Virgin Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and low friction, making it ideal for applications requiring pure, uncontaminated performance. Filled Teflon incorporates materials like glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity, catering to more demanding mechanical environments. Choosing between virgin and filled Teflon depends on balancing chemical purity with improved durability and structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
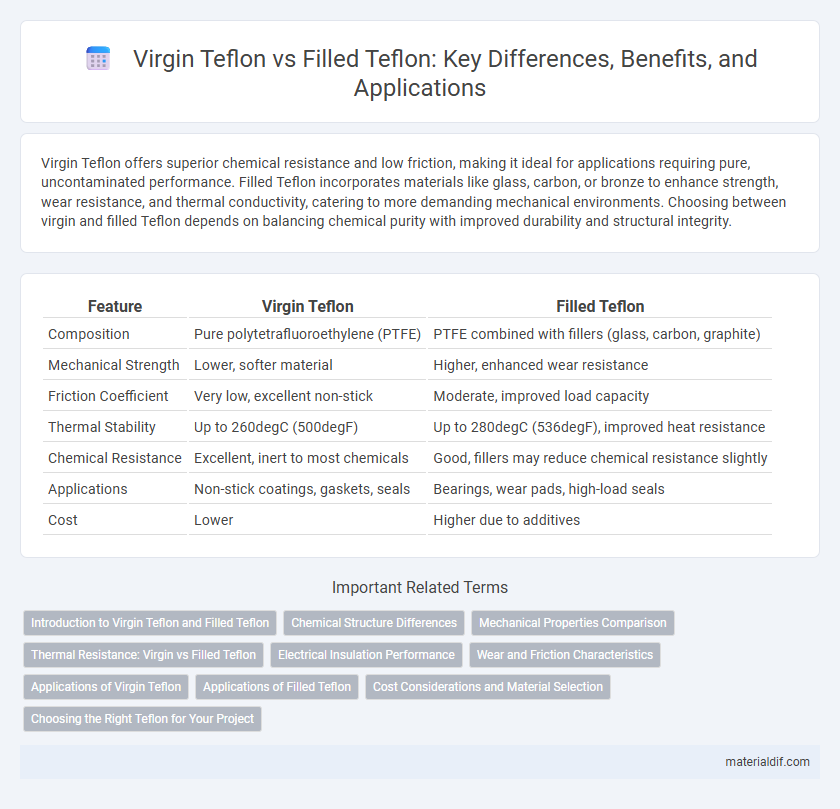
| Feature | Virgin Teflon | Filled Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | PTFE combined with fillers (glass, carbon, graphite) |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower, softer material | Higher, enhanced wear resistance |
| Friction Coefficient | Very low, excellent non-stick | Moderate, improved load capacity |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 280degC (536degF), improved heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, inert to most chemicals | Good, fillers may reduce chemical resistance slightly |
| Applications | Non-stick coatings, gaskets, seals | Bearings, wear pads, high-load seals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to additives |
Introduction to Virgin Teflon and Filled Teflon
Virgin Teflon is pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and high thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring non-reactive surfaces. Filled Teflon incorporates additives such as glass, carbon, or graphite to enhance mechanical properties like wear resistance, dimensional stability, and load-bearing capacity. These variations enable tailored performance in industries ranging from aerospace to chemical processing where specific material characteristics are critical.
Chemical Structure Differences
Virgin Teflon consists of pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer chains with a fully fluorinated carbon backbone, providing exceptional chemical inertness and low friction. Filled Teflon incorporates additives such as glass fibers, carbon, or graphite particles within the PTFE matrix to enhance mechanical strength and wear resistance, altering its chemical microstructure by introducing interaction sites. These compositional differences impact thermal conductivity, chemical reactivity, and mechanical properties, making filled Teflon suitable for demanding industrial applications compared to virgin PTFE's ultra-pure chemical stability.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Virgin Teflon exhibits exceptional chemical resistance and low friction but has relatively lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to filled Teflon. Filled Teflon incorporates additives such as glass, carbon, or bronze, which significantly enhance its tensile strength, rigidity, and abrasion resistance. This reinforcement enables filled Teflon grades to perform better in high-load and high-wear applications, maintaining dimensional stability under mechanical stress.
Thermal Resistance: Virgin vs Filled Teflon
Virgin Teflon offers excellent thermal resistance with continuous service temperatures up to 260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Filled Teflon variants, enhanced with additives such as glass fibers or carbon, improve structural strength and thermal conductivity but may slightly reduce maximum thermal stability compared to virgin material. The choice between virgin and filled Teflon depends on the balance between required thermal resistance and mechanical reinforcement.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Virgin Teflon offers superior electrical insulation with a high dielectric strength of approximately 600 to 700 volts per mil, ensuring excellent resistance to electrical breakdown. Filled Teflon incorporates additives like glass, carbon, or bronze, which enhance mechanical properties but can reduce dielectric strength to around 300 to 500 volts per mil, potentially affecting insulation performance. Selecting the appropriate Teflon type depends on the balance between electrical insulation requirements and mechanical durability for specific applications.
Wear and Friction Characteristics
Virgin Teflon exhibits exceptional low friction and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal wear over time. Filled Teflon, enhanced with additives like glass, carbon, or graphite, significantly improves wear resistance and reduces friction in high-load or abrasive environments. The choice between virgin and filled Teflon depends on the specific wear conditions and frictional forces encountered in the application.
Applications of Virgin Teflon
Virgin Teflon is widely used in applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance and high purity, such as pharmaceutical processing, food handling, and semiconductor manufacturing, where contamination must be minimized. Its unmatched non-stick properties and electrical insulation make it ideal for coatings, liners, and seals in medical devices and laboratory equipment. Virgin Teflon's excellent temperature stability and low friction coefficient also enhance performance in aerospace and automotive components.
Applications of Filled Teflon
Filled Teflon is widely used in demanding industrial applications such as chemical processing, electrical insulation, and high-performance sealing solutions due to its enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to virgin Teflon. Common fillers include glass fibers, carbon, and graphite, which significantly improve thermal conductivity, dimensional stability, and frictional properties, making it ideal for dynamic seals, bearings, and pump parts. These enhanced properties enable filled Teflon to perform reliably in harsh environments involving high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and continuous mechanical stress.
Cost Considerations and Material Selection
Virgin Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and purity at a higher cost, making it ideal for applications requiring exceptional performance. Filled Teflon incorporates additives like glass or carbon to enhance mechanical strength and wear resistance while reducing material expenses. Selecting between virgin and filled Teflon depends on balancing budget constraints with specific application demands for durability and chemical compatibility.
Choosing the Right Teflon for Your Project
Virgin Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and a smooth, non-stick surface ideal for applications requiring high purity and low friction. Filled Teflon incorporates additives such as glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heavy-duty or high-load environments. Selecting between virgin and filled Teflon depends on the project's specific demands for durability, temperature range, and friction requirements.
Virgin Teflon vs Filled Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com