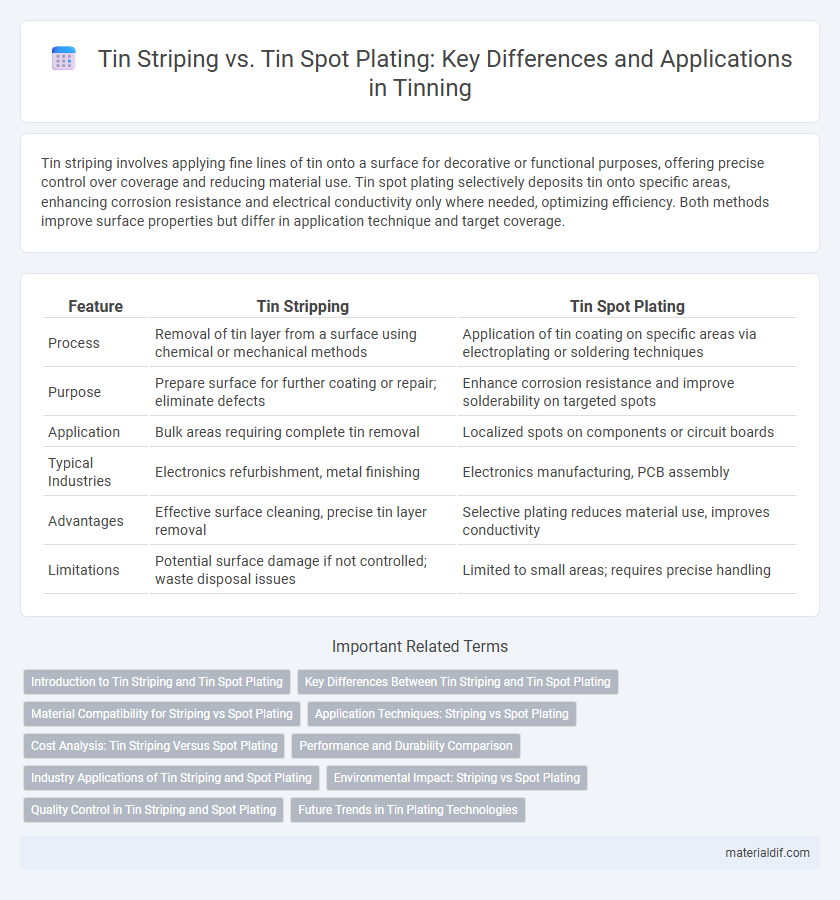
Tin striping involves applying fine lines of tin onto a surface for decorative or functional purposes, offering precise control over coverage and reducing material use. Tin spot plating selectively deposits tin onto specific areas, enhancing corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity only where needed, optimizing efficiency. Both methods improve surface properties but differ in application technique and target coverage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tin Stripping | Tin Spot Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Removal of tin layer from a surface using chemical or mechanical methods | Application of tin coating on specific areas via electroplating or soldering techniques |
| Purpose | Prepare surface for further coating or repair; eliminate defects | Enhance corrosion resistance and improve solderability on targeted spots |
| Application | Bulk areas requiring complete tin removal | Localized spots on components or circuit boards |
| Typical Industries | Electronics refurbishment, metal finishing | Electronics manufacturing, PCB assembly |
| Advantages | Effective surface cleaning, precise tin layer removal | Selective plating reduces material use, improves conductivity |
| Limitations | Potential surface damage if not controlled; waste disposal issues | Limited to small areas; requires precise handling |
Introduction to Tin Striping and Tin Spot Plating
Tin striping involves the selective application of a thin layer of tin onto specific areas of a metal substrate, improving corrosion resistance and solderability while reducing material usage. Tin spot plating, on the other hand, deposits tin in discrete spots rather than continuous strips, enhancing localized protection and electrical conductivity in targeted regions. Both processes are essential in electronics manufacturing, with tin striping commonly used for edge connectors and tin spot plating applied in circuit board contacts.
Key Differences Between Tin Striping and Tin Spot Plating
Tin striping involves applying thin, continuous lines of tin onto a metal surface for enhanced corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, whereas tin spot plating deposits small, localized areas of tin for targeted protection or solderability. Striping offers uniform coverage beneficial for large surface areas, while spot plating is ideal for precise areas requiring tin's protective or conductive properties. The main differences center on coverage extent, application technique, and the specific functional outcomes needed for electronic or industrial components.
Material Compatibility for Striping vs Spot Plating
Tin striping offers superior material compatibility by providing uniform coverage on substrates with varied surface energies, ensuring consistent adhesion and corrosion resistance. Spot plating of tin targets specific areas, which may result in incomplete surface protection and potential galvanic corrosion when adjacent metals with differing electrochemical properties are exposed. Selecting the appropriate tin plating method depends on the substrate material and the desired balance between protective coverage and localized conductivity.
Application Techniques: Striping vs Spot Plating
Tin striping involves applying narrow, continuous lines of tin onto a substrate, ideal for precise electrical circuits and connectors requiring controlled tin coverage. Tin spot plating deposits discrete, localized tin spots, enhancing corrosion resistance and solderability on specific areas without covering the entire surface. This selective application technique optimizes material usage and performance in electronics manufacturing and PCB assembly.
Cost Analysis: Tin Striping Versus Spot Plating
Tin striping generally incurs higher initial costs due to the extensive use of tin material and longer processing times, whereas tin spot plating offers a cost-efficient alternative by applying tin selectively only to high-wear or corrosion-prone areas. The cost-effectiveness of tin spot plating becomes significant in large-scale manufacturing where material savings and reduced labor expenses lower overall production costs. Evaluating project-specific factors such as component complexity, required corrosion resistance, and volume can determine whether the upfront investment in striping justifies its benefits compared to the streamlined expenses of spot plating.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Tin striping provides superior corrosion resistance by creating a uniform, smooth coating that enhances electrical conductivity and reduces the risk of oxidation. In contrast, tin spot plating offers targeted protection but may result in uneven coverage, potentially compromising long-term durability and performance under harsh environmental conditions. The continuous layer formed by tin striping ensures better wear resistance and adhesion, making it more suitable for applications requiring consistent protection and longevity.
Industry Applications of Tin Striping and Spot Plating
Tin striping and tin spot plating are essential for enhancing corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity in electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries. Tin striping provides continuous, uniform coverage ideal for printed circuit boards and connectors, while tin spot plating offers targeted protection in mechanical parts and battery components. Both techniques improve solderability and durability, optimizing performance in demanding industrial applications.
Environmental Impact: Striping vs Spot Plating
Tin striping generates less hazardous waste compared to tin spot plating, as it uses minimal chemicals and reduces metal ion discharge. Tin spot plating often involves higher concentrations of plating solutions, leading to increased wastewater treatment demands and potential heavy metal contamination. Choosing tin striping can significantly lower environmental risks linked to hazardous effluents and resource consumption in industrial tin plating processes.
Quality Control in Tin Striping and Spot Plating
Quality control in tin striping emphasizes uniform thickness and adhesion strength to prevent corrosion and enhance electrical conductivity, with precise monitoring via X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and coating thickness gauges. Tin spot plating requires stringent inspection of spot size, distribution, and bonding quality to ensure optimal solderability and corrosion resistance, often verified through microscopic analysis and pull testing. Both processes demand consistent surface preparation and environmental controls to achieve reliable and high-performance tin coatings.
Future Trends in Tin Plating Technologies
Future trends in tin plating technologies emphasize eco-friendly processes and enhanced corrosion resistance, with tin striping gaining attention for precise, pattern-based applications that reduce material waste. Advances in tin spot plating utilize laser and plasma techniques to improve adhesion and surface uniformity, supporting miniaturization in electronics. Integration of AI-driven quality control and real-time monitoring further optimizes tin plating efficiency and sustainability.
Tin striping vs tin spot plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com