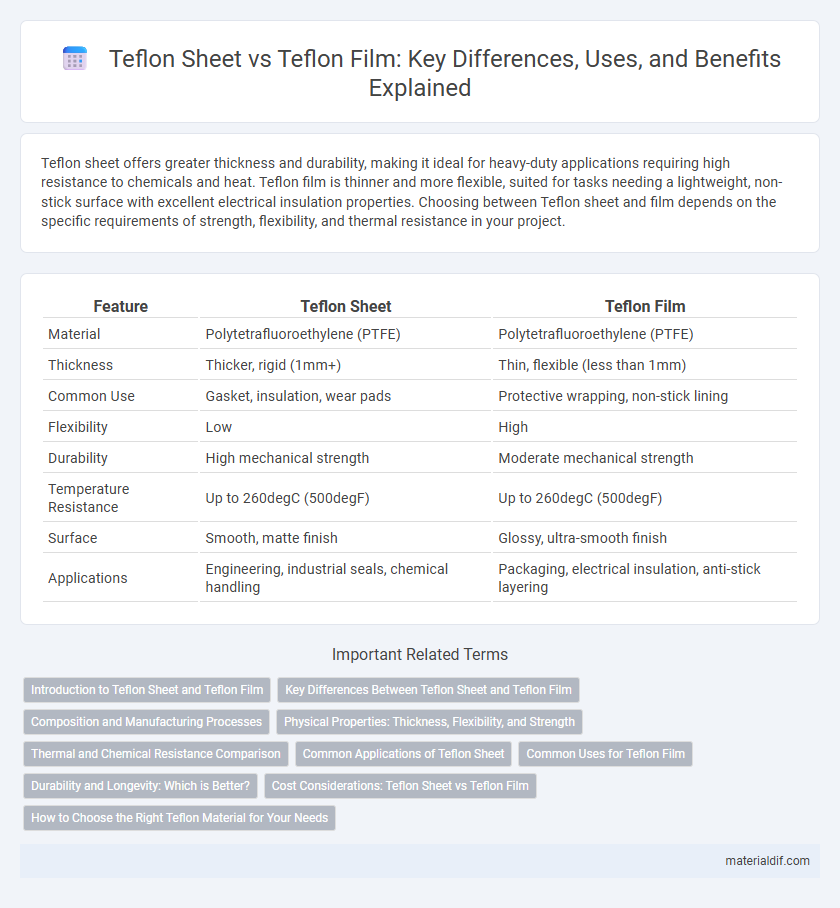
Teflon sheet offers greater thickness and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high resistance to chemicals and heat. Teflon film is thinner and more flexible, suited for tasks needing a lightweight, non-stick surface with excellent electrical insulation properties. Choosing between Teflon sheet and film depends on the specific requirements of strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Teflon Sheet | Teflon Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Thickness | Thicker, rigid (1mm+) | Thin, flexible (less than 1mm) |
| Common Use | Gasket, insulation, wear pads | Protective wrapping, non-stick lining |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Moderate mechanical strength |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Surface | Smooth, matte finish | Glossy, ultra-smooth finish |
| Applications | Engineering, industrial seals, chemical handling | Packaging, electrical insulation, anti-stick layering |
Introduction to Teflon Sheet and Teflon Film
Teflon sheet and Teflon film are both made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), known for their excellent chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and high-temperature tolerance. Teflon sheets are thicker, providing robust durability and insulation for industrial applications, while Teflon films are thinner, flexible, and suited for lightweight coatings or protective layers. Both forms maintain PTFE's low friction coefficient and hydrophobic characteristics, making them essential in various manufacturing and engineering processes.
Key Differences Between Teflon Sheet and Teflon Film
Teflon sheets are thick, durable, and rigid, designed for applications requiring structural support and high resistance to wear, while Teflon films are thin, flexible, and often used for insulation or protective coatings. The manufacturing processes differ, with sheets typically produced via compression molding or skiving, and films created through extrusion or calendaring, resulting in distinct mechanical properties. Thickness, flexibility, and application areas constitute key factors when choosing between Teflon sheet and film for industrial or consumer uses.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Teflon sheets and Teflon films both consist primarily of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), but their manufacturing processes differ significantly, influencing their properties and applications. Teflon sheets are typically produced through a paste extrusion or compression molding process, resulting in thicker, more rigid materials suitable for industrial uses requiring durability and chemical resistance. In contrast, Teflon films are created by skiving thin layers from extruded PTFE billets or by ram extrusion, producing flexible, ultra-thin films ideal for electrical insulation and non-stick coatings.
Physical Properties: Thickness, Flexibility, and Strength
Teflon sheets typically have a greater thickness, ranging from 0.5 mm to several millimeters, offering enhanced strength and rigidity suitable for structural applications. In contrast, Teflon films are much thinner, often below 0.1 mm, providing superior flexibility ideal for insulation and barrier layers. Both materials maintain excellent chemical resistance and low friction, but sheets prioritize durability while films emphasize pliability.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Teflon sheets offer superior thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 260degC (500degF), making them ideal for high-heat industrial applications, while Teflon films generally handle slightly lower thermal limits around 200degC (392degF). In terms of chemical resistance, both Teflon sheets and films provide exceptional inertness to acids, bases, and solvents, but sheets tend to have a thicker barrier that enhances durability against aggressive chemicals in corrosive environments. Choosing between Teflon sheet and film depends on the specific thermal and chemical exposure requirements, with sheets preferred for demanding thermal stability and films favored for lightweight, flexible applications.
Common Applications of Teflon Sheet
Teflon sheets are widely used in applications requiring high chemical resistance, non-stick surfaces, and excellent electrical insulation, such as gaskets, seals, and lining materials in chemical processing industries. Their thicker, durable structure makes them ideal for heavy-duty uses, including protective barriers and insulation pads. Teflon sheets also serve critical roles in food processing equipment and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and non-reactivity are essential.
Common Uses for Teflon Film
Teflon film is widely used for electrical insulation, packaging, and protective coatings due to its excellent dielectric properties and chemical resistance. It offers flexibility and thinness, making it ideal for applications in flexible printed circuits and release liners. Unlike thicker Teflon sheets, Teflon film provides a lightweight, transparent alternative suitable for precise, high-performance industrial uses.
Durability and Longevity: Which is Better?
Teflon sheets offer superior durability due to their thicker composition, making them ideal for high-stress applications that require resistance to wear, chemicals, and temperature extremes. In contrast, Teflon films, while flexible and lightweight, typically have a shorter lifespan under heavy mechanical stress or abrasive environments. For long-term performance and maximum longevity, Teflon sheets generally provide better durability compared to Teflon films.
Cost Considerations: Teflon Sheet vs Teflon Film
Teflon sheets generally cost more than Teflon films due to their thicker, more durable construction suitable for heavy-duty applications. Teflon films are thinner, making them more affordable and ideal for lightweight, flexible uses where high durability is less critical. When budgeting, consider that sheets offer long-term value in structural strength, whereas films provide cost savings for less demanding environments.
How to Choose the Right Teflon Material for Your Needs
Teflon sheets provide a thicker, more durable option ideal for applications requiring strong chemical resistance and mechanical toughness, such as gaskets and seals. Teflon films offer a thinner, flexible solution suitable for insulation, packaging, and non-stick surfaces where lightweight and adaptability are essential. Selecting the right Teflon material depends on factors like required thickness, flexibility, temperature resistance, and chemical exposure in your specific application.
Teflon Sheet vs Teflon Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com