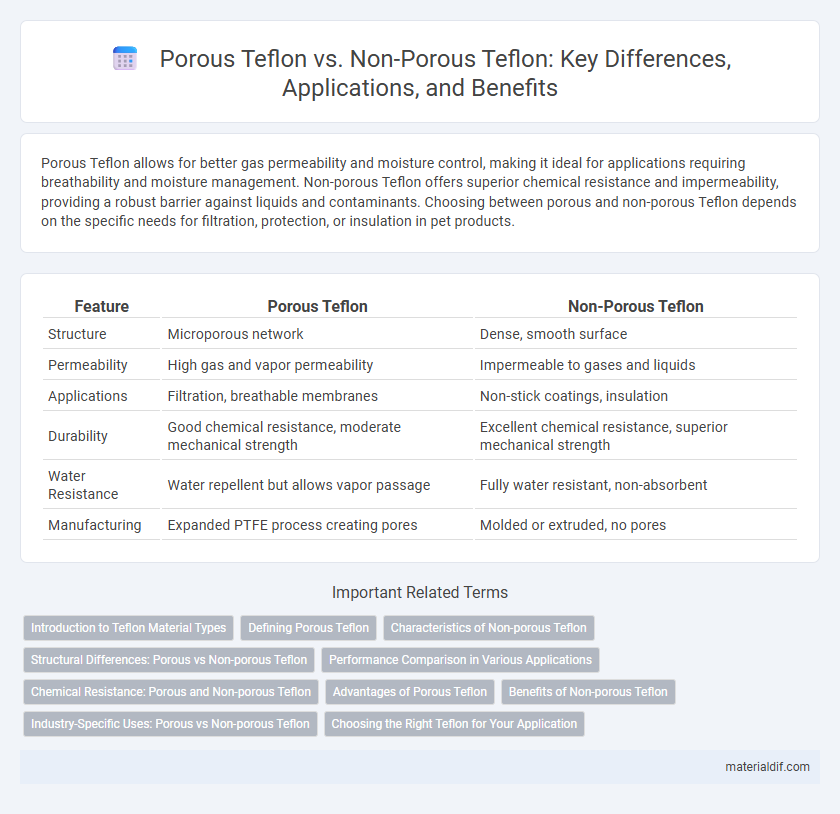
Porous Teflon allows for better gas permeability and moisture control, making it ideal for applications requiring breathability and moisture management. Non-porous Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and impermeability, providing a robust barrier against liquids and contaminants. Choosing between porous and non-porous Teflon depends on the specific needs for filtration, protection, or insulation in pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porous Teflon | Non-Porous Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Microporous network | Dense, smooth surface |
| Permeability | High gas and vapor permeability | Impermeable to gases and liquids |
| Applications | Filtration, breathable membranes | Non-stick coatings, insulation |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, moderate mechanical strength | Excellent chemical resistance, superior mechanical strength |
| Water Resistance | Water repellent but allows vapor passage | Fully water resistant, non-absorbent |
| Manufacturing | Expanded PTFE process creating pores | Molded or extruded, no pores |
Introduction to Teflon Material Types
Porous Teflon features microscopic openings that allow for gas permeability and fluid flow, making it ideal for filtration and breathability applications. Non-porous Teflon is characterized by a solid, impermeable surface providing excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation, commonly used in coatings and gaskets. Both types retain PTFE's inherent properties such as high temperature resistance, low friction, and non-stick surfaces, but their structural differences dictate distinct industrial uses.
Defining Porous Teflon
Porous Teflon consists of a network of interconnected microscopic voids, allowing for gas permeability and selective filtration, unlike its non-porous counterpart which is fully dense and impermeable. This unique porosity enables applications in breathable membranes, filtration systems, and insulation where gas exchange is critical. The material's controlled pore size and distribution define its performance in chemical resistance, hydrophobicity, and mechanical strength.
Characteristics of Non-porous Teflon
Non-porous Teflon exhibits a smooth, dense surface structure that provides excellent chemical resistance and low friction properties, making it ideal for applications requiring non-stick and corrosion-resistant coatings. Its impermeability to gases and liquids prevents contamination and enhances durability in harsh environments. This type of Teflon is commonly used in cookware, seals, and gaskets where barrier protection and easy cleaning are critical.
Structural Differences: Porous vs Non-porous Teflon
Porous Teflon features a microstructure with interconnected voids that allow gas or liquid permeability, enhancing applications such as filtration and breathability. Non-porous Teflon consists of a dense, solid matrix with no void spaces, providing superior chemical resistance and insulation properties. The structural difference impacts mechanical flexibility and surface interaction, where porous Teflon offers increased surface area while non-porous Teflon ensures impermeability and durability.
Performance Comparison in Various Applications
Porous Teflon exhibits superior breathability and filtration efficiency, making it ideal for applications such as gas diffusion layers and breathable membranes. Non-porous Teflon provides excellent chemical resistance and impermeability, ensuring reliable performance in sealing, insulation, and protective coatings. The choice between porous and non-porous Teflon depends on specific demands for permeability versus barrier properties in industries like electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
Chemical Resistance: Porous and Non-porous Teflon
Porous Teflon exhibits enhanced chemical resistance due to its micro-structured surface, allowing it to resist aggressive solvents and acids while facilitating controlled permeability for gas or liquid exchange. Non-porous Teflon provides a uniform, impermeable barrier that offers superior resistance to a wider range of chemicals without absorption or degradation, ideal for applications demanding absolute chemical isolation. Both forms maintain exceptional resistance to high temperatures and corrosive environments, but porous Teflon's selective permeability makes it advantageous in filtration and catalytic processes.
Advantages of Porous Teflon
Porous Teflon offers superior breathability, allowing gases and vapors to pass through while maintaining chemical resistance and hydrophobicity, which prevents liquid absorption. Its unique microstructure enhances filtration efficiency and reduces clogging in industrial applications compared to non-porous Teflon. This makes porous Teflon ideal for use in membranes, vents, and breathable protective coatings where moisture permeability and durability are crucial.
Benefits of Non-porous Teflon
Non-porous Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability compared to porous variants, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting, non-reactive surfaces. Its smooth, impermeable surface prevents liquid absorption and contamination, ensuring consistent performance in food processing, medical devices, and industrial coatings. The non-porous structure also simplifies cleaning and maintenance, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Industry-Specific Uses: Porous vs Non-porous Teflon
Porous Teflon, characterized by its microporous structure, is widely used in filtration systems, environmental monitoring, and breathable protective clothing due to its ability to allow gas and vapor passage while blocking liquids and particulates. Non-porous Teflon, valued for its chemical inertness and low friction properties, finds applications in gasket seals, medical tubing, and cookware coatings where impermeability and contamination prevention are critical. Industry-specific deployment hinges on whether permeability or barrier properties best suit needs in sectors like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace.
Choosing the Right Teflon for Your Application
Porous Teflon features microscopic voids that enhance breathability and filtration, making it ideal for applications such as chemical-resistant membranes and breathable protective gear. Non-porous Teflon offers superior chemical resistance and is impermeable to gases and liquids, making it suitable for coatings, seals, and non-stick surfaces. Selecting the right Teflon depends on the specific requirements of permeability, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability in your application.
Porous Teflon vs Non-porous Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com