Virgin PTFE offers superior chemical resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for applications requiring high purity and low friction. Filled PTFE, enhanced with materials like glass, carbon, or bronze, improves mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability, extending the material's range of applications. Choosing between virgin and filled PTFE depends on balancing the need for chemical inertness against the demand for enhanced durability and performance under mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
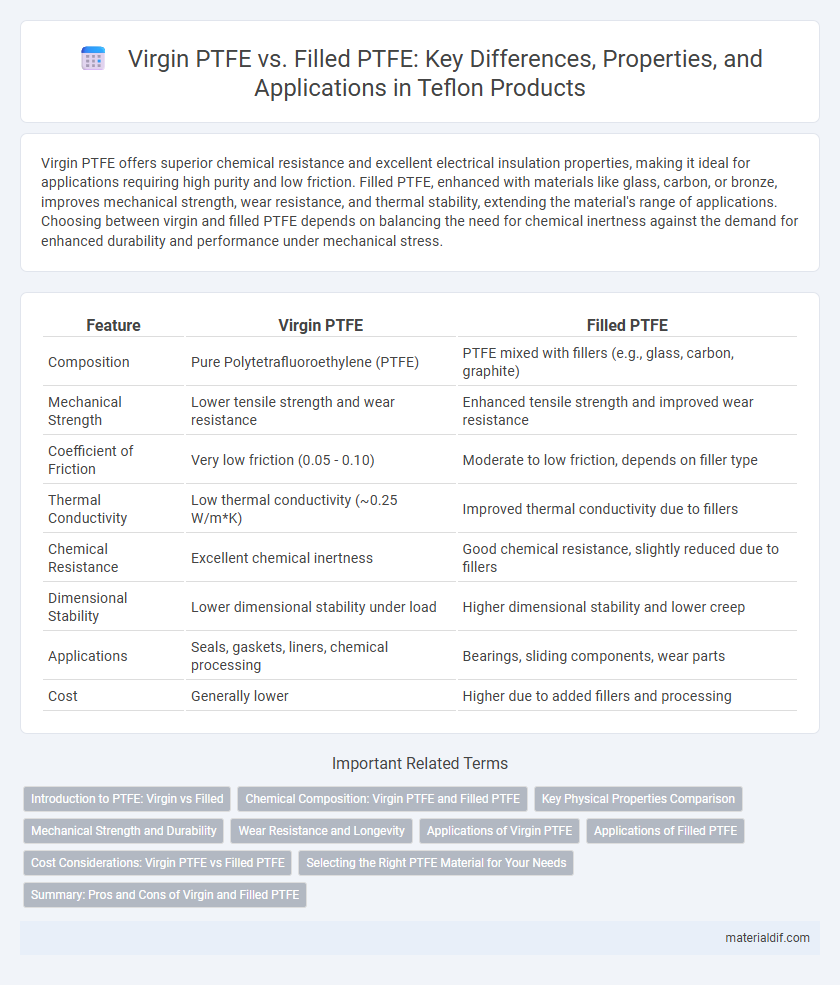
| Feature | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | PTFE mixed with fillers (e.g., glass, carbon, graphite) |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength and wear resistance | Enhanced tensile strength and improved wear resistance |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very low friction (0.05 - 0.10) | Moderate to low friction, depends on filler type |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity (~0.25 W/m*K) | Improved thermal conductivity due to fillers |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical inertness | Good chemical resistance, slightly reduced due to fillers |
| Dimensional Stability | Lower dimensional stability under load | Higher dimensional stability and lower creep |
| Applications | Seals, gaskets, liners, chemical processing | Bearings, sliding components, wear parts |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to added fillers and processing |
Introduction to PTFE: Virgin vs Filled
Virgin PTFE is a high-purity polymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Filled PTFE incorporates additives such as glass fibers, carbon, or graphite to enhance mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, addressing limitations of pure PTFE in load-bearing environments. Understanding the key differences between virgin and filled PTFE enables optimized material selection based on performance requirements in sealing, coating, and insulation applications.
Chemical Composition: Virgin PTFE and Filled PTFE
Virgin PTFE consists of pure polytetrafluoroethylene with a highly crystalline structure, offering exceptional chemical inertness and resistance to solvents, acids, and bases. Filled PTFE incorporates reinforcing materials such as glass fibers, carbon, or graphite to enhance mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability while slightly altering its chemical composition. The addition of fillers may reduce the chemical purity but improves performance characteristics in abrasive or high-load environments.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Virgin PTFE offers superior chemical resistance and excellent electrical insulation but has a relatively low tensile strength and higher creep compared to filled PTFE. Filled PTFE incorporates additives such as glass, carbon, or graphite, enhancing mechanical strength, reducing wear, and improving thermal conductivity while maintaining good chemical resistance. The choice between virgin and filled PTFE depends on specific application requirements, balancing properties like hardness, friction coefficient, and dimensional stability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Virgin PTFE offers exceptional chemical resistance and low friction but has relatively lower mechanical strength and wear resistance. Filled PTFE compounds, enhanced with additives like glass fibers, carbon, or bronze, significantly improve mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and durability under high-stress conditions. These reinforcements reduce deformation and extend lifespan in applications demanding enhanced load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Virgin PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance and low friction but has lower wear resistance and shorter lifespan compared to filled PTFE variants. Filled PTFE incorporates reinforcing materials such as glass, carbon, or bronze, significantly enhancing wear resistance and extending operational longevity in demanding applications. Selecting filled PTFE improves durability and reduces maintenance frequency in high-wear environments, making it ideal for industrial seals, bearings, and sliding components.
Applications of Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE offers exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, making it ideal for medical devices, food processing equipment, and chemical processing applications. Its high purity ensures contaminant-free performance in pharmaceutical and semiconductor industries. The material's excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability also support its use in electrical insulation and gasket manufacturing.
Applications of Filled PTFE
Filled PTFE enhances properties like wear resistance, thermal conductivity, and compressive strength, making it ideal for applications in automotive components, industrial seals, and electrical insulation. Its improved mechanical performance suits use in bearing materials, valve seats, and sliding bearings under high load conditions. These advancements allow filled PTFE to perform reliably in demanding environments where virgin PTFE may fail due to deformation or excessive wear.
Cost Considerations: Virgin PTFE vs Filled PTFE
Virgin PTFE generally incurs higher production costs due to its pure polymer composition and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Filled PTFE, which contains additives such as glass, carbon, or graphite, offers enhanced mechanical properties and wear resistance at a lower cost, providing a cost-effective solution for industrial uses where extreme purity is not essential. Cost considerations between virgin and filled PTFE often depend on the specific application's performance requirements versus budget constraints.
Selecting the Right PTFE Material for Your Needs
Virgin PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance, low friction, and high purity, making it ideal for applications requiring non-contaminating and inert materials. Filled PTFE compounds, enhanced with additives such as glass, carbon, or bronze, provide improved mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity for demanding environments. Choose virgin PTFE for high-purity, low-wear scenarios and filled PTFE when enhanced durability and performance under stress are critical.
Summary: Pros and Cons of Virgin and Filled PTFE
Virgin PTFE offers superior chemical resistance, low friction, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring pure, uncontaminated performance. Filled PTFE enhances mechanical properties like wear resistance and strength by incorporating materials such as glass, carbon, or bronze, but may slightly reduce chemical inertness and increase friction. The choice between virgin and filled PTFE depends on the balance between the need for extreme purity versus improved durability and load-bearing capabilities.
Virgin PTFE vs Filled PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com