Porous Teflon offers superior filtration and breathability due to its microscopic pores, making it ideal for applications requiring airflow and fluid separation. Dense Teflon exhibits excellent chemical resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for seals, gaskets, and protective coatings where impermeability is critical. Selecting between porous and dense Teflon depends on the balance between permeability and durability required by specific pet product designs.
Table of Comparison
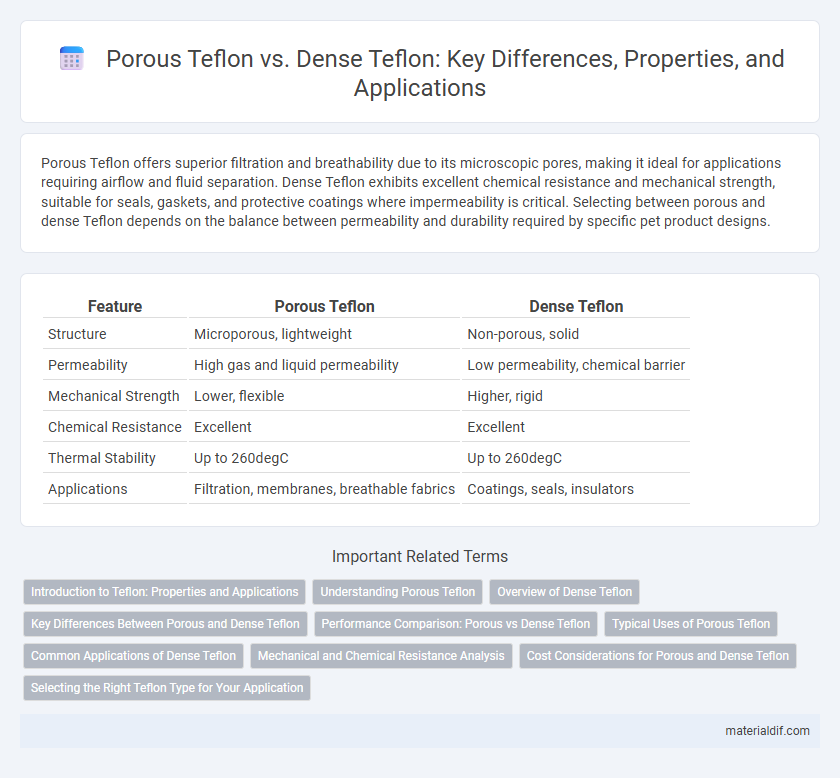
| Feature | Porous Teflon | Dense Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Microporous, lightweight | Non-porous, solid |
| Permeability | High gas and liquid permeability | Low permeability, chemical barrier |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower, flexible | Higher, rigid |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260degC | Up to 260degC |
| Applications | Filtration, membranes, breathable fabrics | Coatings, seals, insulators |
Introduction to Teflon: Properties and Applications
Porous Teflon exhibits high permeability and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for filtration and breathable membranes, whereas Dense Teflon offers superior mechanical strength, low friction, and exceptional insulation properties used in cookware, electrical insulation, and gaskets. Both forms of Teflon share chemical inertness, high thermal stability, and non-stick characteristics, derived from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer structures. Their unique microstructures define application-specific advantages, with Porous Teflon enabling fluid transfer and Dense Teflon providing durability and protection in harsh environments.
Understanding Porous Teflon
Porous Teflon features a microporous structure that enables superior breathability and chemical filtration compared to Dense Teflon, which is solid and non-porous. This unique permeability allows Porous Teflon to function effectively in applications requiring gas exchange while maintaining resistance to liquids and contaminants. Engineered with interconnected micropores, Porous Teflon is widely used in filtration membranes, breathable fabrics, and protective coatings where durability and selective permeability are critical.
Overview of Dense Teflon
Dense Teflon, also known as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), features a tightly packed molecular structure that provides superior chemical resistance and an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This non-porous material resists moisture absorption and ensures excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Dense Teflon's durability under extreme temperatures and chemical exposure distinguishes it from porous variants, which exhibit higher gas permeability and reduced mechanical strength.
Key Differences Between Porous and Dense Teflon
Porous Teflon features a microstructure with interconnected voids, allowing high permeability and flexibility, making it ideal for filtration and breathable seals. Dense Teflon has a tightly packed molecular structure, resulting in superior chemical resistance, low friction, and impermeability, suitable for non-stick coatings and insulating applications. The key difference lies in porosity, influencing mechanical properties and functional performance in varying industrial uses.
Performance Comparison: Porous vs Dense Teflon
Porous Teflon exhibits superior breathability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for filtration and gasketing applications, while Dense Teflon offers enhanced mechanical strength and impermeability suited for piping and lining. The microstructure of Porous Teflon allows fluid and gas permeability, which significantly reduces pressure drop in filtration systems compared to Dense Teflon's solid, non-porous matrix. Performance metrics such as tensile strength and thermal stability are higher in Dense Teflon, but Porous Teflon maintains better flexibility and lower density, influencing material selection based on operational demands.
Typical Uses of Porous Teflon
Porous Teflon is commonly used in filtration systems, gas diffusion layers, and venting applications due to its breathable structure that allows gas and liquid passage while preventing particulate contamination. Its microporous nature makes it ideal for chemical processing, environmental protection, and medical device manufacturing where pressure equalization and contaminant filtration are critical. Dense Teflon, by contrast, serves primarily in applications requiring chemical resistance, non-stick surfaces, and electrical insulation without permeability.
Common Applications of Dense Teflon
Dense Teflon is commonly used in applications requiring chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and low friction surfaces, such as gaskets, seals, and tubing in the chemical and food processing industries. Its non-porous structure provides superior impermeability, making it ideal for high-purity environments and aggressive chemical exposure. Dense Teflon also finds frequent use in electrical insulation components and non-stick coatings for cookware.
Mechanical and Chemical Resistance Analysis
Porous Teflon exhibits enhanced chemical resistance due to its micro-porous structure, allowing superior resistance to aggressive solvents and acids, while dense Teflon provides higher mechanical strength with greater tensile strength and durability under stress. Mechanical resistance analysis reveals dense Teflon's advantage in applications requiring robust abrasion and impact resistance, whereas porous Teflon offers significant advantages in filtration and gas permeability without compromising chemical inertness. Both forms maintain exceptional non-reactivity, but the choice depends on balancing mechanical load requirements against chemical exposure conditions.
Cost Considerations for Porous and Dense Teflon
Porous Teflon generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to its complex production process involving controlled porosity formation, which demands specialized equipment and quality control measures. Dense Teflon, produced through standard molding or extrusion methods, offers lower production expenses, making it more cost-effective for large-scale applications. When evaluating cost considerations, the specific performance benefits of Porous Teflon, such as improved filtration or breathability, must justify its premium price compared to Dense Teflon's affordability and ease of fabrication.
Selecting the Right Teflon Type for Your Application
Porous Teflon offers superior breathability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for filtration and gasketing applications where moisture or gas permeability is required. Dense Teflon provides excellent non-stick properties, high dielectric strength, and exceptional chemical inertness, suitable for sealing, insulation, and protective coatings in harsh environments. Selecting the right Teflon type depends on factors like permeability needs, mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and chemical exposure specific to your application.
Porous Teflon vs Dense Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com