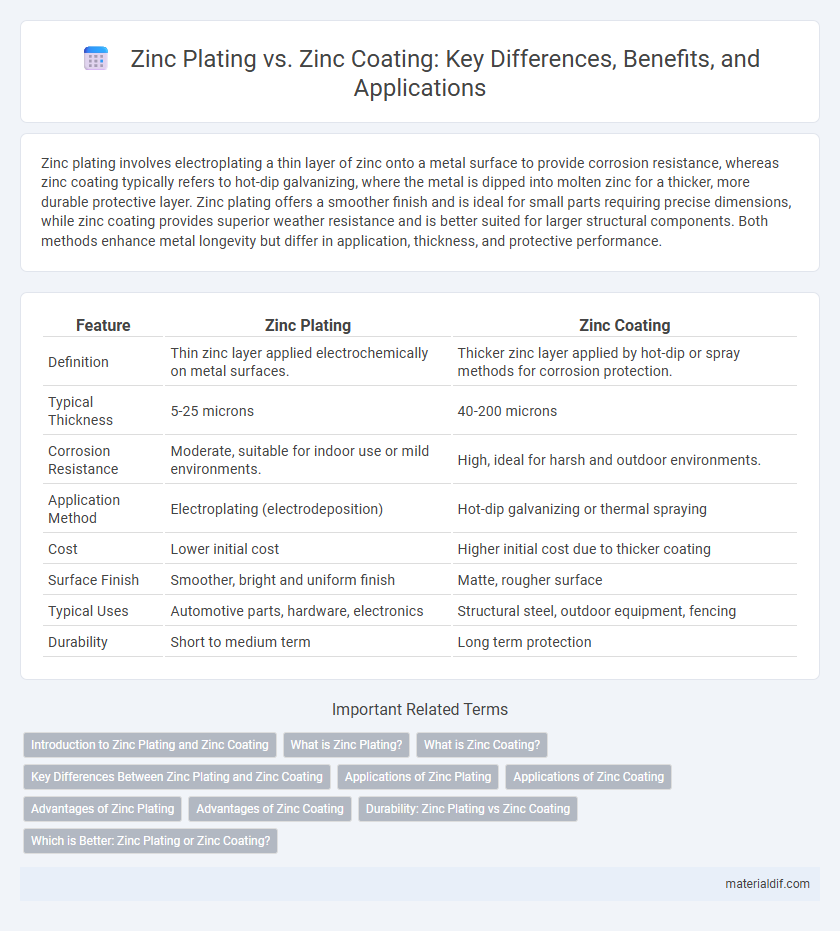
Zinc plating involves electroplating a thin layer of zinc onto a metal surface to provide corrosion resistance, whereas zinc coating typically refers to hot-dip galvanizing, where the metal is dipped into molten zinc for a thicker, more durable protective layer. Zinc plating offers a smoother finish and is ideal for small parts requiring precise dimensions, while zinc coating provides superior weather resistance and is better suited for larger structural components. Both methods enhance metal longevity but differ in application, thickness, and protective performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Plating | Zinc Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thin zinc layer applied electrochemically on metal surfaces. | Thicker zinc layer applied by hot-dip or spray methods for corrosion protection. |
| Typical Thickness | 5-25 microns | 40-200 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, suitable for indoor use or mild environments. | High, ideal for harsh and outdoor environments. |
| Application Method | Electroplating (electrodeposition) | Hot-dip galvanizing or thermal spraying |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to thicker coating |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, bright and uniform finish | Matte, rougher surface |
| Typical Uses | Automotive parts, hardware, electronics | Structural steel, outdoor equipment, fencing |
| Durability | Short to medium term | Long term protection |
Introduction to Zinc Plating and Zinc Coating
Zinc plating involves applying a thin layer of zinc onto a metal surface through electrochemical or mechanical processes to provide corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Zinc coating typically refers to a broader range of methods, such as hot-dip galvanizing, where a thicker zinc layer is applied by immersing the metal in molten zinc, offering enhanced durability against environmental factors. Zinc plating is ideal for precision components requiring fine finishes, while zinc coating is preferred for heavy-duty structural steel needing robust protection.
What is Zinc Plating?
Zinc plating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin layer of zinc onto the surface of a metal to provide corrosion resistance and enhance durability. This method involves submerging the metal in a zinc-containing electrolyte solution and applying an electric current, resulting in a uniform and adherent zinc layer. Zinc plating offers superior protection against rust and is commonly used for automotive parts, hardware, and fasteners.
What is Zinc Coating?
Zinc coating refers to the process of applying a protective layer of zinc on metal surfaces to prevent corrosion and extend the lifespan of the underlying material. This coating acts as a sacrificial barrier, meaning it corrodes preferentially to protect the base metal from rust and environmental damage. Zinc coating is commonly applied through hot-dip galvanizing, electroplating, or mechanical processes, each offering varying thicknesses and durability levels.
Key Differences Between Zinc Plating and Zinc Coating
Zinc plating involves electroplating a thin layer of zinc onto a metal surface to provide corrosion resistance and decorative appeal, typically measuring a few microns in thickness. Zinc coating, often applied through hot-dip galvanizing, creates a thicker, more durable layer by immersing metal into molten zinc, enhancing protection against harsh environmental conditions. The key differences lie in application methods, layer thickness, and corrosion resistance, with zinc coating offering superior durability and zinc plating preferred for precision and aesthetic finishes.
Applications of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is widely used in automotive, construction, and electronics industries for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal of metal parts. It provides a thin, uniform layer of zinc, enhancing adhesion and conductivity while protecting steel components from rust. Applications include fasteners, hardware, and consumer electronics, where precision and durability are crucial.
Applications of Zinc Coating
Zinc coating is widely used in automotive, construction, and electrical industries to protect steel and iron from corrosion through galvanization. Key applications include coating structural steel, fasteners, and automotive parts, where enhanced durability and rust resistance are critical. This protective layer extends the lifespan of components exposed to harsh environments, making zinc coating essential for industrial and outdoor applications.
Advantages of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating offers superior corrosion resistance by creating a uniform, tightly bonded metal layer that protects steel components from rust and environmental damage. This method enables precise control over coating thickness, ensuring enhanced durability while maintaining the original shape and dimensions of the parts. Zinc plating also improves aesthetic appeal with a bright, smooth finish, making it ideal for automotive, electronics, and hardware applications.
Advantages of Zinc Coating
Zinc coating provides superior corrosion resistance by forming a stable oxide layer that protects steel surfaces from moisture and environmental damage. Unlike zinc plating, zinc coating offers greater durability and longer-lasting protection, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. The thicker, more uniform zinc layer also enhances wear resistance and decreases maintenance costs over time.
Durability: Zinc Plating vs Zinc Coating
Zinc plating offers a thinner, more uniform layer ideal for aesthetic and light corrosion resistance, typically lasting a few years under mild conditions. Zinc coating, often applied through hot-dip galvanizing, provides a thicker, more robust barrier that significantly extends durability and corrosion protection in harsh environments, lasting decades. The choice between them depends on the required lifespan and exposure conditions; zinc coating excels in long-term outdoor applications.
Which is Better: Zinc Plating or Zinc Coating?
Zinc plating and zinc coating both provide corrosion resistance by applying a protective zinc layer to metal surfaces, but zinc plating offers a thinner, more uniform layer ideal for precision parts requiring fine detail. Zinc coating, often through hot-dip galvanizing, produces a thicker, more durable layer better suited for outdoor, heavy-duty applications exposed to harsh environments. Choosing between zinc plating and zinc coating depends on factors such as the required layer thickness, environmental exposure, and part function, with zinc plating excelling in aesthetic and precise applications and zinc coating providing superior long-term protection against corrosion.
Zinc plating vs Zinc coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com