Tin cans provide superior durability and excellent protection for food and beverages, ensuring long shelf life and resistance to external damage. Tetra Pak offers lightweight packaging with efficient space-saving design and reduced environmental impact due to its recyclability and reduced use of metal. Choosing between tin cans and Tetra Pak depends on factors such as product type, shelf life needs, storage conditions, and sustainability priorities.
Table of Comparison
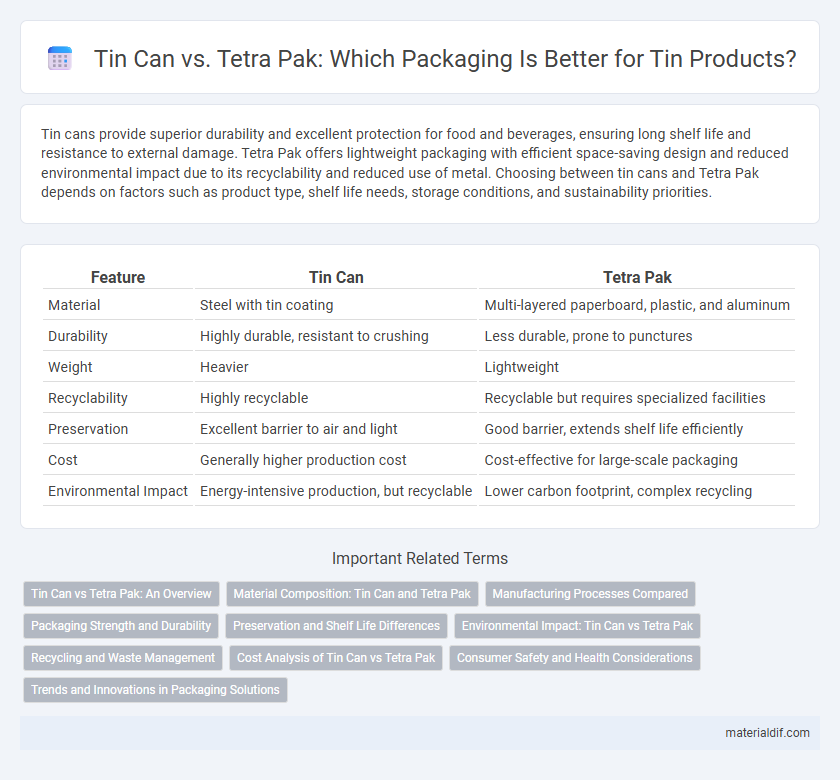
| Feature | Tin Can | Tetra Pak |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel with tin coating | Multi-layered paperboard, plastic, and aluminum |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to crushing | Less durable, prone to punctures |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable | Recyclable but requires specialized facilities |
| Preservation | Excellent barrier to air and light | Good barrier, extends shelf life efficiently |
| Cost | Generally higher production cost | Cost-effective for large-scale packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-intensive production, but recyclable | Lower carbon footprint, complex recycling |
Tin Can vs Tetra Pak: An Overview
Tin cans offer superior durability and airtight sealing, making them ideal for long-term food storage and heavy-duty applications. Tetra Pak cartons provide lightweight, space-efficient packaging with extended shelf life due to multi-layered materials that protect against light, air, and bacteria. Choice between tin cans and Tetra Pak depends on factors like product type, environmental impact, and recycling infrastructure.
Material Composition: Tin Can and Tetra Pak
Tin cans are primarily made from steel coated with a thin layer of tin to prevent corrosion, offering excellent durability and recyclability. Tetra Pak packaging combines multiple layers of paperboard, polyethylene, and aluminum foil, creating a lightweight, aseptic container ideal for preserving liquid foods. The metal content in tin cans provides superior protection against light and oxygen, whereas Tetra Pak's composite structure emphasizes sustainability and reduced material usage.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Tin cans involve a stamping and seaming process to form durable, airtight containers from thin steel sheets coated with tin to prevent corrosion, ensuring product preservation. Tetra Pak utilizes aseptic packaging technology, combining paperboard, polyethylene, and aluminum layers through a high-speed converting process that sterilizes and seals liquid food products without refrigeration. The tin can manufacturing requires more energy-intensive metal processing, whereas Tetra Pak's process emphasizes lightweight, renewable materials and efficient assembly for environmentally conscious packaging.
Packaging Strength and Durability
Tin cans provide superior packaging strength and durability due to their metal construction, offering excellent protection against physical damage, light, and oxygen infiltration. Tetra Pak cartons, made from layers of paperboard, plastic, and aluminum, offer moderate strength but are more susceptible to punctures and crushing compared to tin cans. The corrosion resistance and hermetic sealing of tin cans ensure longer shelf life and robustness in harsh storage conditions.
Preservation and Shelf Life Differences
Tin cans provide superior preservation by creating an airtight, metal barrier that protects contents from light, oxygen, and contaminants, ensuring a shelf life of up to five years for many products. Tetra Pak cartons use multilayered materials including aluminum foil and plastic, offering excellent protection against light and oxygen but generally provide a shorter shelf life, typically up to 12 months without refrigeration. The choice between tin cans and Tetra Pak depends on the product type, with tin cans favored for long-term storage and Tetra Pak for lightweight, convenience-focused packaging.
Environmental Impact: Tin Can vs Tetra Pak
Tin cans are highly recyclable, with recycling rates often exceeding 70%, and their metal content can be repeatedly reused without quality loss, significantly reducing environmental impact. Tetra Pak cartons, composed of paper, plastic, and aluminum layers, present challenges in material separation and recycling, leading to lower recycling rates compared to tin cans. The production of tin cans generally involves higher energy use, but their closed-loop recycling system minimizes landfill waste, while Tetra Pak's composite structure complicates recycling and can contribute more to waste accumulation.
Recycling and Waste Management
Tin cans are highly recyclable, with a recycling rate exceeding 70% globally, as their steel and tin components can be efficiently separated and reused in manufacturing. Tetra Pak cartons pose greater challenges in recycling due to their composite layers of paper, plastic, and aluminum, requiring specialized facilities to process and often leading to lower recycling rates. Effective waste management favors tin cans for circular economy goals, as their material recovery supports reduced environmental impact and resource conservation.
Cost Analysis of Tin Can vs Tetra Pak
Tin cans generally have higher initial manufacturing costs due to metal sourcing and fabrication but offer superior durability and recyclability compared to Tetra Pak cartons, which use laminated paperboard and plastic layers allowing lower production expenses but complicate recycling processes. From a cost perspective, tin cans often result in higher transportation costs because of their weight, whereas Tetra Pak packaging benefits from lightweight materials, reducing logistics expenses and carbon footprint. Long-term cost analysis also considers market trends where fluctuations in metal prices can significantly impact tin can expenses, while Tetra Pak relies more on pulp prices and plastic resin costs, making each suitable for different budget and sustainability priorities.
Consumer Safety and Health Considerations
Tin cans provide robust protection against microbial contamination and physical damage, ensuring product safety and extended shelf life, but concerns about BPA linings persist, prompting the use of BPA-free alternatives. Tetra Pak cartons feature multiple layers, including aluminum and polyethylene, creating a strong barrier against light, air, and bacteria, which helps preserve nutritional quality and reduce spoilage. Both packaging types are designed to maintain food safety and prevent chemical leaching, with ongoing improvements targeting consumer health and environmental sustainability.
Trends and Innovations in Packaging Solutions
Tin cans remain a dominant choice for durable food packaging due to their superior preservation qualities and recyclability, while Tetra Pak innovates with lightweight, aseptic cartons that extend shelf life without refrigeration. Emerging trends favor hybrid packaging combining metal and paperboard layers to enhance sustainability, reduce carbon footprint, and improve consumer convenience. Advances in smart packaging technologies, including QR codes and freshness indicators, are increasingly integrated into both tin cans and Tetra Pak cartons to meet evolving demands for transparency and product safety.
Tin can vs Tetra Pak Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com