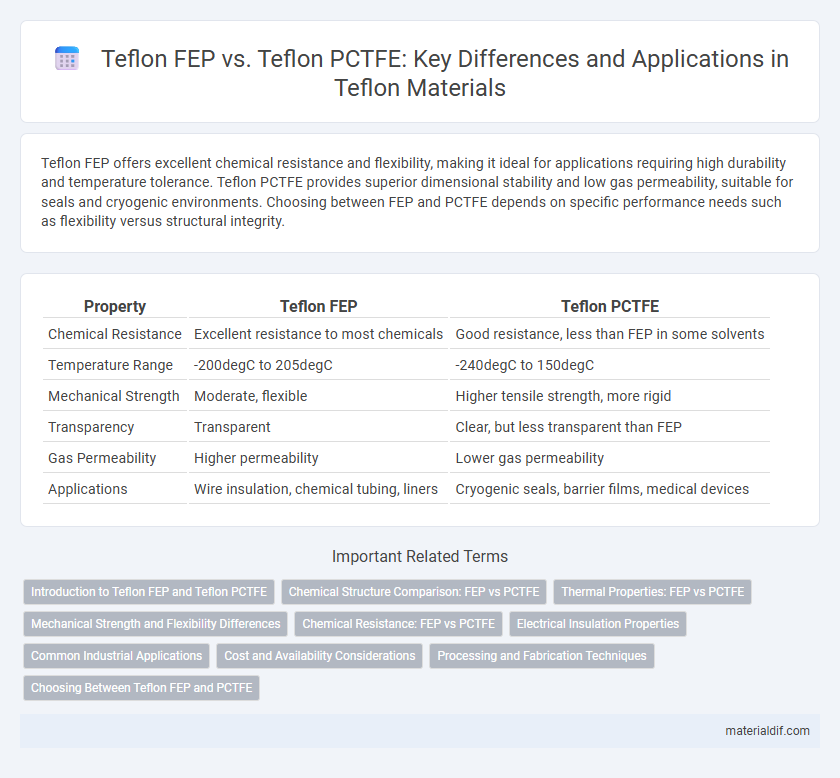
Teflon FEP offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and temperature tolerance. Teflon PCTFE provides superior dimensional stability and low gas permeability, suitable for seals and cryogenic environments. Choosing between FEP and PCTFE depends on specific performance needs such as flexibility versus structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Teflon FEP | Teflon PCTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to most chemicals | Good resistance, less than FEP in some solvents |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 205degC | -240degC to 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, flexible | Higher tensile strength, more rigid |
| Transparency | Transparent | Clear, but less transparent than FEP |
| Gas Permeability | Higher permeability | Lower gas permeability |
| Applications | Wire insulation, chemical tubing, liners | Cryogenic seals, barrier films, medical devices |
Introduction to Teflon FEP and Teflon PCTFE
Teflon FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) is a copolymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, high dielectric strength, and flexibility, commonly used in wire insulation and chemical processing applications. Teflon PCTFE (polychlorotrifluoroethylene) offers superior barrier properties, low moisture absorption, and exceptional dimensional stability, making it ideal for cryogenic seals and pharmaceutical packaging. Both materials belong to the Teflon family but differ significantly in mechanical properties and temperature resistance, tailored to specific industry requirements.
Chemical Structure Comparison: FEP vs PCTFE
Teflon FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) consists of tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene monomers, resulting in a copolymer with flexible and non-polar properties due to its partially fluorinated side chains. In contrast, Teflon PCTFE (polychlorotrifluoroethylene) features chlorine atoms replacing some fluorine atoms in the polymer backbone, which increases polarity and crystallinity while enhancing chemical resistance and barrier properties. The chemical structure difference directly impacts their application suitability, with FEP offering superior flexibility and PCTFE providing higher mechanical strength and resistance to permeation.
Thermal Properties: FEP vs PCTFE
Teflon FEP exhibits a higher continuous service temperature, typically up to 205degC, compared to Teflon PCTFE, which handles temperatures up to 150degC. FEP also has superior thermal stability and excellent resistance to thermal degradation over prolonged exposure. PCTFE offers better low-temperature performance, retaining toughness and chemical resistance down to -240degC, unlike FEP whose flexibility decreases at very low temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Differences
Teflon FEP exhibits superior flexibility and moderate mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications requiring repeated bending and complex shapes. In contrast, Teflon PCTFE offers higher mechanical strength and rigidity but lower flexibility, suited for demanding structural components. The choice between FEP and PCTFE depends on balancing flexibility needs against mechanical load requirements in industrial use.
Chemical Resistance: FEP vs PCTFE
Teflon FEP exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, effectively withstanding strong acids, bases, and solvents, making it ideal for aggressive chemical environments. Teflon PCTFE offers superior resistance to halogenated solvents and excellent performance against hydrocarbons, oils, and lubricants. While both materials provide excellent chemical resistance, FEP is preferred for broader chemical compatibility, whereas PCTFE excels in applications requiring low permeability and strong resistance to organic solvents.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Teflon FEP offers excellent electrical insulation properties with a dielectric constant of approximately 2.1 and a dielectric strength around 400 V/mil, making it suitable for high-frequency and high-voltage applications. Teflon PCTFE, while still providing good insulation, has a slightly higher dielectric constant near 2.8 but lower dielectric strength, typically about 300 V/mil, which impacts its performance in demanding electrical environments. The choice between FEP and PCTFE depends on specific insulation requirements, such as operating frequency, voltage levels, and environmental conditions.
Common Industrial Applications
Teflon FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) is widely used in chemical processing industries due to its excellent chemical resistance and non-stick properties, ideal for lining pipes, tanks, and valves. Teflon PCTFE (polychlorotrifluoroethylene) offers superior dimensional stability and low gas permeability, making it suitable for applications in cryogenics, electrical insulation, and food packaging. Both materials are chosen based on specific industrial requirements such as temperature tolerance and chemical compatibility.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Teflon FEP generally offers greater cost-efficiency and wider availability compared to Teflon PCTFE, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Suppliers often stock FEP in larger quantities due to its extensive use, which positively impacts pricing and lead times. In contrast, Teflon PCTFE tends to be more expensive with limited availability, as it is specialized for applications requiring higher chemical resistance and mechanical strength.
Processing and Fabrication Techniques
Teflon FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) offers excellent melt processability, making it suitable for extrusion, injection molding, and film production due to its lower melting point and good flow characteristics. Teflon PCTFE (polychlorotrifluoroethylene) requires more specialized processing techniques such as compression molding and machining because of its higher crystallinity and limited melt processability. Selecting between FEP and PCTFE depends on the specific fabrication requirements, with FEP favored for complex shapes and thin films, while PCTFE is ideal for precision components demanding chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
Choosing Between Teflon FEP and PCTFE
Teflon FEP offers exceptional chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring high corrosion resistance and ease of fabrication. Teflon PCTFE boasts superior mechanical strength and low gas permeability, suitable for cryogenic and vacuum environments where durability and moisture barrier properties are critical. Choosing between Teflon FEP and PCTFE depends on the specific requirements for thermal range, chemical exposure, and mechanical performance in your application.
Teflon FEP vs Teflon PCTFE Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com