Extruding PTFE creates continuous, uniform shapes ideal for tubing and rods, offering high mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Molding PTFE allows complex geometries and precise dimensions but may introduce slight porosity affecting material density. Choosing between extruding and molding depends on application requirements like shape complexity, performance, and production volume.
Table of Comparison
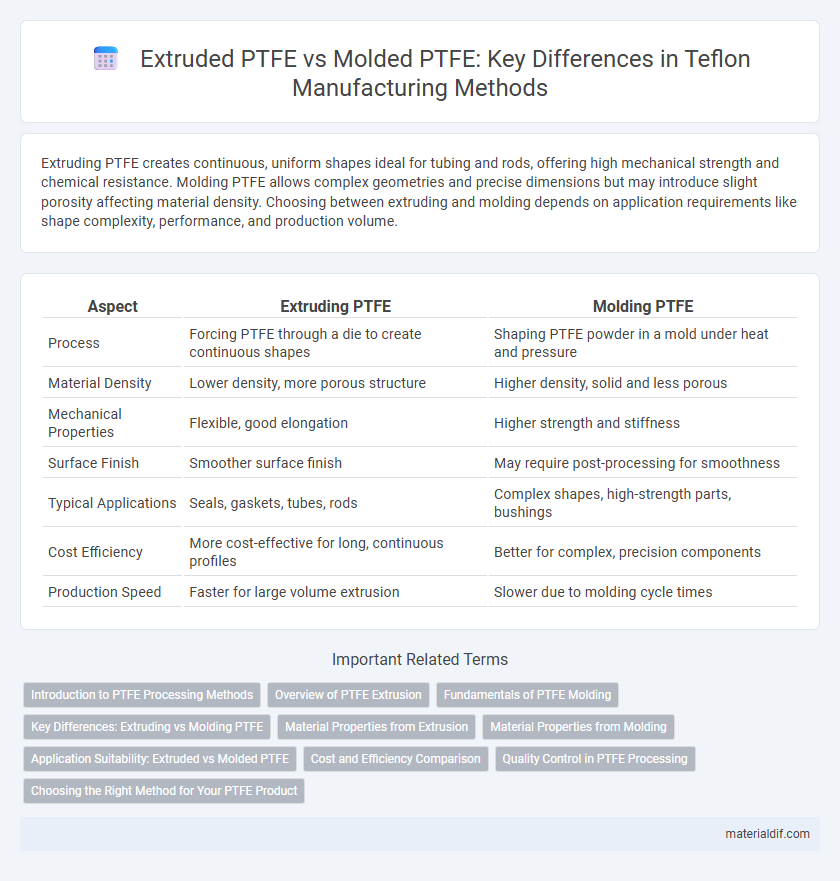
| Aspect | Extruding PTFE | Molding PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Forcing PTFE through a die to create continuous shapes | Shaping PTFE powder in a mold under heat and pressure |
| Material Density | Lower density, more porous structure | Higher density, solid and less porous |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, good elongation | Higher strength and stiffness |
| Surface Finish | Smoother surface finish | May require post-processing for smoothness |
| Typical Applications | Seals, gaskets, tubes, rods | Complex shapes, high-strength parts, bushings |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective for long, continuous profiles | Better for complex, precision components |
| Production Speed | Faster for large volume extrusion | Slower due to molding cycle times |
Introduction to PTFE Processing Methods
Extruding PTFE produces dense, homogeneous parts with excellent mechanical properties and surface finish, ideal for tubing and rods, while molding PTFE allows for complex shapes and high-volume production using compression or ram extrusion molds. Both methods start with fine PTFE powders but differ in particle consolidation and sintering techniques, affecting the material's crystallinity and porosity. Understanding extrusion and molding processes is essential for optimizing PTFE components in applications requiring chemical inertness and high temperature resistance.
Overview of PTFE Extrusion
PTFE extrusion involves forcing softened PTFE resin through a shaped die to create continuous profiles such as tubes, rods, or sheets with consistent cross-sections. This process enhances material density and mechanical properties by aligning polymer chains, resulting in improved strength and durability compared to molded PTFE parts. Extruded PTFE is ideal for applications requiring uniform geometry and enhanced structural integrity, such as seals, gaskets, and insulating components.
Fundamentals of PTFE Molding
PTFE molding involves compressing powdered resin into a specific shape before sintering, enabling complex geometries and tight tolerances that extrusion cannot achieve. This process allows for greater control over density and mechanical properties, essential for applications requiring enhanced chemical resistance and wear performance. Molding PTFE produces parts with uniform molecular orientation, resulting in improved structural integrity compared to extruded PTFE components.
Key Differences: Extruding vs Molding PTFE
Extruding PTFE involves forcing softened resin through a die to create continuous shapes like rods and tubes, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and consistent microstructure. Molding PTFE uses compression or ram methods to shape powdered resin into complex parts, offering higher dimensional accuracy but potentially lower tensile strength. Differences in processing temperatures and pressures between extruding and molding impact the crystallinity and surface finish of the final PTFE products.
Material Properties from Extrusion
Extruding PTFE enhances the material's density and mechanical strength by aligning polymer chains during the manufacturing process, resulting in improved tensile strength and wear resistance compared to molded PTFE. The extrusion process reduces porosity, which increases chemical resistance and lowers permeability, making extruded PTFE ideal for applications requiring superior durability. Unlike molded PTFE, extruded PTFE also exhibits greater dimensional stability and enhanced dielectric properties due to its uniform microstructure.
Material Properties from Molding
Molded PTFE exhibits lower tensile strength and density compared to extruded PTFE, resulting in slightly reduced mechanical durability but enhanced chemical resistance. Its isotropic molecular structure provides uniform thermal expansion and excellent dielectric properties, making it ideal for complex geometries and electrical insulation applications. The molding process allows for precise dimensional control and the formation of intricate shapes, though it may introduce porosity affecting permeability in certain high-performance applications.
Application Suitability: Extruded vs Molded PTFE
Extruded PTFE offers improved mechanical strength and is ideal for producing uniform, continuous shapes such as rods, tubes, and sheets for applications requiring dimensional stability and smooth surfaces. Molded PTFE provides greater design flexibility and is better suited for complex, custom parts used in seals, gaskets, and intricate components where intricate geometries are essential. Choosing between extruded and molded PTFE depends on the specific requirements of the application, including mechanical properties, shape complexity, and dimensional tolerances.
Cost and Efficiency Comparison
Extruding PTFE offers higher production efficiency with faster cycle times and lower labor costs, making it more suitable for large-scale manufacturing. Molding PTFE incurs higher material waste and energy consumption, resulting in increased overall costs despite better precision and complex shape capabilities. Cost analysis reveals extruded PTFE is more economical for simple profiles, whereas molded PTFE suits specialized applications requiring tight tolerances.
Quality Control in PTFE Processing
Extruding PTFE ensures consistent density and uniform molecular alignment, leading to superior mechanical properties and enhanced dimensional accuracy compared to molding. Quality control during PTFE extruding involves precise monitoring of temperature, pressure, and extrusion speed to prevent defects like voids or uneven surface texture. In molding PTFE, maintaining strict control over mold temperature and cooling rate is critical to avoid internal stresses and ensure homogeneity, but extruded PTFE typically offers more reliable quality reproducibility.
Choosing the Right Method for Your PTFE Product
Extruding PTFE produces continuous, uniform tubes, rods, and films ideal for seamless, flexible products, while molding PTFE is suited for complex, precise shapes requiring detailed features. The choice depends on product geometry, production volume, and mechanical performance needs, with extrusion favored for long-length applications and molding preferred for intricate, custom parts. Understanding these distinctions ensures optimal material properties and cost-efficiency in PTFE manufacturing.
Extruding PTFE vs Molding PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com