Etched Teflon surfaces enhance adhesion properties by increasing surface roughness, making them ideal for applications requiring strong bonding of coatings or adhesives. Unetched Teflon retains its smooth, non-stick characteristics but offers limited adhesion, suitable for environments prioritizing chemical resistance and ease of cleaning. Choosing between etched and unetched Teflon depends on the balance between adhesion requirements and the need for non-stick, low-friction surfaces.
Table of Comparison
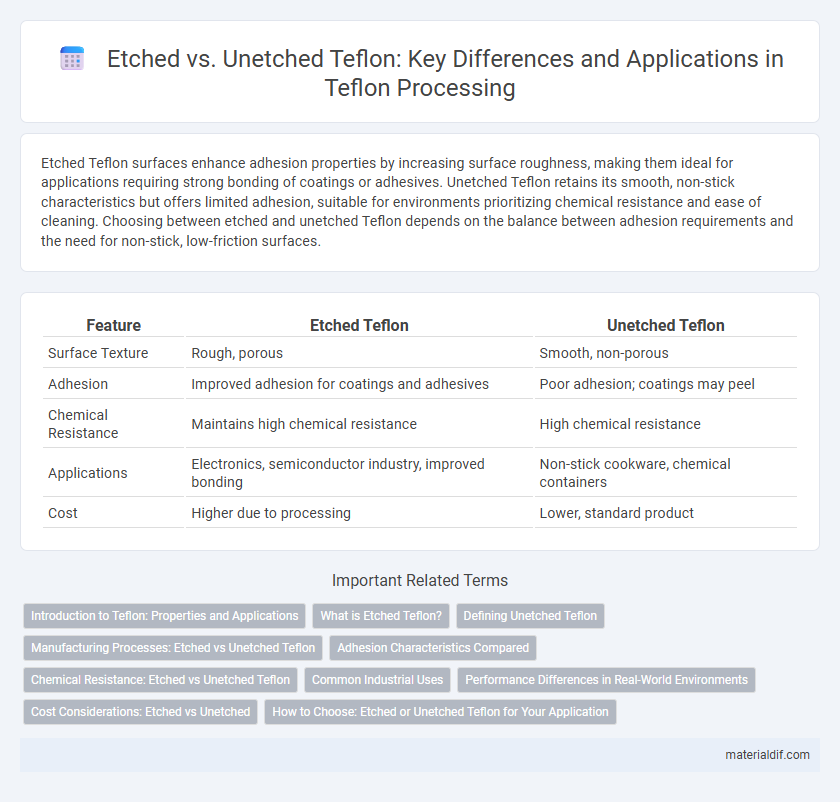
| Feature | Etched Teflon | Unetched Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Texture | Rough, porous | Smooth, non-porous |
| Adhesion | Improved adhesion for coatings and adhesives | Poor adhesion; coatings may peel |
| Chemical Resistance | Maintains high chemical resistance | High chemical resistance |
| Applications | Electronics, semiconductor industry, improved bonding | Non-stick cookware, chemical containers |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower, standard product |
Introduction to Teflon: Properties and Applications
Etched Teflon offers enhanced surface roughness compared to unetched Teflon, significantly improving adhesion properties for coatings and adhesives. Unetched Teflon retains its natural non-stick, chemical resistance, and high-temperature stability characteristics, making it ideal for applications requiring low friction and durability. Industrial uses of etched Teflon include printed circuit boards and chemical processing equipment, whereas unetched Teflon is commonly utilized in cookware, seals, and electrical insulation.
What is Etched Teflon?
Etched Teflon refers to Teflon surfaces that have undergone a chemical or plasma treatment to create microscopic roughness, enhancing adhesion properties. This alteration increases surface energy, allowing better bonding with inks, paints, and adhesives, which is typically challenging with smooth, untreated Teflon. In contrast, unetched Teflon maintains its non-stick, low-energy surface, resulting in poor adhesion and limited application in coating or printing processes.
Defining Unetched Teflon
Unetched Teflon refers to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) surfaces that have not undergone any chemical or physical treatment to alter their topography or surface energy. This pristine condition preserves Teflon's natural non-stick, low-friction properties but also results in poor adhesion characteristics for coatings or bonding applications. Unlike etched Teflon, which displays increased surface roughness to improve bonding strength, unetched Teflon maintains its original smoothness and chemical inertness.
Manufacturing Processes: Etched vs Unetched Teflon
Etched Teflon undergoes a plasma or chemical etching process that modifies its non-stick surface by creating microscopic pores, enhancing adhesion properties critical for coating and bonding applications. Unetched Teflon retains its pristine, smooth fluoropolymer surface, providing superior chemical resistance and non-stick performance but limited bonding capability. The manufacturing contrast hinges on etching's ability to increase surface energy, enabling better paint adherence or lamination compared to the inert nature of unetched Teflon.
Adhesion Characteristics Compared
Etched Teflon features a chemically roughened surface that significantly enhances adhesion characteristics compared to unetched Teflon, which has a smooth, inert surface resistant to bonding. The etching process introduces micro-porosity, improving mechanical interlocking and surface energy, resulting in stronger adhesive bonds for coatings, films, and laminates. In contrast, unetched Teflon's low surface energy leads to poor wettability and suboptimal adhesion in industrial applications.
Chemical Resistance: Etched vs Unetched Teflon
Etched Teflon exhibits a reduced chemical resistance compared to unetched Teflon due to its altered surface morphology, which can increase susceptibility to certain aggressive solvents. Unetched Teflon maintains its inherent non-reactive and corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for environments requiring maximum chemical inertness. The etching process enhances adhesion properties but compromises the polymer's original chemical stability, impacting its performance in highly corrosive applications.
Common Industrial Uses
Etched Teflon exhibits increased surface roughness, enhancing adhesion properties essential for applications such as circuit board manufacturing and coating adhesion in aerospace components. Unetched Teflon, with its smooth and chemically inert surface, is preferred for chemical processing equipment, non-stick coatings, and insulation in electrical applications. The choice between etched and unetched Teflon depends on whether surface bonding or chemical resistance is the priority in specific industrial uses.
Performance Differences in Real-World Environments
Etched Teflon surfaces exhibit enhanced adhesion properties and improved wettability compared to unetched Teflon, leading to superior coating durability and reduced surface contamination in real-world applications. The microscopic roughness increase from the etching process facilitates better bonding with adhesives and paints, which is critical in aerospace and electronic industries. In contrast, unetched Teflon retains its naturally low surface energy, resulting in excellent non-stick behavior but limited mechanical adhesion and susceptibility to surface wear under harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Considerations: Etched vs Unetched
Etched Teflon typically incurs higher costs due to the additional surface modification process that enhances adhesion properties for coatings and adhesives. Unetched Teflon is more cost-effective as it retains the material's native low surface energy without extra treatments, making it suitable for applications with less stringent bonding requirements. Choosing between etched and unetched Teflon depends on balancing budget constraints with the specific performance needs of the application.
How to Choose: Etched or Unetched Teflon for Your Application
Choosing between etched and unetched Teflon depends on the surface adhesion requirements of your application, with etched Teflon offering enhanced bonding capabilities due to its chemically treated surface. Unetched Teflon retains its natural non-stick and chemical resistance properties but may not adhere well to paints, adhesives, or coatings. Consider etched Teflon when superior adhesion is critical for components exposed to stress or environmental factors, while unetched Teflon suits applications prioritizing maximum non-stick performance and chemical inertness.
Etched Teflon vs Unetched Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com