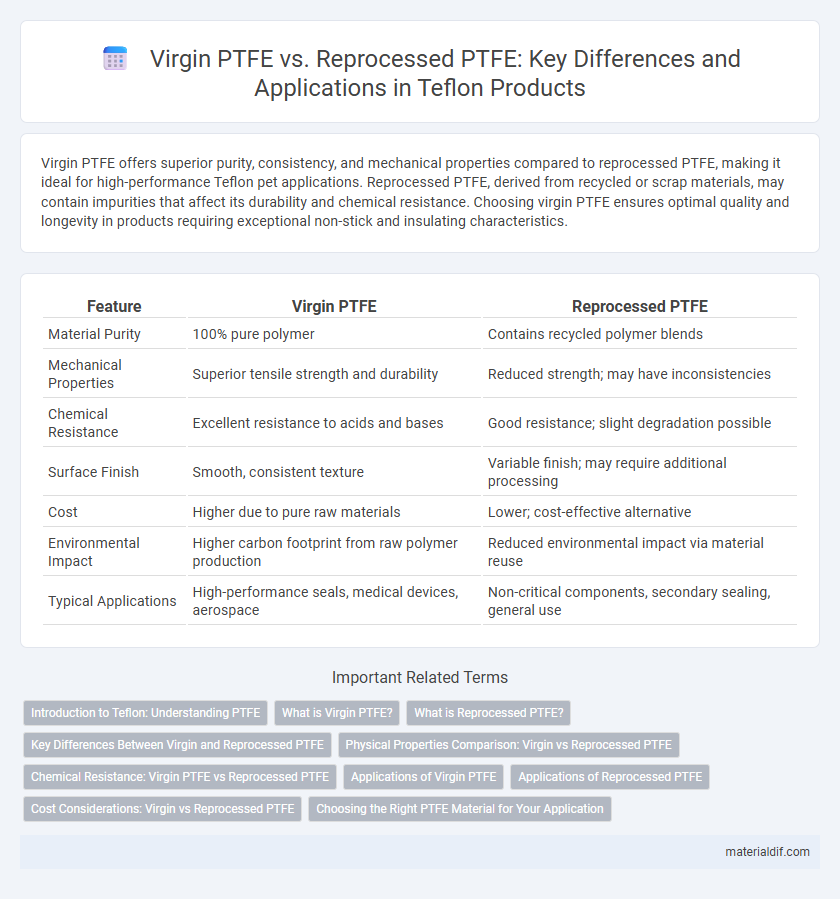
Virgin PTFE offers superior purity, consistency, and mechanical properties compared to reprocessed PTFE, making it ideal for high-performance Teflon pet applications. Reprocessed PTFE, derived from recycled or scrap materials, may contain impurities that affect its durability and chemical resistance. Choosing virgin PTFE ensures optimal quality and longevity in products requiring exceptional non-stick and insulating characteristics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Virgin PTFE | Reprocessed PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | 100% pure polymer | Contains recycled polymer blends |
| Mechanical Properties | Superior tensile strength and durability | Reduced strength; may have inconsistencies |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and bases | Good resistance; slight degradation possible |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent texture | Variable finish; may require additional processing |
| Cost | Higher due to pure raw materials | Lower; cost-effective alternative |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint from raw polymer production | Reduced environmental impact via material reuse |
| Typical Applications | High-performance seals, medical devices, aerospace | Non-critical components, secondary sealing, general use |
Introduction to Teflon: Understanding PTFE
Virgin PTFE, made from pure polymer resin, offers superior chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and mechanical properties compared to reprocessed PTFE, which contains recycled material and may exhibit reduced performance consistency. Teflon, a brand name for PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), is known for its non-stick, low-friction, and high-temperature resistance characteristics used in various industrial applications. Understanding the differences between virgin and reprocessed PTFE is crucial for selecting the right material to ensure durability, reliability, and optimal functionality in specialized environments.
What is Virgin PTFE?
Virgin PTFE refers to polytetrafluoroethylene manufactured from pure, newly polymerized tetrafluoroethylene monomers without any recycled content. It offers superior chemical resistance, higher purity, and enhanced mechanical properties compared to reprocessed PTFE. Industries such as aerospace, medical, and electronics rely on virgin PTFE for applications demanding consistent performance and minimal contamination.
What is Reprocessed PTFE?
Reprocessed PTFE is polytetrafluoroethylene material that has been recycled from manufacturing scrap or rejected parts and then melted and reshaped for reuse. Unlike virgin PTFE, which is made from raw polymer resin offering consistent purity and performance, reprocessed PTFE may contain impurities or altered molecular weight affecting its mechanical and chemical properties. This recycled form is often used in cost-sensitive applications where slightly reduced quality is acceptable compared to the high-purity characteristics of virgin PTFE.
Key Differences Between Virgin and Reprocessed PTFE
Virgin PTFE offers superior purity and consistent molecular structure, ensuring optimal chemical resistance and mechanical performance. Reprocessed PTFE may contain impurities or altered polymer chains due to recycling, resulting in slightly reduced physical properties and potential variability in applications. The choice between virgin and reprocessed PTFE depends on performance requirements, with virgin PTFE favored for high-precision uses and reprocessed PTFE suitable for cost-sensitive, less critical applications.
Physical Properties Comparison: Virgin vs Reprocessed PTFE
Virgin PTFE exhibits superior tensile strength, higher elongation at break, and lower surface roughness compared to reprocessed PTFE, which often shows diminished mechanical integrity due to thermal and mechanical degradation. The crystallinity level in virgin PTFE is consistently higher, contributing to enhanced chemical resistance and reduced permeability, whereas reprocessed PTFE tends to have increased porosity and microvoids affecting its physical durability. Thermal stability and wear resistance are significantly better in virgin PTFE, ensuring longer service life in demanding applications relative to reprocessed PTFE materials.
Chemical Resistance: Virgin PTFE vs Reprocessed PTFE
Virgin PTFE exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its pure polymer structure, ensuring optimal performance in highly corrosive environments. Reprocessed PTFE may contain impurities and slight structural inconsistencies, resulting in marginally reduced resistance to aggressive chemicals. In applications demanding maximum chemical inertness, Virgin PTFE remains the preferred choice for maintaining durability and longevity.
Applications of Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE offers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for demanding applications such as aerospace components, medical devices, and high-purity chemical processing equipment. Its uncontaminated, consistent molecular structure ensures optimal insulation in electrical applications and low friction in precision seals and bearings. Industries relying on stringent purity and performance standards extensively utilize virgin PTFE for critical sealing, coating, and lining purposes.
Applications of Reprocessed PTFE
Reprocessed PTFE is widely used in applications where cost efficiency and adequate chemical resistance are critical, such as in gasket manufacturing, seals, and insulation components. Its properties remain suitable for most industrial environments including chemical processing, food production, and electrical insulation, despite slightly reduced mechanical strength compared to virgin PTFE. The ability to recycle and reuse PTFE supports sustainability efforts while meeting demanding performance requirements in non-critical sealing and lining tasks.
Cost Considerations: Virgin vs Reprocessed PTFE
Virgin PTFE generally incurs higher costs due to its pure polymer composition and the energy-intensive manufacturing process ensuring consistent performance and chemical resistance. Reprocessed PTFE offers significant cost savings by recycling scrap materials, reducing raw material expenditure while maintaining adequate functionality for less critical applications. Cost efficiency drives the choice between virgin and reprocessed PTFE, balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in industrial and consumer product manufacturing.
Choosing the Right PTFE Material for Your Application
Virgin PTFE offers superior mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and purity compared to reprocessed PTFE, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical devices, and food processing. Reprocessed PTFE provides cost-effective material options for non-critical uses where slight compromises in strength and consistency are acceptable, such as in gasket manufacturing and general-purpose seals. Selecting the right PTFE material depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints while considering factors like temperature resistance, dielectric properties, and contamination sensitivity.
Virgin PTFE vs Reprocessed PTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com