Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and provides a smoother, solderable surface ideal for electrical components, while zinc plating is favored for its robust protection against rust and cost-effectiveness in automotive and construction applications. Zinc plating forms a sacrificial layer that prevents underlying steel from oxidizing, making it suitable for outdoor use, whereas tin plating resists oxidation and enhances conductivity in electronic parts. Choosing between tin plating and zinc plating depends on the specific requirements for durability, conductivity, and environmental exposure in the intended application.
Table of Comparison
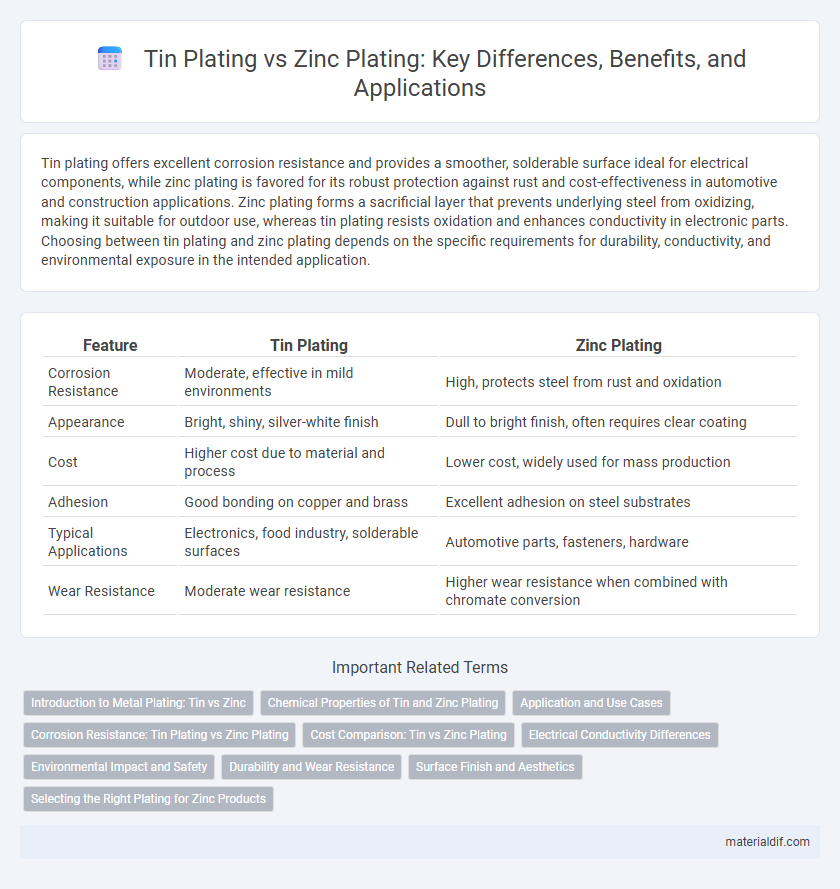
| Feature | Tin Plating | Zinc Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, effective in mild environments | High, protects steel from rust and oxidation |
| Appearance | Bright, shiny, silver-white finish | Dull to bright finish, often requires clear coating |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material and process | Lower cost, widely used for mass production |
| Adhesion | Good bonding on copper and brass | Excellent adhesion on steel substrates |
| Typical Applications | Electronics, food industry, solderable surfaces | Automotive parts, fasteners, hardware |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | Higher wear resistance when combined with chromate conversion |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Tin vs Zinc
Metal plating enhances corrosion resistance and surface durability, with tin and zinc being popular options. Tin plating provides excellent solderability and corrosion resistance in food-grade and electronic applications, while zinc plating offers superior protection against rust and environmental wear, commonly used in automotive and construction industries. Choosing between tin and zinc plating depends on the required corrosion protection, conductivity, and application environment.
Chemical Properties of Tin and Zinc Plating
Tin plating offers superior corrosion resistance due to its stable, non-toxic oxide layer, making it ideal for food-related and electronic applications. Zinc plating provides sacrificial protection by corroding preferentially, effectively protecting underlying steel in automotive and construction industries. The chemical inertness of tin contrasts with zinc's active oxidation, influencing their respective plating durability and environmental suitability.
Application and Use Cases
Tin plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic components, food packaging, and automotive parts that require a non-toxic coating. Zinc plating offers superior galvanic protection against rust and is commonly used in construction, hardware, and automotive fasteners exposed to harsh outdoor environments. While tin plating excels in electrical conductivity and food safety applications, zinc plating is preferred for robust corrosion prevention and durability in industrial settings.
Corrosion Resistance: Tin Plating vs Zinc Plating
Tin plating offers superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments due to its ability to resist oxidation and sulfur-based contaminants. Zinc plating provides sacrificial protection by corroding first, effectively shielding the base metal but is less effective in prolonged exposure to moisture and salty conditions. For applications requiring thin, durable coatings with excellent solderability, tin plating is preferred, while zinc plating suits applications needing cost-effective, sacrificial corrosion defense.
Cost Comparison: Tin vs Zinc Plating
Tin plating generally costs more than zinc plating due to higher material prices and more complex application processes. Zinc plating offers a more cost-effective corrosion-resistant solution, making it preferred for large-scale industrial use. The selection between tin and zinc plating often balances budget constraints with specific performance requirements.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Tin plating offers superior electrical conductivity compared to zinc plating, making it ideal for electronic and electrical applications requiring low resistance connections. Zinc plating primarily provides excellent corrosion resistance but has lower conductivity due to its metallic structure and oxide formation. For optimal performance in circuits and connectors, tin plating ensures consistent current flow and reduced signal loss.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Tin plating offers superior corrosion resistance without the use of toxic heavy metals, making it a safer choice for food and electronics applications regarding environmental impact. Zinc plating provides excellent sacrificial protection but can result in hazardous waste containing heavy metals and requires strict handling procedures to prevent environmental contamination. Both methods require proper disposal practices, but tin plating generally poses fewer health risks and has a lower environmental footprint.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Tin plating offers moderate durability and wear resistance, making it suitable for low-corrosion environments and providing excellent solderability. Zinc plating provides superior corrosion resistance and enhanced wear protection, especially when combined with chromate conversion coatings, ideal for outdoor or harsh conditions. The choice between tin and zinc plating depends on the specific application requirements, emphasizing zinc plating for durability and wear in demanding environments.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Tin plating provides a bright, smooth surface finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced solderability and a shiny, silver-like appearance. Zinc plating offers a duller, matte finish with effective protection against rust, commonly used for structural parts where aesthetics are less critical. Both coatings improve durability, but tin plating is preferred for superior visual appeal and fine surface detail preservation.
Selecting the Right Plating for Zinc Products
Tin plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and solderability, making it ideal for electronic connectors and components requiring reliable electrical conductivity. Zinc plating provides strong protection against rust and is cost-effective for automotive and construction materials exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Choosing between tin and zinc plating depends on the specific application, balancing factors like corrosion resistance, electrical requirements, and budget constraints for zinc-based products.
Tin Plating vs Zinc Plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com