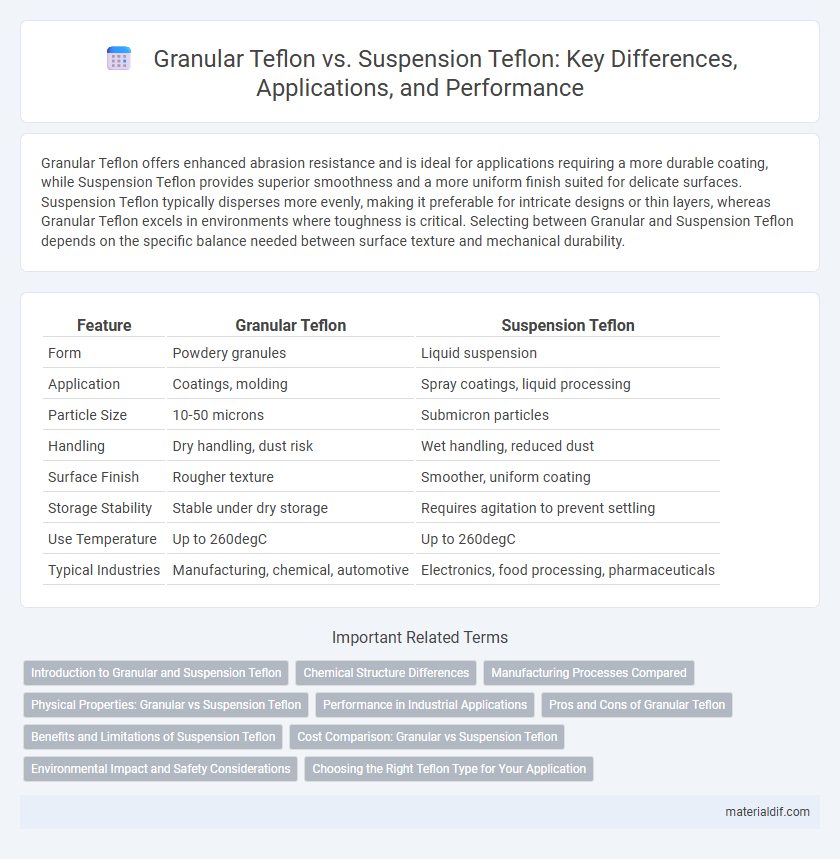
Granular Teflon offers enhanced abrasion resistance and is ideal for applications requiring a more durable coating, while Suspension Teflon provides superior smoothness and a more uniform finish suited for delicate surfaces. Suspension Teflon typically disperses more evenly, making it preferable for intricate designs or thin layers, whereas Granular Teflon excels in environments where toughness is critical. Selecting between Granular and Suspension Teflon depends on the specific balance needed between surface texture and mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Granular Teflon | Suspension Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Powdery granules | Liquid suspension |
| Application | Coatings, molding | Spray coatings, liquid processing |
| Particle Size | 10-50 microns | Submicron particles |
| Handling | Dry handling, dust risk | Wet handling, reduced dust |
| Surface Finish | Rougher texture | Smoother, uniform coating |
| Storage Stability | Stable under dry storage | Requires agitation to prevent settling |
| Use Temperature | Up to 260degC | Up to 260degC |
| Typical Industries | Manufacturing, chemical, automotive | Electronics, food processing, pharmaceuticals |
Introduction to Granular and Suspension Teflon
Granular Teflon consists of solid particles ideal for molding and sintering processes, offering high purity and consistent particle size for uniform applications. Suspension Teflon is a finely dispersed form of PTFE in water, suitable for coatings and emulsions, ensuring excellent adhesion and smooth film formation. Both forms enable diverse industrial uses but differ in physical state and processing methods, influencing their functional performance.
Chemical Structure Differences
Granular Teflon consists of larger, discrete polymer particles, resulting in a less uniform structure compared to Suspension Teflon, which features finely dispersed polymer particles suspended in a medium, leading to a more homogenous chemical composition. The chemical structure of Granular Teflon exhibits longer polymer chains aggregated in granular form, whereas Suspension Teflon contains shorter chains evenly distributed, enhancing its processability and coating uniformity. Differences in particle size and polymer dispersion critically influence the molecular weight distribution and surface chemistry of these Teflon types.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Granular Teflon is produced through suspension polymerization, where tetrafluoroethylene monomers form discrete polymer particles suspended in water, yielding uniform granules ideal for molding and extrusion. Suspension Teflon also involves suspension polymerization but typically results in a finer, more powder-like form suited for coatings and films due to its enhanced dispersion properties. Differences in particle size and morphology between granular and suspension Teflon directly impact processing techniques and final product applications, with granular variants favoring bulk applications and suspension types optimized for surface treatments.
Physical Properties: Granular vs Suspension Teflon
Granular Teflon consists of solid particles that provide higher mechanical strength and better thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and abrasion resistance. Suspension Teflon, on the other hand, has a finer particle size suspended in a liquid medium, offering superior film uniformity and easier application on complex surfaces. The choice between granular and suspension Teflon depends on the required physical properties, such as tensile strength, particle size distribution, and surface finish quality.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Granular Teflon offers enhanced durability and consistent particle size, making it ideal for precise coating applications requiring high wear resistance and chemical inertness. Suspension Teflon provides superior dispersion in liquid mediums, enabling uniform thin-film coatings with excellent adhesion and flexibility in complex geometries. Industrial performance depends on choosing Granular Teflon for abrasion resistance tasks and Suspension Teflon for applications demanding smooth, even layering on intricate surfaces.
Pros and Cons of Granular Teflon
Granular Teflon offers enhanced control over particle size distribution, leading to improved dispersion in composite materials and coatings, which is ideal for applications requiring consistent surface lubrication and non-stick properties. Its solid particulate form allows easier handling and storage compared to Suspension Teflon, but it may require longer mixing times to achieve uniform blending in liquid systems. However, Granular Teflon's limited solubility and slower incorporation rate can pose challenges in certain formulations demanding rapid or homogeneous integration.
Benefits and Limitations of Suspension Teflon
Suspension Teflon offers improved coating uniformity and better control over film thickness compared to Granular Teflon, making it ideal for intricate applications requiring precision. Its fine dispersion enhances adhesion and coverage on complex surfaces, but the processing cost is higher and it requires specialized equipment. Limitations include potential stability issues in suspension form and sensitivity to storage conditions, impacting shelf life and consistency.
Cost Comparison: Granular vs Suspension Teflon
Granular Teflon typically incurs lower production and handling costs due to its solid form, which reduces transportation expenses and storage complexities compared to Suspension Teflon. Suspension Teflon often requires specialized equipment and processing conditions, increasing overall operational costs. Cost efficiency between Granular and Suspension Teflon depends on the specific application requirements and scalability of production methods.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Granular Teflon particles tend to have a lower environmental persistence compared to Suspension Teflon, which contains fine particles that can more easily disperse in water and air, increasing the risk of bioaccumulation and pollution. Safety considerations highlight that Suspension Teflon pose a higher inhalation risk due to its fine particulate nature, potentially leading to respiratory issues in workers handling the material. Proper containment and disposal protocols are critical for Suspension Teflon to mitigate its environmental and health impacts, whereas Granular Teflon allows for safer handling and reduced environmental contamination potential.
Choosing the Right Teflon Type for Your Application
Granular Teflon offers superior abrasion resistance and is ideal for applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability, such as sealing and gasketing. Suspension Teflon provides a smoother finish and better adhesion properties, making it suitable for coatings and thin-film applications. Selecting the right Teflon type depends on the specific demands of your application, including surface texture, durability, and chemical resistance requirements.
Granular Teflon vs Suspension Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com