Zinc-coated steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance at a lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it ideal for budget-friendly applications. Stainless steel provides superior durability, corrosion resistance, and a more attractive finish, suitable for long-term use in pet environments. Choosing between the two depends on balancing cost efficiency with longevity and maintenance needs in zinc pet products.
Table of Comparison
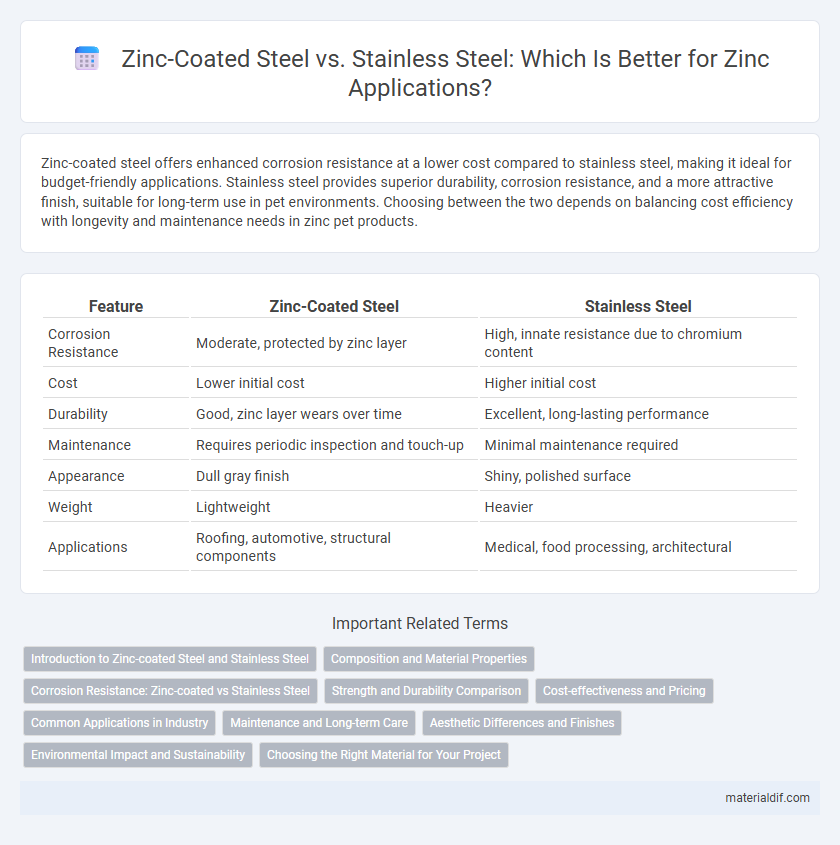
| Feature | Zinc-Coated Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, protected by zinc layer | High, innate resistance due to chromium content |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Good, zinc layer wears over time | Excellent, long-lasting performance |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic inspection and touch-up | Minimal maintenance required |
| Appearance | Dull gray finish | Shiny, polished surface |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Applications | Roofing, automotive, structural components | Medical, food processing, architectural |
Introduction to Zinc-coated Steel and Stainless Steel
Zinc-coated steel, also known as galvanized steel, features a protective zinc layer that enhances corrosion resistance and extends the material's lifespan in outdoor and industrial applications. Stainless steel contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which forms a passive oxide layer to prevent rust and provide superior durability in harsh environments. Both materials offer distinct advantages: zinc-coated steel delivers cost-effective corrosion protection while stainless steel provides higher strength and exceptional resistance to oxidation and staining.
Composition and Material Properties
Zinc-coated steel consists of a carbon steel core with a thin layer of zinc applied through galvanization, providing enhanced corrosion resistance by acting as a sacrificial anode. Stainless steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium (typically 10.5% or more), and sometimes nickel and molybdenum, which imparts superior corrosion resistance through the formation of a passive chromium oxide layer. Zinc-coated steel offers good corrosion protection at a lower cost, while stainless steel provides greater durability, strength, and resistance to oxidation and staining in harsh environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Zinc-coated vs Stainless Steel
Zinc-coated steel offers effective corrosion resistance through a sacrificial zinc layer that protects the underlying steel from rust and environmental damage. Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance due to its chromium content, forming a passive oxide layer that withstands moisture, chemicals, and extreme conditions without degrading. In aggressive or highly corrosive environments, stainless steel outperforms zinc-coated steel by maintaining structural integrity and appearance over extended periods.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zinc-coated steel, also known as galvanized steel, offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its protective zinc layer, making it highly durable in outdoor and humid environments. Stainless steel, composed primarily of iron, chromium, and nickel, provides superior strength and exceptional resistance to rust, pitting, and staining, maintaining structural integrity under extreme conditions. While stainless steel generally outperforms zinc-coated steel in long-term strength and durability, galvanized steel is a cost-effective solution for moderate strength requirements with reliable corrosion protection.
Cost-effectiveness and Pricing
Zinc-coated steel typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to stainless steel due to lower material and production costs. While stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance and durability, its higher price point often makes zinc-coated steel a preferable choice for budget-sensitive applications requiring moderate protection. The pricing advantage of zinc-coated steel makes it suitable for construction and automotive industries where balance between cost and performance is essential.
Common Applications in Industry
Zinc-coated steel is widely used in automotive manufacturing, construction, and electrical appliances due to its corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. Stainless steel finds common applications in food processing, medical instruments, and chemical equipment for its superior durability and resistance to heat and chemicals. Both materials are integral in industrial settings where strength and longevity under varying environmental conditions are critical.
Maintenance and Long-term Care
Zinc-coated steel requires regular inspection and occasional touch-up of the zinc layer to prevent rust and prolong its lifespan, especially in harsh environments. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance with minimal maintenance, making it ideal for applications demanding long-term durability and low upkeep. Proper cleaning of stainless steel involves mild detergents and avoids abrasive materials to preserve its protective chromium oxide layer.
Aesthetic Differences and Finishes
Zinc-coated steel typically offers a matte, metallic gray finish with a slightly rough texture due to the galvanization process, providing a protective layer that resists corrosion but can develop a patina over time. Stainless steel features a smooth, shiny, and often polished surface that retains its luster and resists tarnishing, making it ideal for applications where a sleek, modern aesthetic is desired. While zinc-coated steel emphasizes durability with a utilitarian appearance, stainless steel prioritizes visual appeal through various finishes such as brushed, mirror, or satin.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Zinc-coated steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance through its protective zinc layer, which extends the lifespan of steel products and reduces the need for frequent replacement, lowering overall resource consumption. Stainless steel, though highly durable and resistant to corrosion without additional coatings, requires substantial energy during production, contributing to a higher carbon footprint compared to zinc-coated steel. Recycling rates for both materials are high, but zinc-coated steel's lighter weight can result in reduced transportation emissions, supporting more sustainable supply chains.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Zinc-coated steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its protective zinc layer, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial projects where cost-effectiveness and durability are key. Stainless steel provides superior resistance to rust and chemical exposure, making it suitable for environments requiring high hygiene standards or exposure to moisture. Selecting between zinc-coated steel and stainless steel depends on factors such as environmental conditions, budget constraints, and specific project requirements for longevity and maintenance.
Zinc-coated steel vs stainless steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com