Heat shrink PTFE tubing offers a tight, seamless fit over irregular shapes, providing enhanced insulation and chemical resistance compared to non-shrink PTFE, which maintains a consistent diameter and is ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability. The shrinkable variant contracts when heated, allowing for secure sealing and protection in electrical and automotive uses, while non-shrink PTFE remains flexible and resistant to high temperatures without the need for heat application. Choosing between heat shrink and non-shrink PTFE depends on the specific requirements for insulation, sealing, and environmental resistance in your project.
Table of Comparison
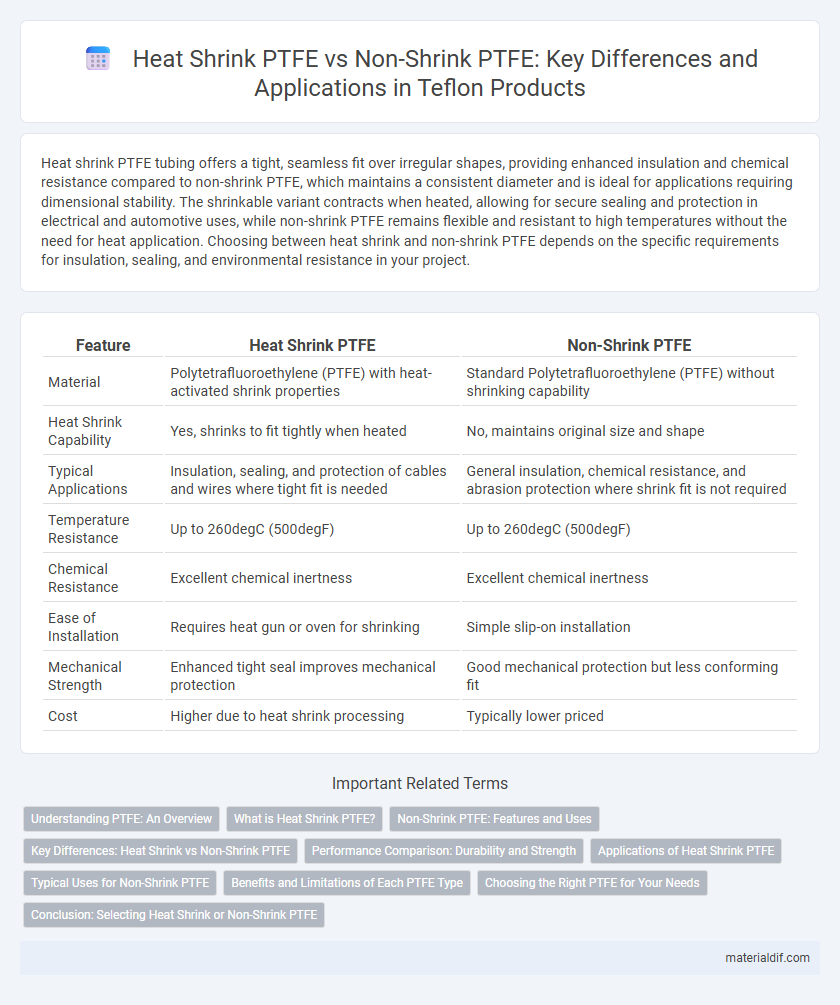
| Feature | Heat Shrink PTFE | Non-Shrink PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with heat-activated shrink properties | Standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) without shrinking capability |
| Heat Shrink Capability | Yes, shrinks to fit tightly when heated | No, maintains original size and shape |
| Typical Applications | Insulation, sealing, and protection of cables and wires where tight fit is needed | General insulation, chemical resistance, and abrasion protection where shrink fit is not required |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical inertness | Excellent chemical inertness |
| Ease of Installation | Requires heat gun or oven for shrinking | Simple slip-on installation |
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced tight seal improves mechanical protection | Good mechanical protection but less conforming fit |
| Cost | Higher due to heat shrink processing | Typically lower priced |
Understanding PTFE: An Overview
Heat shrink PTFE tubing offers superior sealing properties and flexibility due to its ability to contract when heated, providing tight protection for wires and components. Non-shrink PTFE tubing maintains a consistent diameter under heat, offering excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation without altering its shape. Both types utilize polytetrafluoroethylene's inherent non-stick, high-temperature, and corrosion-resistant characteristics essential for demanding industrial applications.
What is Heat Shrink PTFE?
Heat Shrink PTFE is a type of polytetrafluoroethylene tubing that contracts when exposed to heat, providing a tight, protective insulation around wires and components. This material offers high chemical resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -200degC to 260degC. Its ability to shrink ensures a secure, durable fit, distinguishing it from Non-Shrink PTFE, which maintains its original shape and size.
Non-Shrink PTFE: Features and Uses
Non-shrink PTFE offers superior chemical resistance and electrical insulation without altering the original size during heat exposure, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability. Its flexibility and non-adhesive surface enable easy installation on sensitive components in aerospace and electronics industries. Commonly used as protective sleeves and insulating tubing, non-shrink PTFE maintains performance under extreme temperatures from -200degC to 260degC.
Key Differences: Heat Shrink vs Non-Shrink PTFE
Heat Shrink PTFE tubing contracts when exposed to heat, providing a tight, conformal fit ideal for insulation and protection of irregular or complex shapes. Non-Shrink PTFE tubing maintains its original dimensions under heat, offering consistent dielectric properties and chemical resistance without altering size. The key difference lies in the heat response: Heat Shrink PTFE offers customizable fitting and improved mechanical protection, while Non-Shrink PTFE delivers stable insulation in applications requiring dimensional consistency.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Strength
Heat shrink PTFE offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to non-shrink PTFE, making it ideal for applications requiring secure, tight sealing under varying thermal conditions. Non-shrink PTFE provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility but lacks the ability to conform tightly around irregular shapes, resulting in less effective protection against environmental stressors. The heat shrink variant maintains structural integrity at higher temperatures, ensuring reliable performance in demanding industrial environments.
Applications of Heat Shrink PTFE
Heat shrink PTFE tubing is widely used in electrical insulation, providing superior protection for wires and cables in harsh environments due to its excellent chemical resistance and high heat tolerance up to 260degC. It is ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries where precise, tight sealing and environmental protection against moisture, dust, and chemicals are critical. Heat shrink PTFE also enhances mechanical strength and flexibility, making it suitable for harnessing and insulating components in complex assemblies requiring reliable, long-lasting performance.
Typical Uses for Non-Shrink PTFE
Non-shrink PTFE is commonly used for insulation in electrical wiring, chemical-resistant tubing, and seals where dimensional stability is critical under extreme heat. It provides excellent dielectric properties and chemical inertness, making it ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. Its resistance to thermal expansion ensures reliable performance in environments requiring consistent, non-shrinking insulation materials.
Benefits and Limitations of Each PTFE Type
Heat shrink PTFE offers excellent conformability and a tight seal around complex shapes, providing superior insulation and resistance to chemicals and high temperatures up to 260degC, making it ideal for protecting wiring and components in harsh environments. Non-shrink PTFE provides stable dimensions and mechanical strength without shrinking, ensuring consistent insulation performance and durability in applications requiring precise fitting and structural integrity under similar thermal and chemical stress conditions. Heat shrink PTFE may have limitations in high-pressure sealing applications due to its shrinking nature, whereas non-shrink PTFE can be less adaptable to irregular surfaces but excels in maintaining shape and physical properties over time.
Choosing the Right PTFE for Your Needs
Heat shrink PTFE offers superior insulation and protection by conforming tightly to complex shapes when heated, making it ideal for applications requiring a secure, moisture-resistant seal. Non-shrink PTFE provides consistent thickness and durability without altering size, suitable for environments where dimensional stability and chemical resistance are critical. Selecting between heat shrink and non-shrink PTFE depends on specific performance requirements such as flexibility, sealing capability, and environmental exposure.
Conclusion: Selecting Heat Shrink or Non-Shrink PTFE
When selecting between Heat Shrink PTFE and Non-Shrink PTFE, consider the application's dimensional and environmental requirements as Heat Shrink PTFE offers tight, conforming insulation ideal for sealing and abrasion resistance. Non-Shrink PTFE provides stable dimensions without contraction, preferred for applications needing consistent thickness and minimal stress on components. Optimal choice hinges on balancing flexibility, mechanical protection, and thermal stability for enhanced performance.
Heat Shrink PTFE vs Non-Shrink PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com