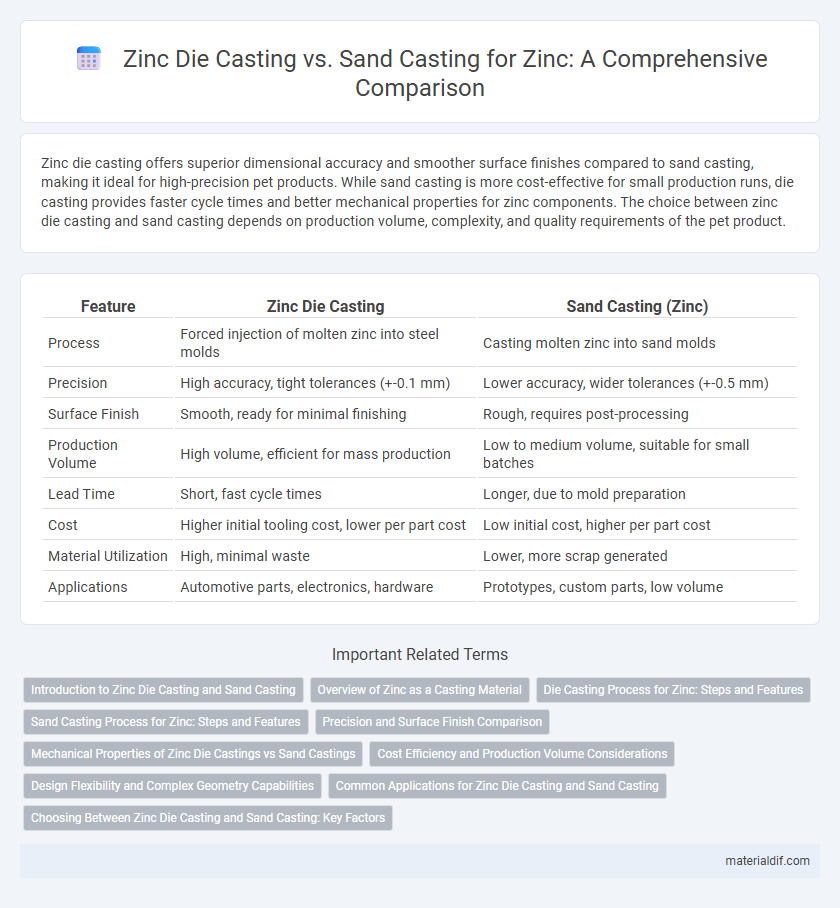
Zinc die casting offers superior dimensional accuracy and smoother surface finishes compared to sand casting, making it ideal for high-precision pet products. While sand casting is more cost-effective for small production runs, die casting provides faster cycle times and better mechanical properties for zinc components. The choice between zinc die casting and sand casting depends on production volume, complexity, and quality requirements of the pet product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Die Casting | Sand Casting (Zinc) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Forced injection of molten zinc into steel molds | Casting molten zinc into sand molds |
| Precision | High accuracy, tight tolerances (+-0.1 mm) | Lower accuracy, wider tolerances (+-0.5 mm) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ready for minimal finishing | Rough, requires post-processing |
| Production Volume | High volume, efficient for mass production | Low to medium volume, suitable for small batches |
| Lead Time | Short, fast cycle times | Longer, due to mold preparation |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost, lower per part cost | Low initial cost, higher per part cost |
| Material Utilization | High, minimal waste | Lower, more scrap generated |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, hardware | Prototypes, custom parts, low volume |
Introduction to Zinc Die Casting and Sand Casting
Zinc die casting involves injecting molten zinc into steel molds under high pressure, producing highly precise and complex shapes with smooth surfaces and excellent dimensional accuracy. In contrast, sand casting for zinc uses sand molds, suitable for larger, less intricate parts but resulting in rougher surfaces and lower dimensional precision. Die casting offers faster production rates and better mechanical properties, while sand casting provides flexibility in design changes and is cost-effective for small production runs.
Overview of Zinc as a Casting Material
Zinc is highly valued in casting for its low melting point, excellent fluidity, and superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for both die casting and sand casting processes. Zinc die casting offers precise detail, high dimensional accuracy, and smooth surface finishes, while sand casting provides flexibility for larger, less complex parts with cost-efficient tooling. Its corrosion resistance and recyclability further enhance zinc's suitability for diverse industrial applications.
Die Casting Process for Zinc: Steps and Features
The zinc die casting process involves injecting molten zinc alloy into a steel mold under high pressure, ensuring precise, complex shapes with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. Key steps include mold preparation, zinc melting, high-pressure injection, cooling, and ejection of the solidified part, enabling rapid production cycles. This method excels in producing durable, dimensionally accurate components suitable for automotive, electronics, and hardware industries, outperforming sand casting in speed and detail quality.
Sand Casting Process for Zinc: Steps and Features
The sand casting process for zinc involves creating a mold by compacting sand around a pattern of the desired shape, allowing for complex geometries and larger component sizes with relatively low tooling costs. Key steps include preparing the sand mold, melting the zinc alloy, pouring the molten zinc into the cavity, and cooling before mold removal. This process offers versatility and cost-effectiveness for medium to large zinc parts but typically results in lower dimensional accuracy and surface finish compared to zinc die casting.
Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
Zinc die casting offers superior precision compared to sand casting, with tolerances as tight as +-0.1 mm, making it ideal for intricate components requiring high dimensional accuracy. The surface finish of zinc die cast parts is significantly smoother, often achieving Ra values between 0.4 to 1.2 micrometers, whereas sand cast zinc parts typically have rougher textures due to the granular nature of the molding sand. These differences make zinc die casting the preferred method for applications demanding fine detail and minimal post-processing surface treatment.
Mechanical Properties of Zinc Die Castings vs Sand Castings
Zinc die castings exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to sand castings, including higher tensile strength and better surface finish due to the fine grain structure achieved in the die casting process. Die cast zinc parts typically demonstrate enhanced dimensional accuracy and improved hardness, resulting in greater wear resistance and durability. In contrast, sand cast zinc components often show coarser microstructures and lower mechanical strength, making them less suitable for high-stress or precision applications.
Cost Efficiency and Production Volume Considerations
Zinc die casting offers superior cost efficiency and faster production cycles compared to sand casting, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing due to its automation and minimal post-processing requirements. Sand casting, while more flexible for low-volume or custom parts, incurs higher costs per unit and longer lead times because of manual labor and mold preparation. Selecting zinc die casting optimizes economies of scale and reduces overall production expenses in large-scale operations.
Design Flexibility and Complex Geometry Capabilities
Zinc die casting offers superior design flexibility and the ability to produce highly complex geometries with tight tolerances, making it ideal for intricate components requiring fine details and consistent quality. Sand casting for zinc is more limited in design complexity due to the granular nature of the mold, which restricts fine detailing and results in lower dimensional accuracy. These differences make zinc die casting preferable for advanced applications demanding precision and complex shapes.
Common Applications for Zinc Die Casting and Sand Casting
Zinc die casting is commonly used for producing intricate automotive components, electrical housings, and consumer electronics due to its high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish. Sand casting for zinc is preferred in manufacturing larger, less detailed parts such as plumbing fittings, heavy machinery components, and industrial valves where versatility and lower tooling costs are essential. Both processes leverage zinc's excellent corrosion resistance and strength, but die casting excels in high-volume precision parts while sand casting suits larger, more robust components.
Choosing Between Zinc Die Casting and Sand Casting: Key Factors
Choosing between zinc die casting and sand casting depends on production volume, detail precision, and cost considerations. Zinc die casting offers high-speed production and excellent dimensional accuracy, ideal for complex, high-volume parts, while sand casting suits lower volumes with simpler geometries and thicker sections. Material properties like zinc's low melting point and good fluidity enhance die casting efficiency, whereas sand casting provides flexibility for larger, custom components with lower tooling costs.
Zinc die casting vs Sand casting (for zinc) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com