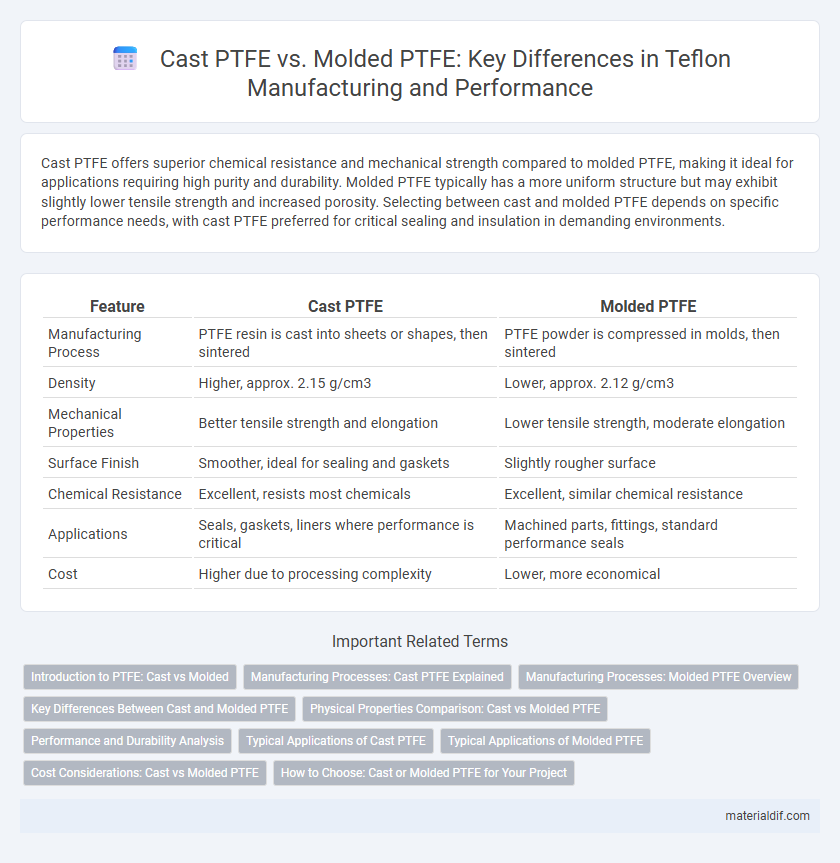
Cast PTFE offers superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to molded PTFE, making it ideal for applications requiring high purity and durability. Molded PTFE typically has a more uniform structure but may exhibit slightly lower tensile strength and increased porosity. Selecting between cast and molded PTFE depends on specific performance needs, with cast PTFE preferred for critical sealing and insulation in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast PTFE | Molded PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | PTFE resin is cast into sheets or shapes, then sintered | PTFE powder is compressed in molds, then sintered |
| Density | Higher, approx. 2.15 g/cm3 | Lower, approx. 2.12 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Properties | Better tensile strength and elongation | Lower tensile strength, moderate elongation |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, ideal for sealing and gaskets | Slightly rougher surface |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resists most chemicals | Excellent, similar chemical resistance |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, liners where performance is critical | Machined parts, fittings, standard performance seals |
| Cost | Higher due to processing complexity | Lower, more economical |
Introduction to PTFE: Cast vs Molded
Cast PTFE is produced by polymerizing hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene in a fluid state, resulting in superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to molded PTFE. Molded PTFE is formed by compression molding fine PTFE powder, offering a cost-effective option with lower density and slightly reduced durability. The choice between cast and molded PTFE depends on application-specific requirements such as temperature tolerance, wear resistance, and precision of dimensions.
Manufacturing Processes: Cast PTFE Explained
Cast PTFE is manufactured by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene into a fine powder, which is then thoroughly mixed with a lubricant to create a homogeneous mass. This mass is placed into molds and subjected to heat and pressure, causing the polymer particles to fuse without melting, resulting in high-density, uniform sheets. The casting process produces PTFE with superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability compared to molded PTFE.
Manufacturing Processes: Molded PTFE Overview
Molded PTFE is produced by compressing and sintering PTFE powder into desired shapes using methods like compression molding, transfer molding, or ram extrusion, resulting in components with enhanced dimensional stability and structural integrity. This manufacturing process allows for complex geometries and tighter tolerances compared to cast PTFE, making it ideal for precision applications in aerospace, chemical processing, and medical industries. The sintering phase ensures a high-density material with superior chemical resistance and low friction properties characteristic of PTFE.
Key Differences Between Cast and Molded PTFE
Cast PTFE exhibits superior mechanical strength, higher purity, and better chemical resistance due to its manufacturing process involving the polymerization of monomer solutions. Molded PTFE, produced by compressing and sintering PTFE powders, tends to have lower mechanical properties but allows for more complex shapes and cost-effective production. Key differences include cast PTFE's enhanced wear resistance and dimensional stability versus molded PTFE's versatility in machining and scalability for mass production.
Physical Properties Comparison: Cast vs Molded PTFE
Cast PTFE exhibits superior mechanical strength, higher purity, and better chemical resistance compared to molded PTFE, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Molded PTFE typically has lower tensile strength and slightly higher porosity, which can affect its performance in high-stress environments. The density of cast PTFE ranges from 2.12 to 2.17 g/cm3, whereas molded PTFE usually falls between 2.10 and 2.14 g/cm3, influencing distinct physical durability and wear resistance characteristics.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Cast PTFE offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance compared to Molded PTFE due to its denser molecular structure, resulting in enhanced performance in high-stress applications. Molded PTFE typically exhibits lower mechanical properties but provides cost-effective solutions for simpler components with moderate durability requirements. The increased crystallinity in Cast PTFE contributes to improved wear resistance and longevity, making it preferable for demanding industrial environments.
Typical Applications of Cast PTFE
Cast PTFE is widely used in chemical processing equipment, seals, and gaskets due to its superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to molded PTFE. Its dense, homogenous structure enhances its performance in high-purity applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing and pharmaceutical production. Typical applications also include linings for pipes and tanks, where resistance to aggressive chemicals and temperature extremes is critical.
Typical Applications of Molded PTFE
Molded PTFE is widely used in chemical processing equipment, seals, and gaskets due to its superior chemical resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. Its typical applications include valve seats, linings, and custom parts for the pharmaceutical and food industries where non-reactivity and cleanliness are critical. Molded PTFE's durability and low friction also make it ideal for components in pumps, compressors, and electrical insulation.
Cost Considerations: Cast vs Molded PTFE
Cast PTFE typically incurs higher production costs due to its longer processing time and more complex manufacturing methods compared to molded PTFE. Molded PTFE offers cost advantages through faster cycle times and efficient material usage, making it more suitable for high-volume production runs. Budget considerations should weigh the superior mechanical properties and surface finish of cast PTFE against the economic benefits of molded PTFE in large-scale applications.
How to Choose: Cast or Molded PTFE for Your Project
Choosing between cast PTFE and molded PTFE depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability. Cast PTFE offers superior purity, enhanced chemical resistance, and better mechanical properties, making it ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and long-term durability. Molded PTFE is generally more cost-effective and suitable for simpler shapes or less demanding environments, but it may exhibit slightly lower mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy compared to cast PTFE.
Cast PTFE vs Molded PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com