Teflon coating provides a non-stick surface that resists food adhesion and allows for easy cleaning, making it ideal for low-fat cooking. Anodized aluminum offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance with a naturally non-reactive surface, ensuring even heat distribution and longer-lasting cookware. Choosing between Teflon-coated and anodized aluminum cookware depends on your preference for non-stick convenience versus robust performance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
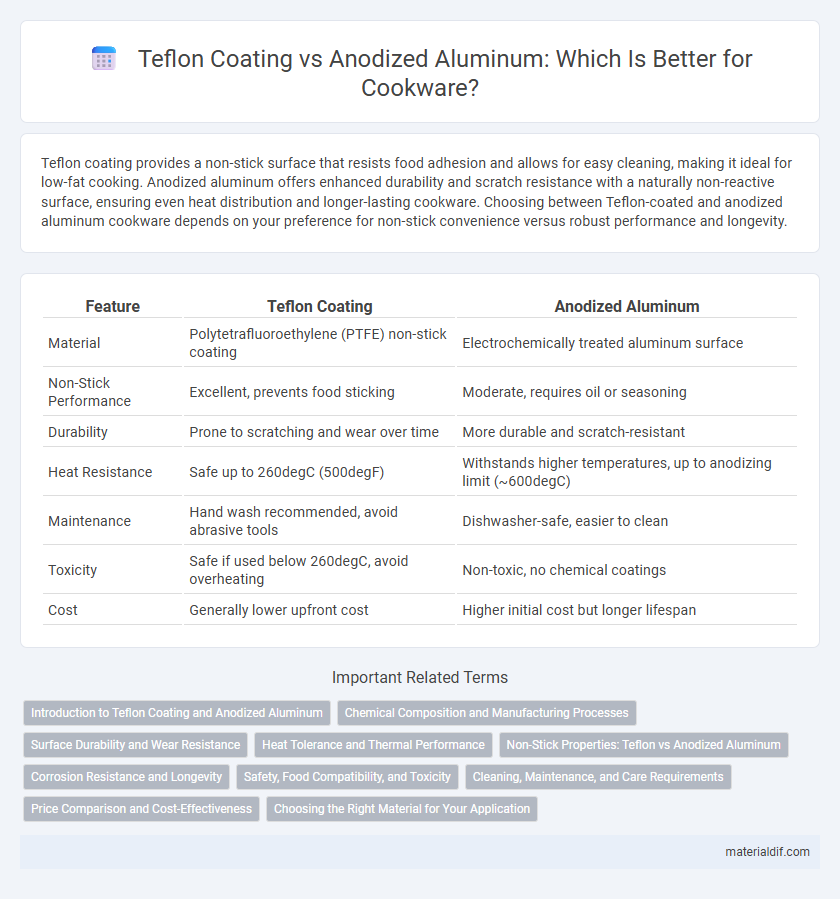
| Feature | Teflon Coating | Anodized Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) non-stick coating | Electrochemically treated aluminum surface |
| Non-Stick Performance | Excellent, prevents food sticking | Moderate, requires oil or seasoning |
| Durability | Prone to scratching and wear over time | More durable and scratch-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Safe up to 260degC (500degF) | Withstands higher temperatures, up to anodizing limit (~600degC) |
| Maintenance | Hand wash recommended, avoid abrasive tools | Dishwasher-safe, easier to clean |
| Toxicity | Safe if used below 260degC, avoid overheating | Non-toxic, no chemical coatings |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
Introduction to Teflon Coating and Anodized Aluminum
Teflon coating is a non-stick, chemically resistant layer made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly used in cookware and industrial applications to reduce friction and prevent food adhesion. Anodized aluminum undergoes an electrochemical process enhancing corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and durability by forming a thick oxide layer on the aluminum substrate. Both materials improve cookware performance, with Teflon offering superior non-stick properties and anodized aluminum providing enhanced structural strength and heat resistance.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Teflon coating consists primarily of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its non-reactive and high-temperature-resistant properties, applied through a spray or dip-coating process followed by baking to create a durable, non-stick surface. Anodized aluminum is produced by electrolytically oxidizing the aluminum surface to form a thick, protective layer of aluminum oxide, enhancing corrosion resistance and hardness without adding any synthetic polymers. This fundamental difference in chemical composition and manufacturing results in Teflon providing superior non-stick characteristics, while anodized aluminum emphasizes structural durability and scratch resistance.
Surface Durability and Wear Resistance
Teflon coating offers excellent non-stick properties but tends to be less durable and more susceptible to scratches and abrasion compared to anodized aluminum. Anodized aluminum undergoes an electrochemical process that creates a hard, wear-resistant oxide layer, significantly enhancing surface durability and resistance to corrosion and wear. This makes anodized aluminum ideal for applications demanding long-lasting performance and superior mechanical strength.
Heat Tolerance and Thermal Performance
Teflon coating offers excellent non-stick properties but typically withstands temperatures up to 500degF (260degC) before degrading, limiting its use in high-heat applications. Anodized aluminum, with its enhanced surface hardness and resistance to heat, can tolerate temperatures upwards of 1200degF (649degC), making it suitable for intense thermal exposure. The anodization process creates a durable oxide layer that promotes superior heat conduction and longevity compared to Teflon's polymer-based thermal limits.
Non-Stick Properties: Teflon vs Anodized Aluminum
Teflon coating offers superior non-stick properties due to its polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) composition, which reduces friction and prevents food adhesion more effectively than anodized aluminum. Anodized aluminum provides a harder surface and improved scratch resistance but lacks the same level of non-stick performance, often requiring oils or fats for cooking. For applications prioritizing easy food release and effortless cleanup, Teflon-coated cookware remains the preferred choice.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Teflon coating offers superior corrosion resistance by creating a non-reactive, chemically inert surface that prevents rust and degradation over time. Anodized aluminum enhances corrosion resistance through an electrochemical process that forms a durable oxide layer, improving hardness and wear resistance. Though anodized aluminum is more scratch-resistant and longer-lasting in abrasive conditions, Teflon coating excels in environments requiring chemical inertness and easy cleaning, providing longevity in corrosion-prone applications.
Safety, Food Compatibility, and Toxicity
Teflon coating offers excellent non-stick properties but can release harmful fumes when overheated above 500degF, posing safety concerns and potential toxicity. Anodized aluminum provides a durable, non-toxic surface that resists corrosion and does not leach chemicals, ensuring higher food compatibility and safer cooking. Both materials require proper use, but anodized aluminum generally presents fewer health risks regarding toxicity and chemical leaching in everyday cooking applications.
Cleaning, Maintenance, and Care Requirements
Teflon coating offers non-stick properties that make cleaning effortless with just mild soap and water, as food residues rarely adhere to the surface. In contrast, anodized aluminum requires more careful cleaning to avoid scratching or discoloration, often necessitating non-abrasive sponges and gentle detergents. Maintenance for Teflon involves avoiding metal utensils and high heat to prevent coating damage, while anodized aluminum is more heat-resistant but still benefits from regular cleaning to preserve its protective oxide layer.
Price Comparison and Cost-Effectiveness
Teflon coating typically costs less upfront compared to anodized aluminum, making it a budget-friendly option for non-stick cookware. However, anodized aluminum offers superior durability and scratch resistance, which can lead to greater long-term cost-effectiveness due to its extended lifespan. Evaluating the initial price against maintenance and replacement frequency highlights anodized aluminum's value despite its higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Teflon coating offers excellent non-stick properties and chemical resistance, making it ideal for cookware and industrial applications where surface adhesion prevention is critical. Anodized aluminum provides superior durability and corrosion resistance with a hard, wear-resistant surface, suitable for high-traffic or abrasive environments. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as heat tolerance, abrasion resistance, and the need for non-stick characteristics in your specific application.
Teflon Coating vs Anodized Aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com