Hot-dip galvanized zinc coatings offer superior corrosion resistance by immersing the metal in molten zinc, creating a thick, durable layer ideal for outdoor and harsh environments. Electro-galvanized coatings, applied through an electrochemical process, provide a thinner, more uniform finish suitable for indoor use and applications requiring precise thickness control. Choosing between hot-dip and electro-galvanized zinc depends on the specific environmental exposure and mechanical demands of the pet-related product.
Table of Comparison
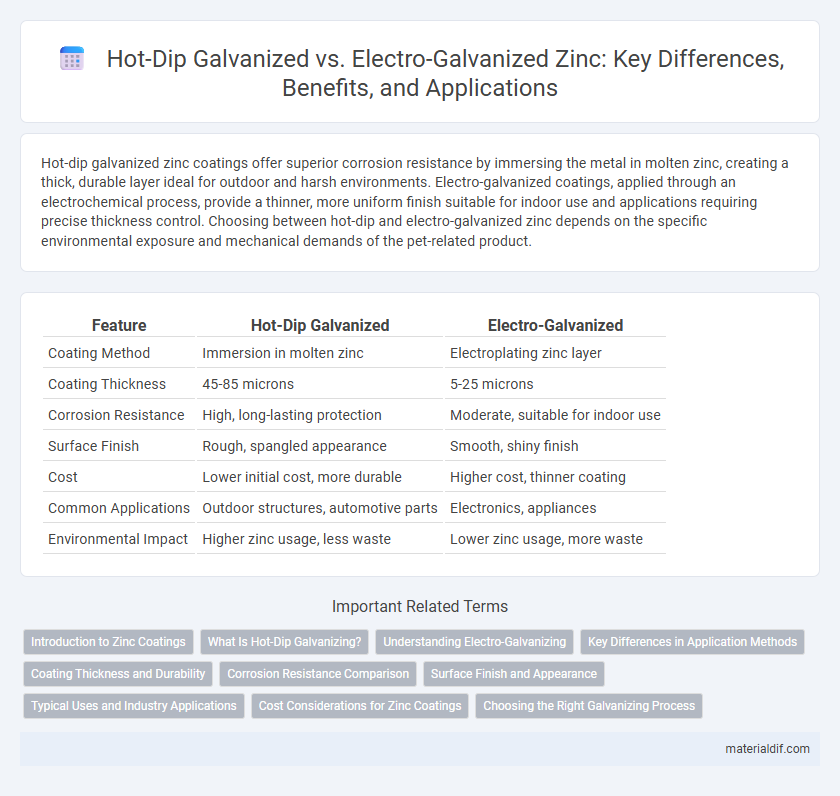
| Feature | Hot-Dip Galvanized | Electro-Galvanized |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Immersion in molten zinc | Electroplating zinc layer |
| Coating Thickness | 45-85 microns | 5-25 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, long-lasting protection | Moderate, suitable for indoor use |
| Surface Finish | Rough, spangled appearance | Smooth, shiny finish |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, more durable | Higher cost, thinner coating |
| Common Applications | Outdoor structures, automotive parts | Electronics, appliances |
| Environmental Impact | Higher zinc usage, less waste | Lower zinc usage, more waste |
Introduction to Zinc Coatings
Zinc coatings provide essential corrosion protection for steel by forming a durable barrier. Hot-dip galvanized coatings are created by immersing steel in molten zinc, resulting in a thick, robust layer that offers superior resistance to harsh environments. Electro-galvanized coatings involve electroplating zinc onto steel, producing a thinner, more uniform layer ideal for indoor applications with moderate corrosion exposure.
What Is Hot-Dip Galvanizing?
Hot-dip galvanizing involves immersing steel or iron into molten zinc, creating a robust, corrosion-resistant coating that bonds metallurgically to the base metal. This process produces a thicker, more durable zinc layer compared to electro-galvanizing, offering superior protection in harsh environments and extended service life. Zinc coatings from hot-dip galvanizing exhibit excellent abrasion resistance and self-healing properties, making them ideal for outdoor construction and industrial applications.
Understanding Electro-Galvanizing
Electro-galvanizing is a zinc coating process that involves the electroplating of a thin, uniform layer of zinc onto steel or iron surfaces, providing corrosion resistance and enhanced aesthetic appeal. This method offers precise thickness control and smooth finishes, making it ideal for automotive parts and indoor applications where appearance and dimension accuracy are critical. The zinc layer in electro-galvanized steel, typically ranging from 5 to 25 microns, provides sacrificial protection but is thinner than hot-dip galvanized coatings, resulting in less resistance to harsh outdoor environments.
Key Differences in Application Methods
Hot-dip galvanizing involves immersing steel into molten zinc, creating a thick, durable coating ideal for outdoor and industrial applications requiring robust corrosion resistance. Electro-galvanizing uses an electrochemical process to deposit a thinner zinc layer, providing a smoother finish better suited for indoor or decorative purposes. The thicker coating from hot-dip galvanizing offers longer-lasting protection but can alter dimensions, whereas electro-galvanizing maintains precise tolerances with less durability.
Coating Thickness and Durability
Hot-dip galvanized coatings typically range from 45 to 85 microns in thickness, providing superior corrosion resistance and durability for outdoor applications. Electro-galvanized coatings are thinner, generally between 5 to 25 microns, resulting in less protection and shorter lifespan under harsh conditions. The thicker zinc layer in hot-dip galvanizing enhances mechanical adhesion and sacrificial protection, making it ideal for industrial and structural uses.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Hot-dip galvanized coatings provide superior corrosion resistance compared to electro-galvanized coatings due to their thicker and more robust zinc layer, which typically ranges from 50 to 150 microns. Electro-galvanized coatings, with thinner zinc layers of about 5 to 25 microns, are more susceptible to mechanical damage and localized corrosion, especially in harsh environments. The metallurgical bonding in hot-dip galvanization creates a durable barrier that better withstands exposure to moisture, salts, and industrial pollutants, making it the preferred choice for outdoor and marine applications.
Surface Finish and Appearance
Hot-dip galvanized zinc coatings offer a thicker, more rugged surface finish characterized by spangled patterns and a matte gray appearance, providing enhanced corrosion resistance. Electro-galvanized zinc coatings produce a smoother and brighter finish with a uniform, shiny silver appearance, ideal for applications requiring aesthetic appeal. The choice between hot-dip and electro-galvanizing depends on balancing durability requirements with desired visual qualities.
Typical Uses and Industry Applications
Hot-dip galvanized zinc coatings are widely used in heavy-duty applications such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure due to their thick, corrosion-resistant layer providing long-term protection in harsh environments. Electro-galvanized zinc coatings offer thinner, more uniform layers ideal for precision parts and electronics, where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are critical, commonly seen in appliances and automotive components. Both methods serve distinct market needs, with hot-dip galvanizing preferred for outdoor and structural steel, while electro-galvanizing fits well in manufacturing sectors requiring aesthetic and functional surface quality.
Cost Considerations for Zinc Coatings
Hot-dip galvanized zinc coatings typically incur higher initial costs due to the thicker and more durable zinc layer applied through immersion, providing superior long-term corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance expenses. Electro-galvanized coatings involve lower upfront costs with thinner zinc layers applied via electrochemical deposition, suitable for indoor or less corrosive environments where cost efficiency is essential. Evaluating project requirements and lifecycle expenses is crucial for choosing between hot-dip and electro-galvanized zinc coatings.
Choosing the Right Galvanizing Process
Hot-dip galvanized coatings provide thicker, more durable protection against corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor and industrial environments exposed to harsh weather conditions. Electro-galvanized coatings offer a thinner, more uniform finish, suited for indoor applications or components requiring precise dimensions and aesthetic appeal. Selecting the right galvanizing process depends on factors such as exposure to elements, desired corrosion resistance, and specific performance requirements of the zinc-coated product.
Hot-Dip Galvanized vs Electro-Galvanized Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com