Zinc coating involves applying a thin layer of zinc to steel or iron surfaces through processes like galvanization to protect against corrosion. Zinc cladding, on the other hand, refers to the use of zinc sheets or panels as a protective and decorative exterior layer, often in architectural applications. Both methods enhance durability and resistance to weathering but serve different functional and aesthetic purposes.
Table of Comparison
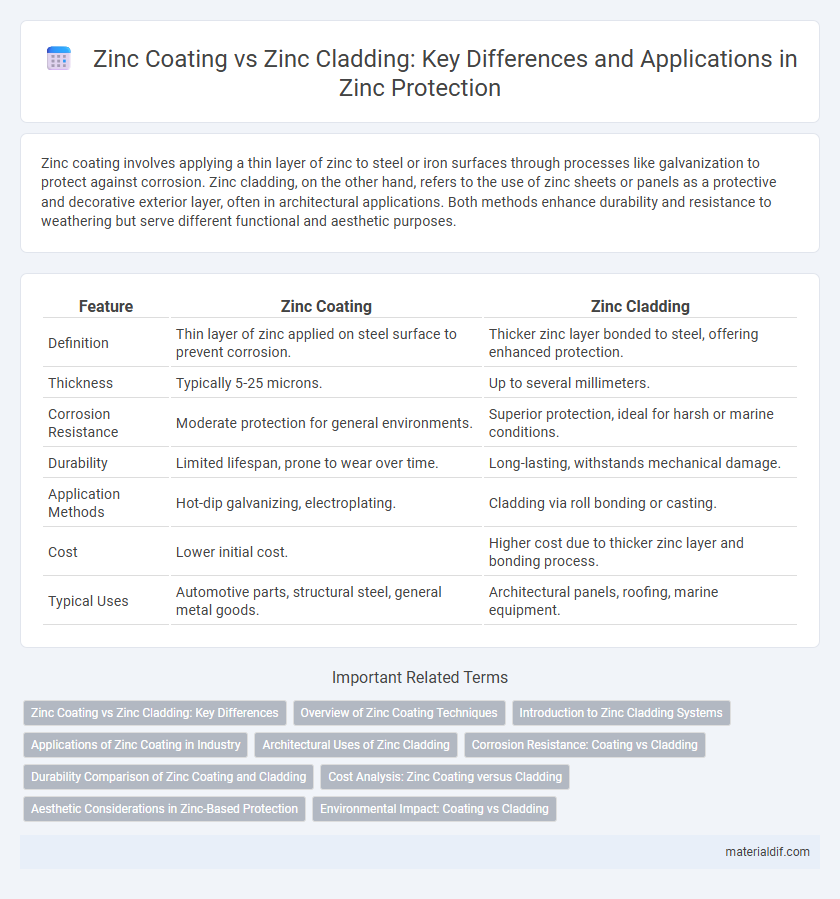
| Feature | Zinc Coating | Zinc Cladding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thin layer of zinc applied on steel surface to prevent corrosion. | Thicker zinc layer bonded to steel, offering enhanced protection. |
| Thickness | Typically 5-25 microns. | Up to several millimeters. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate protection for general environments. | Superior protection, ideal for harsh or marine conditions. |
| Durability | Limited lifespan, prone to wear over time. | Long-lasting, withstands mechanical damage. |
| Application Methods | Hot-dip galvanizing, electroplating. | Cladding via roll bonding or casting. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost. | Higher cost due to thicker zinc layer and bonding process. |
| Typical Uses | Automotive parts, structural steel, general metal goods. | Architectural panels, roofing, marine equipment. |
Zinc Coating vs Zinc Cladding: Key Differences
Zinc coating involves electroplating or hot-dip galvanizing zinc onto a metal surface to provide corrosion resistance, while zinc cladding refers to applying thin sheets of zinc over a substrate for protective or decorative purposes. Zinc coating forms a metallurgical bond with the base metal, enhancing durability and rust resistance, whereas zinc cladding acts as a physical barrier without significant metallurgical interaction. The choice between zinc coating and zinc cladding depends on the application's exposure conditions, required longevity, and aesthetic preferences.
Overview of Zinc Coating Techniques
Zinc coating techniques primarily include hot-dip galvanizing, electro-galvanizing, and sherardizing, each offering distinct protective benefits against corrosion. Hot-dip galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc, creating a robust, thick layer ideal for outdoor applications, while electro-galvanizing applies a thinner, uniform zinc layer through electrochemical deposition, suitable for precision components. Sherardizing uses zinc vapor to coat metal surfaces, providing an even, wear-resistant finish preferred for small parts and complex geometries.
Introduction to Zinc Cladding Systems
Zinc cladding systems provide a durable and aesthetically versatile solution for architectural applications, offering superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional zinc coatings. Unlike zinc coatings that are typically thin layers applied to protect steel substrates, zinc cladding involves thicker, sculpted panels or sheets designed for exterior facades and roofing. These systems leverage zinc's natural patina formation to enhance longevity and require minimal maintenance, making them ideal for sustainable building projects.
Applications of Zinc Coating in Industry
Zinc coating, commonly applied through hot-dip galvanizing and electroplating, provides superior corrosion resistance for steel structures in construction, automotive manufacturing, and electrical appliances. Industrial applications leverage zinc coatings to extend the lifespan of metal components exposed to harsh environments, such as bridges, pipelines, and agricultural equipment. This protective layer prevents rust formation, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing durability compared to zinc cladding, which primarily serves decorative or architectural purposes.
Architectural Uses of Zinc Cladding
Zinc cladding offers superior aesthetic versatility and durability for architectural applications compared to traditional zinc coating, providing a sleek, corrosion-resistant surface ideal for building facades and roofing. Unlike zinc coating, which primarily serves as a protective layer on steel, zinc cladding involves the use of zinc panels designed to enhance both the visual appeal and weather resistance of structures. Its natural patina evolves over time, ensuring long-lasting performance and minimal maintenance in diverse environmental conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Coating vs Cladding
Zinc coating provides a uniform layer of protection against corrosion by forming a barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the underlying metal, ideal for environments with moderate exposure. Zinc cladding offers enhanced corrosion resistance due to its thicker and more durable layer, which physically shields the metal substrate and can withstand harsher conditions such as marine or industrial atmospheres. Both zinc coating and cladding employ sacrificial protection, but cladding's greater thickness significantly extends the lifespan of steel structures in corrosive environments.
Durability Comparison of Zinc Coating and Cladding
Zinc coating typically offers strong corrosion resistance by forming a protective barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the base metal, enhancing durability in various environments. Zinc cladding, however, provides a thicker, more uniform layer of zinc, resulting in superior protection against mechanical damage and prolonged exposure to harsh conditions. In terms of durability, zinc cladding generally outperforms zinc coating due to its enhanced thickness and resistance to wear, making it ideal for more demanding applications.
Cost Analysis: Zinc Coating versus Cladding
Zinc coating generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to zinc cladding, primarily due to its lower material and application expenses. Zinc cladding involves higher initial investment because of thicker material usage and complex installation processes, impacting overall project budgets. Long-term maintenance costs for zinc coating are reduced by its corrosion resistance, making it an economically efficient choice in various industrial and construction applications.
Aesthetic Considerations in Zinc-Based Protection
Zinc coating offers a uniform, matte finish that enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining a consistent appearance ideal for industrial applications. Zinc cladding provides a thicker protective layer with a more varied texture and color, often resulting in a rustic or aged aesthetic favored in architectural designs. Choosing between zinc coating and zinc cladding depends on the desired visual effect and environmental durability requirements for zinc-based protection.
Environmental Impact: Coating vs Cladding
Zinc coating typically involves applying a thin layer of zinc to steel through galvanization, which provides corrosion resistance while utilizing less zinc material, resulting in lower resource consumption and reduced environmental impact. Zinc cladding uses thicker zinc sheets for exterior surfaces, offering enhanced durability and longevity but demanding more zinc production and energy resources, leading to higher environmental footprints. Both methods prevent steel corrosion effectively, but zinc coating presents a more sustainable option due to minimal material usage and better recyclability.
Zinc Coating vs Zinc Cladding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com