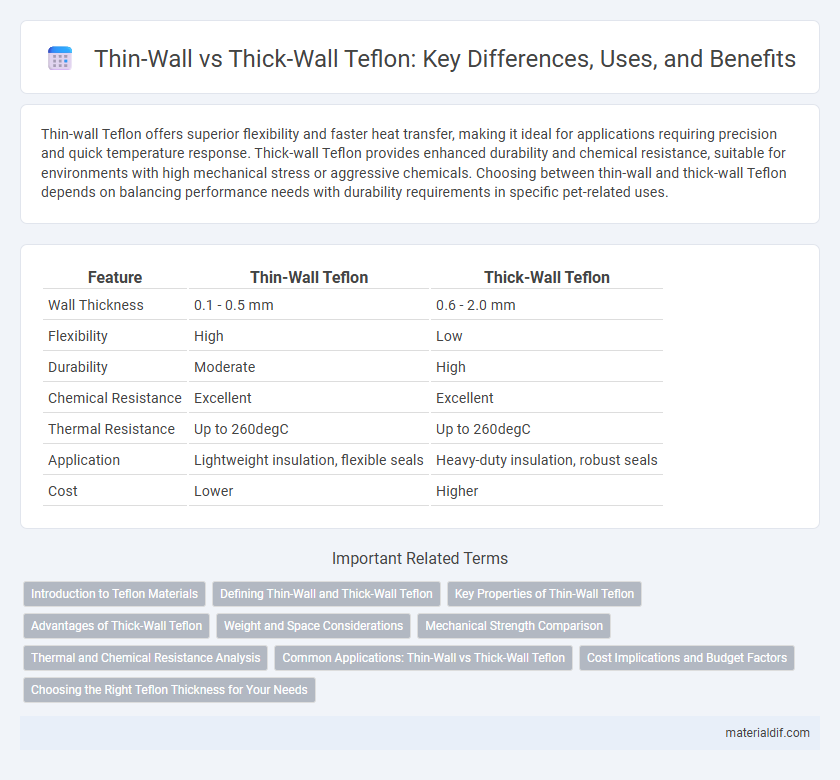
Thin-wall Teflon offers superior flexibility and faster heat transfer, making it ideal for applications requiring precision and quick temperature response. Thick-wall Teflon provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, suitable for environments with high mechanical stress or aggressive chemicals. Choosing between thin-wall and thick-wall Teflon depends on balancing performance needs with durability requirements in specific pet-related uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Thin-Wall Teflon | Thick-Wall Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | 0.1 - 0.5 mm | 0.6 - 2.0 mm |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 260degC | Up to 260degC |
| Application | Lightweight insulation, flexible seals | Heavy-duty insulation, robust seals |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Teflon Materials
Thin-wall Teflon offers superior flexibility and faster heat dissipation, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and precise insulation. Thick-wall Teflon provides enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for demanding industrial environments where durability is critical. Both variants leverage polytetrafluoroethylene's non-stick, high-temperature, and electrical insulating properties, but their structural differences dictate specific usage scenarios.
Defining Thin-Wall and Thick-Wall Teflon
Thin-wall Teflon typically refers to Teflon components with wall thicknesses less than 1 millimeter, offering enhanced flexibility and faster heat dissipation for applications requiring intricate designs and tight tolerances. Thick-wall Teflon, generally exceeding 3 millimeters in thickness, provides superior chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability in demanding industrial environments. These distinct thickness categories influence thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties, guiding selection based on specific engineering requirements.
Key Properties of Thin-Wall Teflon
Thin-wall Teflon offers superior flexibility and lightweight characteristics compared to thick-wall Teflon, enabling enhanced heat resistance up to 260degC without compromising durability. Its low coefficient of friction provides excellent non-stick and anti-corrosive properties, making it ideal for precise, space-constrained applications such as gaskets, seals, and insulating films. The thin-wall design also allows for faster thermal transfer and quicker response times in temperature-sensitive environments, optimizing performance in advanced industrial and medical devices.
Advantages of Thick-Wall Teflon
Thick-wall Teflon offers enhanced chemical resistance and superior durability compared to thin-wall variants, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Its robust structure provides excellent insulation properties and greater mechanical strength, reducing the risk of punctures or tears. The thicker design also improves high-temperature stability, ensuring reliable performance in extreme environments.
Weight and Space Considerations
Thin-wall Teflon offers significant weight reduction compared to thick-wall Teflon, making it ideal for applications where minimizing mass is crucial. The reduced thickness also saves valuable space, enabling more compact designs in industries such as aerospace and electronics. However, careful assessment of mechanical strength is essential to ensure thin-wall configurations meet durability requirements.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Thin-wall Teflon exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to thick-wall Teflon due to its reduced material cross-section, which can lead to increased susceptibility to deformation under stress. Thick-wall Teflon provides enhanced durability and resistance to mechanical wear, making it suitable for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. The difference in wall thickness directly influences tensile strength, impact resistance, and overall structural integrity of Teflon components.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance Analysis
Thin-wall Teflon offers superior thermal conductivity and faster heat dissipation, making it ideal for applications requiring quick temperature adjustments, whereas thick-wall Teflon provides enhanced thermal insulation and prolonged heat retention. Chemically, both thin-wall and thick-wall Teflon exhibit excellent resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, but thick-wall designs enhance durability against aggressive chemical environments due to their increased material mass. The choice between thin and thick-wall Teflon depends on balancing thermal management needs with chemical exposure severity in industrial applications.
Common Applications: Thin-Wall vs Thick-Wall Teflon
Thin-wall Teflon is widely used in applications requiring flexibility and lightweight properties, such as electrical insulation, flexible tubing, and protective coatings for cables. Thick-wall Teflon excels in demanding environments needing superior chemical resistance and structural strength, including industrial piping, valve linings, and high-performance gaskets. Both variants leverage Teflon's non-stick, heat-resistant, and low-friction qualities tailored to specific thickness-dependent application needs.
Cost Implications and Budget Factors
Thin-wall Teflon offers significant cost savings due to reduced material usage and lower manufacturing expenses compared to thick-wall Teflon, making it ideal for budget-sensitive projects. Thick-wall Teflon provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance but involves higher raw material costs and increased machining complexity. Budget factors must balance performance requirements against the cost implications of material thickness, with thin-wall options favored for economical applications where minimal wear is expected.
Choosing the Right Teflon Thickness for Your Needs
Thin-wall Teflon offers enhanced flexibility and faster heat transfer, making it ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control and lightweight components. Thick-wall Teflon provides superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for environments with aggressive chemicals or high-pressure demands. Selecting the right Teflon thickness depends on balancing durability requirements with thermal efficiency to optimize performance and longevity.
Thin-wall Teflon vs Thick-wall Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com