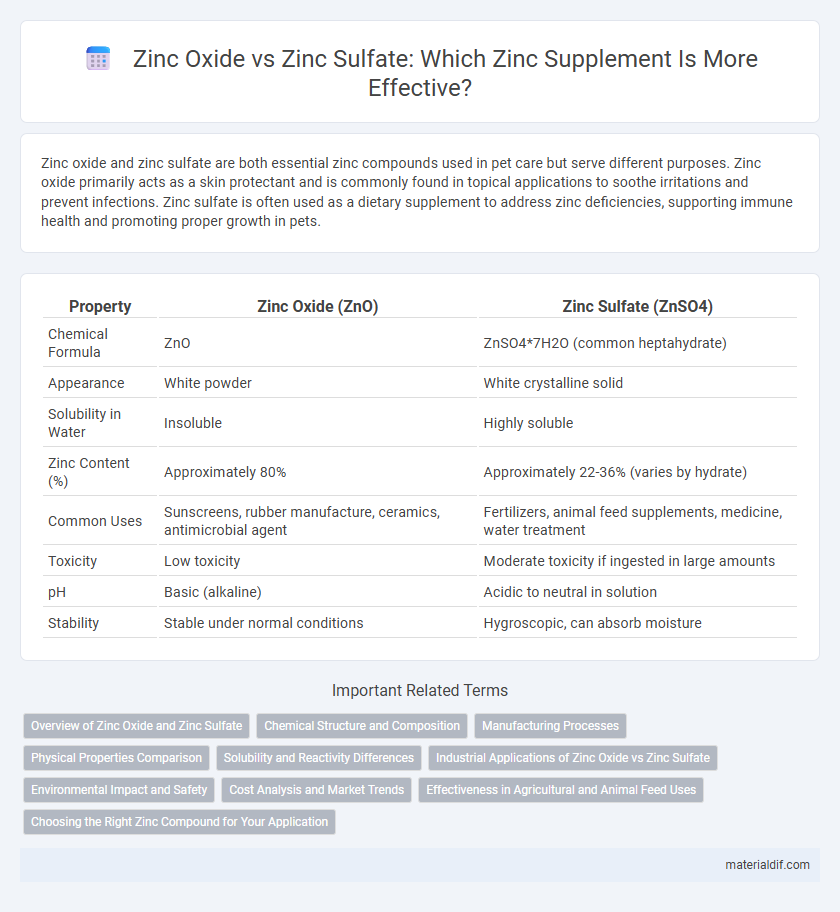
Zinc oxide and zinc sulfate are both essential zinc compounds used in pet care but serve different purposes. Zinc oxide primarily acts as a skin protectant and is commonly found in topical applications to soothe irritations and prevent infections. Zinc sulfate is often used as a dietary supplement to address zinc deficiencies, supporting immune health and promoting proper growth in pets.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zinc Oxide (ZnO) | Zinc Sulfate (ZnSO4) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | ZnO | ZnSO4*7H2O (common heptahydrate) |
| Appearance | White powder | White crystalline solid |
| Solubility in Water | Insoluble | Highly soluble |
| Zinc Content (%) | Approximately 80% | Approximately 22-36% (varies by hydrate) |
| Common Uses | Sunscreens, rubber manufacture, ceramics, antimicrobial agent | Fertilizers, animal feed supplements, medicine, water treatment |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Moderate toxicity if ingested in large amounts |
| pH | Basic (alkaline) | Acidic to neutral in solution |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions | Hygroscopic, can absorb moisture |
Overview of Zinc Oxide and Zinc Sulfate
Zinc oxide is a white, powdery compound widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and as a UV protectant due to its antibacterial and skin-healing properties. Zinc sulfate is a water-soluble zinc salt primarily utilized in agricultural supplements, animal feed, and as a dietary zinc source for treating zinc deficiency. Both compounds serve distinct functions based on solubility and bioavailability, with zinc oxide favored for topical applications and zinc sulfate for ingestion and soil amendment.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is an inorganic compound composed of zinc and oxygen atoms arranged in a lattice structure, displaying amphoteric properties with low solubility in water. Zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) consists of zinc cations bonded to sulfate anions (SO4^2-), forming a water-soluble salt commonly used for nutritional supplementation. The distinct chemical composition impacts their applications, with zinc oxide's oxide ions providing UV-blocking capability, while zinc sulfate's sulfate group enhances bioavailability in aqueous solutions.
Manufacturing Processes
Zinc oxide is typically produced through the indirect (French) process, involving the vaporization of metallic zinc followed by oxidation, or the direct (American) process, where zinc ore reacts with oxygen at high temperatures; this results in a fine white powder widely used in rubber and cosmetics. Zinc sulfate is manufactured by treating zinc or zinc oxide with sulfuric acid, producing a water-soluble compound essential for agricultural fertilizers and dietary supplements. The choice of manufacturing process impacts purity, particle size, and application suitability, with zinc oxide requiring high-temperature vaporization and zinc sulfate relying on acid-base reactions.
Physical Properties Comparison
Zinc oxide appears as a white, powdery solid with high thermal stability and insolubility in water, commonly used in cosmetics and rubber manufacturing. Zinc sulfate, a colorless, crystalline solid, dissolves readily in water, making it useful in agricultural fertilizers and dietary supplements. The distinct physical properties between zinc oxide and zinc sulfate influence their specific industrial applications and handling requirements.
Solubility and Reactivity Differences
Zinc oxide exhibits low solubility in water, making it less reactive and ideal for applications requiring slow zinc release, such as in sunscreens and rubber manufacturing. In contrast, zinc sulfate is highly soluble and reacts quickly in aqueous environments, which enhances its effectiveness in agricultural fertilizers and dietary supplements. The distinct solubility profiles directly influence their reactivity, bioavailability, and suitability across industrial and agricultural uses.
Industrial Applications of Zinc Oxide vs Zinc Sulfate
Zinc oxide is widely used in industrial applications such as rubber manufacturing, ceramics, and chemical production due to its superior UV protection, antimicrobial properties, and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. Zinc sulfate, on the other hand, is primarily utilized in agriculture as a micronutrient fertilizer and in water treatment for controlling algae growth and preventing corrosion. The distinct chemical properties of zinc oxide and zinc sulfate define their specific industrial roles, with zinc oxide favored for material reinforcement and surface protection, while zinc sulfate is essential for nutrient supplementation and environmental management.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Zinc oxide exhibits low solubility, reducing its environmental mobility and toxicity, making it safer for aquatic life compared to the highly soluble and bioavailable zinc sulfate. Zinc sulfate's increased solubility can lead to greater soil and water contamination risks, posing toxicity hazards to plants and aquatic organisms. Proper handling and application of zinc sulfate are critical to minimize environmental impact, whereas zinc oxide's stability offers a safer profile in ecological systems.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Zinc oxide typically costs more than zinc sulfate due to its wider applications in industries like rubber, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals, whereas zinc sulfate is favored in agriculture and animal feed for its higher solubility and bioavailability. Market trends indicate a growing demand for zinc oxide driven by the expanding cosmetic and personal care sectors, while zinc sulfate market growth is propelled by increased agricultural activities and fertilizer use in developing regions. Pricing volatility in both compounds is influenced by fluctuating raw material costs, supply chain disruptions, and shifting regulations affecting mining and production processes worldwide.
Effectiveness in Agricultural and Animal Feed Uses
Zinc oxide provides high bioavailability of zinc, making it effective for correcting zinc deficiency in both soil and animal feed, while also offering antimicrobial properties that enhance animal health. Zinc sulfate is highly soluble and rapidly releases zinc ions, promoting quick uptake by plants and livestock, which supports growth and immune function. Comparative studies indicate zinc sulfate demonstrates superior efficacy in agriculture for soil zinc replenishment, whereas zinc oxide is often preferred in animal nutrition for its sustained release and gut health benefits.
Choosing the Right Zinc Compound for Your Application
Zinc oxide offers excellent UV protection and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for skincare and sunscreen formulations. Zinc sulfate dissolves easily in water, providing superior bioavailability for agricultural and nutritional supplements. Selecting the right zinc compound depends on factors such as solubility, intended use, and target application requirements.
Zinc Oxide vs Zinc Sulfate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com