Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to zinc spray coating, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications where long-term protection is crucial. Zinc spray coating provides a cost-effective and quick solution for light to moderate corrosion protection but may require more frequent reapplication. Both coatings serve to protect metal surfaces, but zinc flake coating delivers a thicker and more uniform layer that enhances performance in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
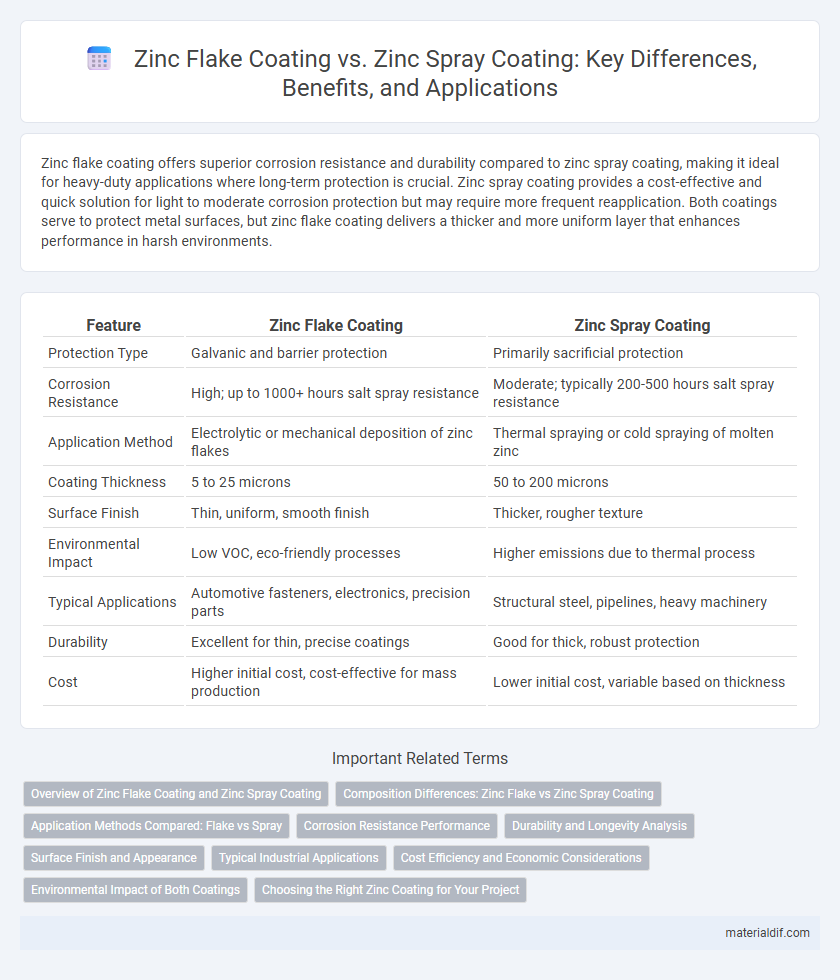
| Feature | Zinc Flake Coating | Zinc Spray Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Type | Galvanic and barrier protection | Primarily sacrificial protection |
| Corrosion Resistance | High; up to 1000+ hours salt spray resistance | Moderate; typically 200-500 hours salt spray resistance |
| Application Method | Electrolytic or mechanical deposition of zinc flakes | Thermal spraying or cold spraying of molten zinc |
| Coating Thickness | 5 to 25 microns | 50 to 200 microns |
| Surface Finish | Thin, uniform, smooth finish | Thicker, rougher texture |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC, eco-friendly processes | Higher emissions due to thermal process |
| Typical Applications | Automotive fasteners, electronics, precision parts | Structural steel, pipelines, heavy machinery |
| Durability | Excellent for thin, precise coatings | Good for thick, robust protection |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective for mass production | Lower initial cost, variable based on thickness |
Overview of Zinc Flake Coating and Zinc Spray Coating
Zinc flake coating offers a thin, uniform layer composed of zinc and aluminum flakes, providing superior corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion without the need for electroplating. Zinc spray coating, often applied via thermal spray techniques, creates a thicker, rougher zinc layer that protects metal surfaces from rust but may require post-treatment for enhanced durability. Both coatings prevent oxidation, yet zinc flake coating excels in achieving high corrosion protection in tight spaces and complex geometries.
Composition Differences: Zinc Flake vs Zinc Spray Coating
Zinc flake coating consists of a combination of zinc and aluminum flakes bound with a resin, offering superior corrosion resistance and a more uniform, thin layer compared to zinc spray coating. In contrast, zinc spray coating predominantly uses pure zinc particles applied through thermal spraying, resulting in thicker, less adherent layers that are more prone to mechanical damage. The composite nature of zinc flake coatings provides enhanced protection in harsh environments by leveraging the synergistic effects of zinc and aluminum, unlike the simpler, single-metal composition of zinc spray coatings.
Application Methods Compared: Flake vs Spray
Zinc flake coating is applied through a galvanic process that involves spraying a fine zinc layer combined with aluminum flakes, resulting in a thin, uniform, and non-electrolytic barrier. Zinc spray coating employs thermal spraying techniques such as arc spraying or flame spraying, which deposit molten zinc particles to form a thicker, rougher protective layer. The flake method excels in corrosion resistance for automotive and industrial fasteners, while spray coating suits large structures requiring thicker zinc buildup for mechanical durability.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc spray coating due to its uniform, thin layer that provides excellent barrier protection and sacrificial anode properties. This coating technology typically endures up to 1000 hours in salt spray tests, significantly outperforming traditional zinc spray coatings which may last only a few hundred hours. Enhanced adhesion and resistance to mechanical wear make zinc flake coatings ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring long-term corrosion protection.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Zinc flake coating provides superior corrosion resistance and longer service life compared to zinc spray coating due to its multi-layered, uniform protection that effectively prevents rust and wear. Zinc spray coating, often used for touch-ups or onsite repairs, offers less durability as it tends to have a thinner, less consistent layer vulnerable to abrasion and environmental damage. In industrial applications requiring extended longevity and robust performance, zinc flake coatings are preferred for their enhanced adhesion and resistance to chemical exposure.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Zinc flake coating provides a uniform, smooth surface finish with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications requiring high durability and aesthetic quality. Zinc spray coating often results in a rougher, uneven appearance due to its thermal application process, which can create a less consistent layer that is prone to irregular texture. The superior homogeneity and thinner film thickness of zinc flake coating contribute to better visual appeal and performance compared to zinc spray coatings.
Typical Industrial Applications
Zinc flake coating is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and electrical industries due to its superior corrosion resistance and thin, uniform layer ideal for high-performance components. Zinc spray coating is preferred for maintenance and repair applications in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and structural steel because it allows for quick, on-site application and effective surface protection. Both coatings play critical roles in extending the lifespan of metal parts by preventing rust and wear in demanding industrial environments.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Zinc flake coating offers superior cost efficiency by providing longer-lasting corrosion protection, reducing maintenance frequency and replacement costs compared to zinc spray coating. Zinc spray coating, while initially cheaper, often incurs higher long-term expenses due to its thinner, less durable layer requiring more frequent reapplication. Economic considerations favor zinc flake coating for industrial applications where durability and lifecycle cost savings are critical.
Environmental Impact of Both Coatings
Zinc flake coating offers superior environmental benefits by eliminating the need for hazardous chromates and reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions compared to traditional zinc spray coatings. Zinc spray coatings often rely on metal particles suspended in solvents, which can release harmful VOCs and heavy metals into the environment during application and curing. Choosing zinc flake coating minimizes ecological footprint through lower VOC emissions, enhanced corrosion resistance, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Choosing the Right Zinc Coating for Your Project
Zinc flake coating offers superior corrosion resistance and uniform coverage, making it ideal for automotive and industrial components exposed to harsh environments. Zinc spray coating provides a cost-effective and quick application, suitable for touch-ups or smaller projects where extensive durability is not critical. Selecting the right zinc coating depends on factors like environmental exposure, project scale, and desired lifespan, ensuring optimal protection and performance.
Zinc Flake Coating vs Zinc Spray Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com