Coating weight directly influences the thickness of a tin pet, affecting its protective properties and durability. Higher coating weight results in a thicker layer, enhancing resistance to corrosion and extending the material's lifespan. Optimizing coating weight balances performance requirements with manufacturing costs for efficient tin pet production.
Table of Comparison
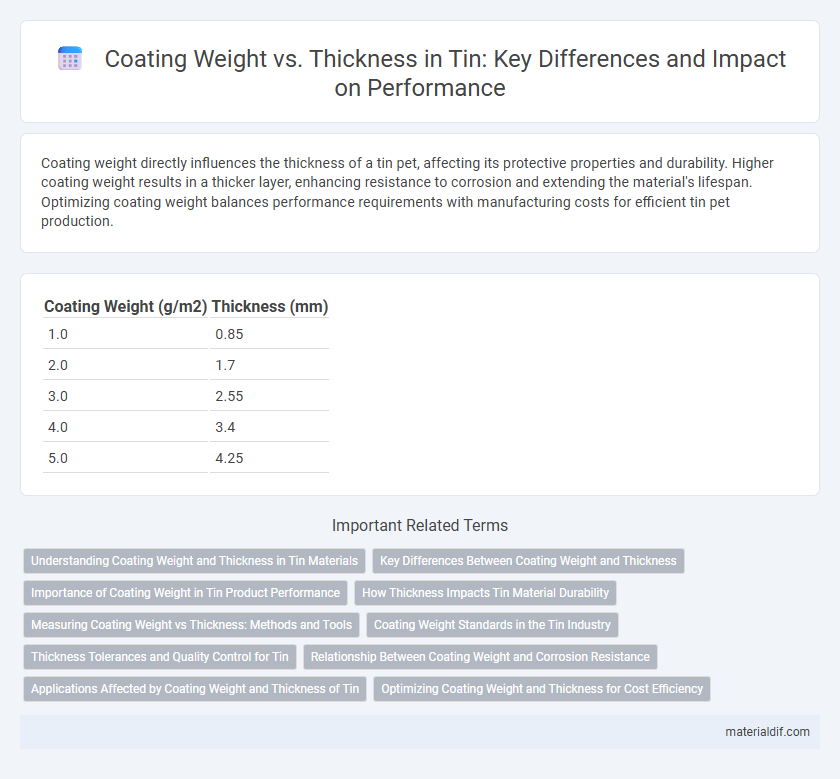
| Coating Weight (g/m2) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 0.85 |
| 2.0 | 1.7 |
| 3.0 | 2.55 |
| 4.0 | 3.4 |
| 5.0 | 4.25 |
Understanding Coating Weight and Thickness in Tin Materials
Coating weight in tin materials refers to the mass of tin applied per unit area, typically measured in grams per square meter (g/m2), while thickness denotes the physical film depth, often expressed in microns or mils. Accurate control of coating weight ensures consistent protection against corrosion and enhances solderability, whereas thickness influences mechanical durability and electrical conductivity. Optimizing both parameters is crucial for achieving desired performance characteristics in tin-coated products across electronics and food packaging industries.
Key Differences Between Coating Weight and Thickness
Coating weight measures the mass of tin applied per unit area, typically expressed in grams per square meter (g/m2), while thickness refers to the physical dimension of the tin layer, usually in micrometers (um). Tin coating weight directly influences corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, whereas thickness affects mechanical properties and surface smoothness. Accurate control of both coating weight and thickness is critical in industries like electronics and food packaging to ensure optimal performance and compliance with standards.
Importance of Coating Weight in Tin Product Performance
Coating weight in tin products directly affects corrosion resistance and solderability, making it a critical parameter for ensuring long-term durability and electrical conductivity. Optimal coating weight ensures proper coverage, preventing substrate exposure and maintaining mechanical strength, while insufficient thickness can lead to premature product failure. Precise control of coating weight enhances product reliability and extends service life in applications such as electronics, food packaging, and automotive components.
How Thickness Impacts Tin Material Durability
Tin coating weight directly influences thickness, which plays a critical role in enhancing material durability by providing increased resistance to corrosion and mechanical wear. Thicker tin layers form a more effective barrier against oxidation and environmental damage, extending the lifespan of coated metal components. Optimizing coating thickness ensures improved performance in applications such as electronics, food packaging, and automotive parts, where long-term protection is essential.
Measuring Coating Weight vs Thickness: Methods and Tools
Measuring coating weight versus thickness for tin layers involves precise methods such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and coulometric techniques, which provide accurate quantification of the coating mass per unit area. Thickness measurements often utilize micrometers, eddy current devices, or beta backscatter gauges to determine the physical layer dimension without damaging the substrate. These tools collectively enable quality control in tin plating by correlating coating weight data with thickness to ensure consistent protection and performance.
Coating Weight Standards in the Tin Industry
Coating weight standards in the tin industry are critical for ensuring consistent corrosion resistance and solderability across various applications. Typical coating weights range from 0.5 to 3 grams per square meter, with specific standards such as ASTM B545 providing detailed guidelines for electroplated tin coatings. Precise control of coating weight directly influences the effective thickness, impacting product performance and adherence to industry regulations.
Thickness Tolerances and Quality Control for Tin
Tin coating thickness tolerances are critical for ensuring consistent protective performance in electronics and plating applications. Precise control within specified micron ranges minimizes defects such as peeling or uneven coverage, directly affecting corrosion resistance and solderability. Advanced metrology techniques and real-time monitoring enhance quality control, maintaining stringent tolerance standards essential for high-reliability tin coatings.
Relationship Between Coating Weight and Corrosion Resistance
The coating weight of tin significantly influences its corrosion resistance by determining the thickness and uniformity of the protective layer formed on metal surfaces. Higher coating weights generally result in thicker tin layers, enhancing barrier properties and reducing permeability to corrosive agents such as moisture and oxygen. Optimizing the balance between coating weight and thickness is critical to achieving maximum corrosion resistance without excessive material costs or compromised mechanical performance.
Applications Affected by Coating Weight and Thickness of Tin
Coating weight and thickness of tin directly influence its performance in applications such as food packaging, electronics, and corrosion protection. Higher coating weights enhance corrosion resistance and solderability, critical for preserving food quality and ensuring reliable electronic connections. Precise control of tin thickness balances cost efficiency and functional durability across these industrial applications.
Optimizing Coating Weight and Thickness for Cost Efficiency
Optimizing tin coating weight and thickness involves balancing protective performance with material cost to achieve maximum cost efficiency. Precise control of coating thickness, typically measured in microns, ensures adequate corrosion resistance while minimizing excess tin usage that drives up expenses. Advanced process monitoring techniques enable manufacturers to maintain consistent coating weight, reducing waste and enhancing overall production economics.
Coating weight vs Thickness Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com