Continuous galvanizing ensures a consistent, high-quality zinc coating on steel by passing the material through a molten zinc bath in a continuous process, offering superior corrosion resistance and uniform thickness compared to batch galvanizing. Batch galvanizing, performed in individual tanks, allows for flexibility in coating different steel sizes and shapes but may result in less uniform coatings and longer production times. Selecting between continuous and batch galvanizing depends on the production volume, steel type, and desired coating properties in zinc-coated steel manufacturing.
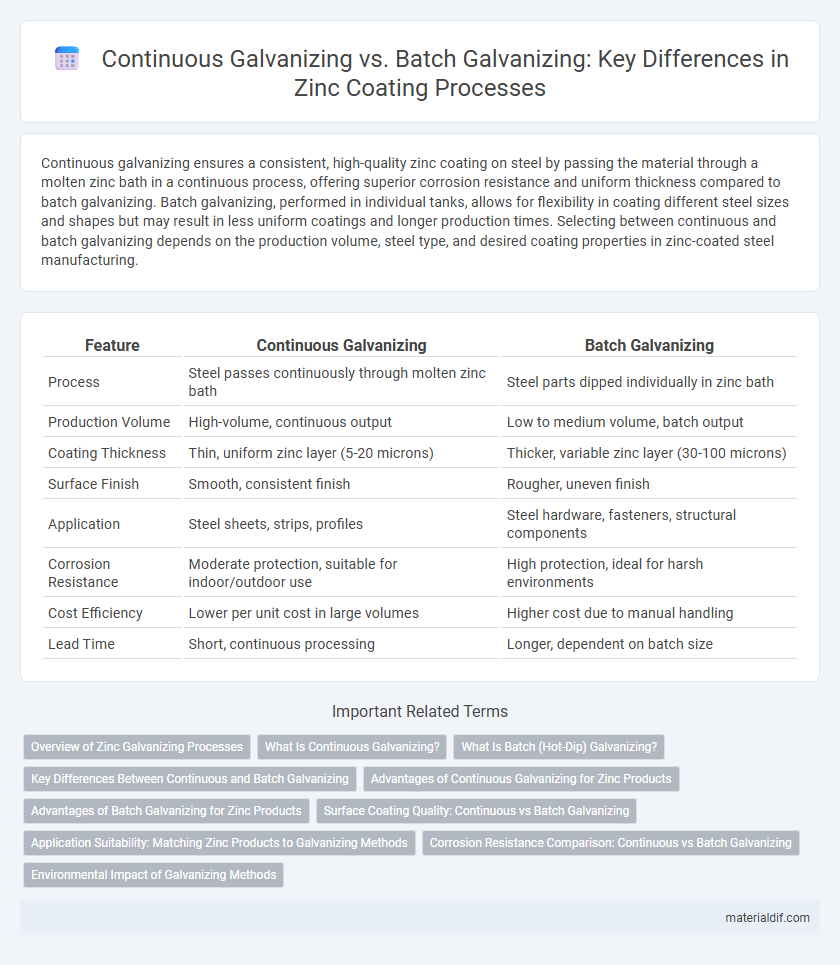
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Continuous Galvanizing | Batch Galvanizing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Steel passes continuously through molten zinc bath | Steel parts dipped individually in zinc bath |
| Production Volume | High-volume, continuous output | Low to medium volume, batch output |
| Coating Thickness | Thin, uniform zinc layer (5-20 microns) | Thicker, variable zinc layer (30-100 microns) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent finish | Rougher, uneven finish |
| Application | Steel sheets, strips, profiles | Steel hardware, fasteners, structural components |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate protection, suitable for indoor/outdoor use | High protection, ideal for harsh environments |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower per unit cost in large volumes | Higher cost due to manual handling |
| Lead Time | Short, continuous processing | Longer, dependent on batch size |
Overview of Zinc Galvanizing Processes
Continuous galvanizing involves passing steel sheets through a molten zinc bath, creating a uniform, corrosion-resistant coating ideal for high-volume production. Batch galvanizing, also known as hot-dip galvanizing, submerges steel components into zinc tanks individually, offering thicker coatings suited for complex shapes and heavy-duty protection. Zinc galvanizing processes enhance metal durability by forming a metallurgical bond between zinc and steel, preventing rust and extending service life.
What Is Continuous Galvanizing?
Continuous galvanizing is a process where steel or metal coils are coated with a layer of zinc by passing them through a molten zinc bath in a continuous, automated line. This method ensures uniform zinc coating thickness, enhanced corrosion resistance, and improved surface quality compared to batch galvanizing. Widely used in industries requiring large volumes of coated steel, continuous galvanizing provides efficiency, consistent production speeds, and cost-effectiveness for applications like automotive panels and construction materials.
What Is Batch (Hot-Dip) Galvanizing?
Batch (Hot-Dip) Galvanizing involves immersing steel components in a molten zinc bath, creating a durable, corrosion-resistant coating. This method is ideal for smaller, complex parts that require thorough zinc coverage and uniform thickness. Unlike continuous galvanizing, batch galvanizing allows for precise coating control on individual items rather than continuous steel coils.
Key Differences Between Continuous and Batch Galvanizing
Continuous galvanizing involves coating steel sheets with zinc in a continuous, automated process ideal for high-volume production, ensuring uniform thickness and superior corrosion resistance. Batch galvanizing, also known as hot-dip galvanizing, immerses individual steel components in molten zinc, offering flexibility for large, complex, or irregularly shaped parts but often results in thicker coatings and variable surface finishes. The primary differences lie in production efficiency, coating uniformity, and suitability for different steel product sizes and shapes.
Advantages of Continuous Galvanizing for Zinc Products
Continuous galvanizing offers superior coating uniformity and enhanced corrosion resistance for zinc products compared to batch galvanizing. This process enables higher production efficiency and consistent zinc layer thickness, reducing material waste and operational costs. Its automated nature ensures precise temperature control and improved surface quality, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications.
Advantages of Batch Galvanizing for Zinc Products
Batch galvanizing offers superior coating thickness control and enhanced corrosion resistance for zinc products, ensuring longer-lasting protection in aggressive environments. It allows for the galvanizing of larger or irregularly shaped components that cannot fit into continuous lines. This process is cost-effective for smaller production volumes, providing flexibility and high-quality finishes tailored to specific zinc applications.
Surface Coating Quality: Continuous vs Batch Galvanizing
Continuous galvanizing offers a uniform zinc coating with consistent thickness and superior adhesion due to its automated, high-speed process on steel coils. Batch galvanizing, while allowing thicker coatings and better protection in corrosive environments, often results in variable surface quality and rougher finishes due to manual handling in individual tanks. The choice between continuous and batch galvanizing significantly impacts surface coating properties, durability, and corrosion resistance of zinc-coated steel products.
Application Suitability: Matching Zinc Products to Galvanizing Methods
Continuous galvanizing suits high-volume steel production, providing uniform zinc coatings ideal for automotive body panels and structural components requiring consistent corrosion resistance. Batch galvanizing offers flexibility for complex or oversized parts, such as heavy machinery and architectural elements, where precise zinc layer control enhances durability and finish quality. Choosing between methods depends on zinc product specifications, steel substrate size, and the intended industrial application's corrosion protection needs.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison: Continuous vs Batch Galvanizing
Continuous galvanizing provides a uniform zinc coating that enhances corrosion resistance by creating a consistent barrier against environmental elements, reducing the likelihood of rust and surface degradation. Batch galvanizing, while offering thicker zinc layers in localized areas, often results in variable coating thickness that can lead to uneven protection and potential weak points in corrosion defense. The homogeneity of the zinc coating in continuous galvanizing typically ensures superior long-term corrosion resistance compared to the spotty coverage typical of batch galvanizing processes.
Environmental Impact of Galvanizing Methods
Continuous galvanizing minimizes energy consumption and zinc waste by using a streamlined, automated coating process, significantly reducing environmental pollutants compared to batch galvanizing. Batch galvanizing involves intermittent processing, leading to higher emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and increased zinc runoff, which can contaminate soil and waterways. Selecting continuous galvanizing enhances sustainability through lower carbon emissions and improved resource efficiency in zinc utilization.
Continuous Galvanizing vs Batch Galvanizing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com