Tin cans offer superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to aluminum cans, making them ideal for preserving food quality and extending shelf life. While aluminum cans are lightweight and highly recyclable, tin cans provide a stronger barrier against light and oxygen, which helps maintain flavor and freshness. The choice between tin and aluminum cans depends on factors such as product type, environmental impact, and cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
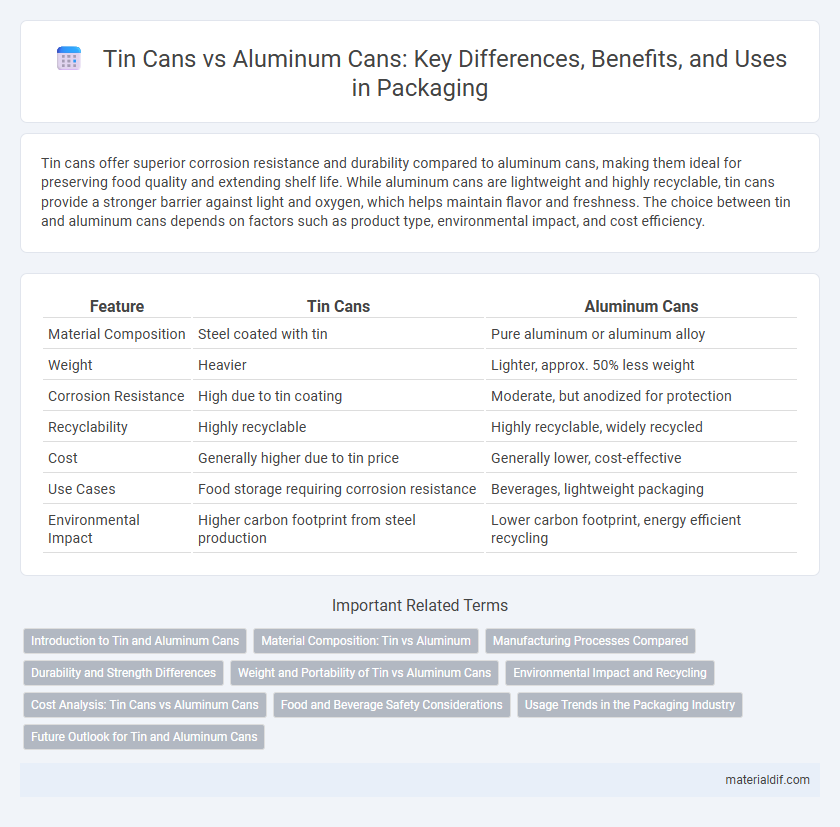
| Feature | Tin Cans | Aluminum Cans |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel coated with tin | Pure aluminum or aluminum alloy |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter, approx. 50% less weight |
| Corrosion Resistance | High due to tin coating | Moderate, but anodized for protection |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Highly recyclable, widely recycled |
| Cost | Generally higher due to tin price | Generally lower, cost-effective |
| Use Cases | Food storage requiring corrosion resistance | Beverages, lightweight packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint from steel production | Lower carbon footprint, energy efficient recycling |
Introduction to Tin and Aluminum Cans
Tin cans, primarily made from steel coated with tin to prevent corrosion, have been used for food packaging since the early 19th century due to their durability and airtight properties. Aluminum cans, introduced later in the 20th century, offer lighter weight and superior recyclability, making them a popular choice for beverages and certain food products. Both materials provide effective preservation, but aluminum's resistance to rust and easier recycling contribute significantly to its growing preference in packaging industries.
Material Composition: Tin vs Aluminum
Tin cans are primarily made of steel coated with a thin layer of tin, providing corrosion resistance and food safety, while aluminum cans consist entirely of lightweight aluminum metal. The tin coating prevents rust and extends shelf life, whereas aluminum cans offer superior corrosion resistance without the need for an internal coating. Aluminum's low density makes it easier to transport and recycle, but tin's protective layer is essential for preserving certain food products.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Tin cans are manufactured using a process called tinplate rolling, where thin sheets of steel are coated with a thin layer of tin to prevent corrosion and enhance weldability, followed by cutting and forming into cylindrical shapes with welded or seamed joints. Aluminum cans are produced through aluminum sheet rolling, deep drawing, and ironing, a process that shapes seamless, lightweight containers, significantly reducing manufacturing steps compared to tinplate cans. The aluminum manufacturing process offers higher efficiency and lower energy consumption, while tin cans require additional coating and welding stages, impacting production speed and cost.
Durability and Strength Differences
Tin cans exhibit superior durability due to their corrosion-resistant properties and thicker metal composition, which enhances their ability to withstand physical impacts and extend shelf life. Aluminum cans, while lightweight and recyclable, are more prone to denting and are less resistant to punctures compared to tin cans. The structural strength of tin provides better protection for packaged goods, making it a preferred choice for products requiring long-term storage.
Weight and Portability of Tin vs Aluminum Cans
Tin cans are generally heavier than aluminum cans, impacting their portability and ease of transport. Aluminum cans offer a lighter weight alternative that reduces shipping costs and enhances convenience for consumers. The lower weight of aluminum also contributes to improved energy efficiency in distribution and handling processes.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Tin cans, typically made from steel coated with a thin layer of tin, have a high recycling rate and are highly durable, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving resources. Aluminum cans require less energy to recycle compared to producing new aluminum, but mining bauxite for aluminum extraction has significant environmental consequences, including habitat destruction and greenhouse gas emissions. Both materials are recyclable, but tin-coated steel cans offer advantages in recyclability due to simpler processing and widespread recycling infrastructure, making them a more sustainable option in certain regions.
Cost Analysis: Tin Cans vs Aluminum Cans
Tin cans typically have higher production costs due to the price of tin plating and more complex manufacturing processes, while aluminum cans benefit from lower raw material costs and efficient mass production. Aluminum's lightweight nature reduces transportation expenses, contributing to overall cost savings in distribution compared to heavier tin cans. Long-term market trends show aluminum cans maintain cost advantages, driven by widespread recycling infrastructure and commodity price stability.
Food and Beverage Safety Considerations
Tin cans provide superior corrosion resistance and prevent chemical leaching, making them a safer option for preserving food and beverages compared to aluminum cans. The tin lining acts as a protective barrier against acidity in food, reducing the risk of contamination and maintaining product integrity. Aluminum cans require additional coatings to avoid aluminum exposure, which can sometimes degrade and compromise safety.
Usage Trends in the Packaging Industry
Tin cans maintain significant usage in packaging, especially for preserving food due to their corrosion resistance and non-reactive properties. Aluminum cans dominate the beverage sector, favored for their lightweight, recyclability, and rapid cooling benefits. The packaging industry trends indicate a shift towards aluminum for sustainability goals, though tin cans remain preferred for long-term storage and specialty food products.
Future Outlook for Tin and Aluminum Cans
The future outlook for tin in packaging centers on its enhanced corrosion resistance and recyclability, making it a preferred material for sustainable tin cans amid tightening environmental regulations. Aluminum cans continue to gain market share due to their lightweight properties, cost-effectiveness, and high recycling rates, driving innovations in alloy composition and manufacturing processes. Increased demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions will likely stimulate advancements in both tin and aluminum can technologies, promoting a competitive landscape focused on durability, resource efficiency, and reducing carbon footprints.
Tin cans vs Aluminum cans Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com