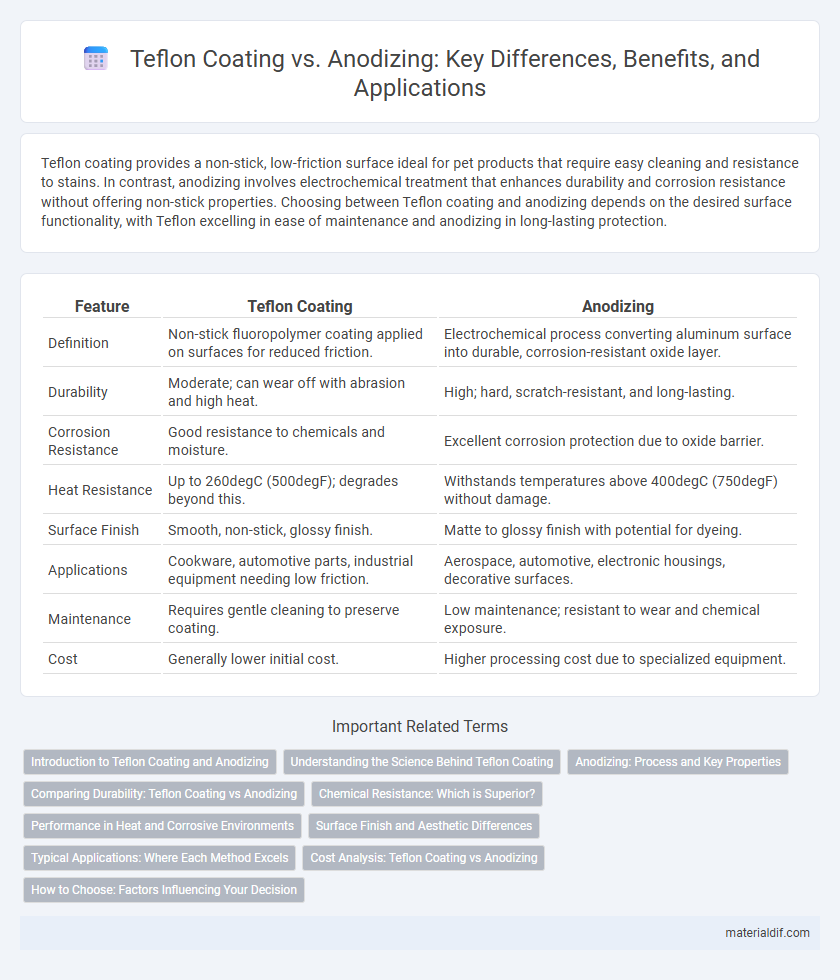
Teflon coating provides a non-stick, low-friction surface ideal for pet products that require easy cleaning and resistance to stains. In contrast, anodizing involves electrochemical treatment that enhances durability and corrosion resistance without offering non-stick properties. Choosing between Teflon coating and anodizing depends on the desired surface functionality, with Teflon excelling in ease of maintenance and anodizing in long-lasting protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Teflon Coating | Anodizing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-stick fluoropolymer coating applied on surfaces for reduced friction. | Electrochemical process converting aluminum surface into durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer. |
| Durability | Moderate; can wear off with abrasion and high heat. | High; hard, scratch-resistant, and long-lasting. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and moisture. | Excellent corrosion protection due to oxide barrier. |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF); degrades beyond this. | Withstands temperatures above 400degC (750degF) without damage. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, non-stick, glossy finish. | Matte to glossy finish with potential for dyeing. |
| Applications | Cookware, automotive parts, industrial equipment needing low friction. | Aerospace, automotive, electronic housings, decorative surfaces. |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning to preserve coating. | Low maintenance; resistant to wear and chemical exposure. |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost. | Higher processing cost due to specialized equipment. |
Introduction to Teflon Coating and Anodizing
Teflon coating involves applying a non-stick polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) layer to metal surfaces, enhancing corrosion resistance and reducing friction. Anodizing is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer on aluminum, improving durability and surface hardness. Both methods improve metal performance but differ significantly in application and protective properties.
Understanding the Science Behind Teflon Coating
Teflon coating involves the application of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its non-stick properties and chemical resistance, creating a smooth, low-friction surface ideal for cookware and industrial applications. Unlike anodizing, which enhances aluminum's surface hardness through an electrochemical oxidation process producing a durable oxide layer, Teflon coating relies on adhesion of the polymer layer to provide corrosion resistance and easy release characteristics. The science behind Teflon's effectiveness lies in its molecular structure, featuring strong carbon-fluorine bonds that repel adhesion and withstand high temperatures up to 260degC without degrading.
Anodizing: Process and Key Properties
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface, typically aluminum, into a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer. This oxide layer enhances surface hardness, improves wear resistance, and provides excellent adhesion for paints and sealants without altering the metal's dimensional integrity. Unlike Teflon coating, anodizing offers superior thermal stability and environmental safety, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting surface protection.
Comparing Durability: Teflon Coating vs Anodizing
Teflon coating provides excellent non-stick properties but is generally less durable under high abrasion or impact compared to anodizing, which creates a hard, corrosion-resistant oxide layer on aluminum surfaces. Anodized finishes offer superior wear resistance and maintain structural integrity better over time, making them ideal for heavy-use applications. While Teflon coatings can degrade with scratches and high temperatures, anodizing enhances surface hardness and protects against environmental damage, contributing to longer-lasting durability.
Chemical Resistance: Which is Superior?
Teflon coating offers exceptional chemical resistance, effectively withstanding strong acids, bases, and solvents without degradation, making it ideal for corrosive environments. Anodizing provides a hard oxide layer primarily for aluminum, enhancing corrosion resistance but is less effective against aggressive chemicals compared to Teflon. Therefore, for superior chemical resistance in industrial applications, Teflon coating outperforms anodizing.
Performance in Heat and Corrosive Environments
Teflon coating offers exceptional resistance to high temperatures up to 260degC and provides excellent chemical inertness, making it ideal for corrosive environments. Anodizing enhances aluminum's surface hardness and corrosion resistance but typically withstands lower temperatures, around 120degC to 150degC. For applications involving extreme heat and aggressive chemicals, Teflon's non-stick and anti-corrosive properties outperform anodized surfaces in durability and maintenance.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Differences
Teflon coating provides a smooth, glossy finish with non-stick properties ideal for cookware, while anodizing creates a matte, textured surface that enhances durability and color retention. The non-reflective anodized surface resists scratches and fading, offering a more industrial and robust aesthetic compared to Teflon's sleek appearance. Both methods improve corrosion resistance but cater to different functional and visual preferences in surface finishing.
Typical Applications: Where Each Method Excels
Teflon coating excels in applications requiring non-stick properties and chemical resistance, such as cookware, industrial machinery parts, and medical devices. Anodizing is ideal for enhancing corrosion resistance and surface hardness in aerospace components, automotive parts, and architectural aluminum products. Each method offers unique benefits tailored to specific performance demands and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Teflon Coating vs Anodizing
Teflon coating generally incurs lower upfront application costs compared to anodizing due to simpler processing and less specialized equipment, making it cost-effective for large-scale production. Anodizing involves higher initial expenses because of complex surface treatment and electricity consumption but offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, Teflon coating suits budget-conscious projects with moderate wear conditions, while anodizing proves more economical for high-durability applications despite greater initial investment.
How to Choose: Factors Influencing Your Decision
Choosing between Teflon coating and anodizing depends on factors such as desired surface hardness, corrosion resistance, and application environment. Teflon coating offers excellent non-stick properties and chemical resistance, ideal for cookware and low-friction surfaces, while anodizing provides increased durability, wear resistance, and enhanced metal adhesion suitable for aerospace and automotive parts. Consider the material compatibility, operating temperature, and budget constraints to determine the optimal surface treatment for your specific requirements.
Teflon Coating vs Anodizing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com