Teflon seals offer superior chemical resistance and durability compared to rubber seals, making them ideal for harsh environments and high-temperature applications. Their low friction properties enhance performance and reduce wear, extending the lifespan of components. Rubber seals provide better elasticity and sealing in dynamic applications but may degrade faster when exposed to oils, chemicals, or extreme heat.
Table of Comparison
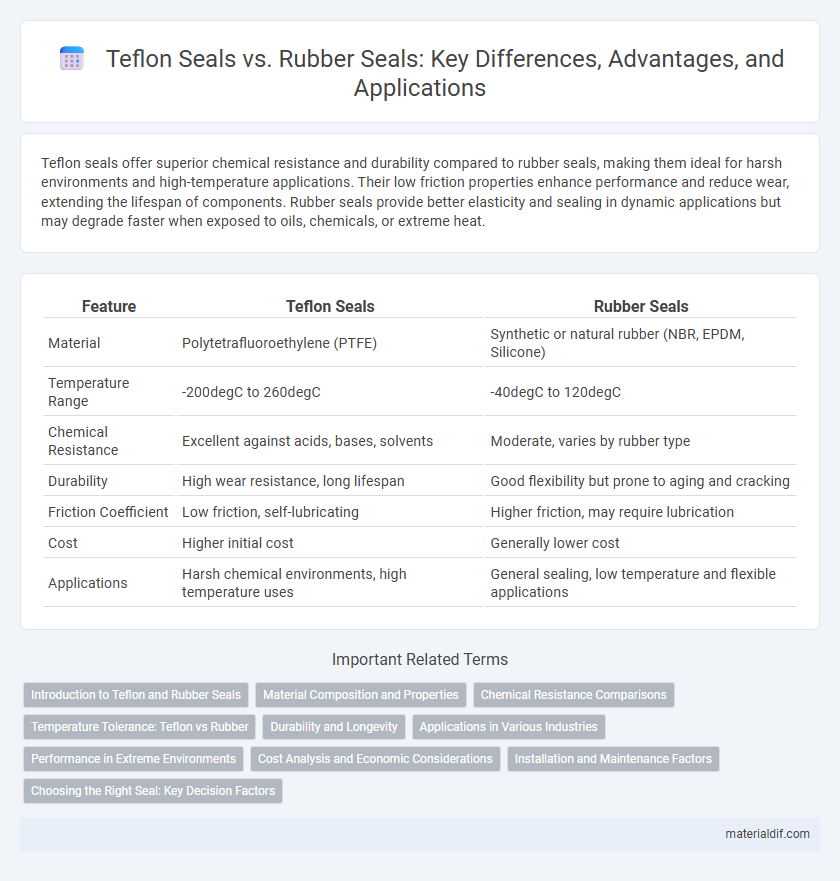
| Feature | Teflon Seals | Rubber Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Synthetic or natural rubber (NBR, EPDM, Silicone) |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 260degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, solvents | Moderate, varies by rubber type |
| Durability | High wear resistance, long lifespan | Good flexibility but prone to aging and cracking |
| Friction Coefficient | Low friction, self-lubricating | Higher friction, may require lubrication |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Generally lower cost |
| Applications | Harsh chemical environments, high temperature uses | General sealing, low temperature and flexible applications |
Introduction to Teflon and Rubber Seals
Teflon seals, made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), offer superior chemical resistance, low friction, and high temperature tolerance compared to rubber seals. Rubber seals, typically composed of elastomers like Nitrile or EPDM, provide excellent elasticity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for dynamic sealing applications. Both materials serve critical roles in sealing technology, with Teflon favored in aggressive environments and rubber preferred for flexible, low-pressure systems.
Material Composition and Properties
Teflon seals, made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), offer superior chemical resistance and withstand high temperatures up to 260degC, outperforming rubber seals whose natural or synthetic elastomers generally tolerate lower temperatures and can degrade with aggressive chemicals. PTFE's low coefficient of friction and non-stick properties result in exceptional wear resistance and reduced maintenance, whereas rubber seals provide better elasticity and compression recovery but are more prone to swelling and abrasion. The inert nature of Teflon makes it ideal for harsh industrial applications, contrasting with rubber's suitability for less demanding environments requiring flexibility and cushioning.
Chemical Resistance Comparisons
Teflon seals offer superior chemical resistance compared to rubber seals, effectively withstanding aggressive chemicals, solvents, and acids without degrading. Rubber seals, such as those made from nitrile or EPDM, are more prone to swelling, cracking, or deterioration when exposed to harsh chemicals. This makes Teflon seals ideal for applications involving aggressive media or extreme pH environments where long-term durability is critical.
Temperature Tolerance: Teflon vs Rubber
Teflon seals exhibit superior temperature tolerance, operating efficiently in a range from -200degC to 260degC, whereas rubber seals typically withstand temperatures between -40degC and 120degC. This expanded thermal resistance makes Teflon seals ideal for high-temperature industrial applications like chemical processing and aerospace. Rubber seals may degrade, lose elasticity, or fail under extreme heat, limiting their use in environments demanding robust thermal stability.
Durability and Longevity
Teflon seals exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to rubber seals due to their exceptional resistance to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and wear. Unlike rubber seals, which can degrade and crack over time when exposed to harsh environments, Teflon seals maintain integrity and performance in extreme conditions for extended periods. This makes Teflon an ideal choice for applications involving aggressive chemicals, high pressure, and fluctuating temperatures where long-lasting, reliable sealing is critical.
Applications in Various Industries
Teflon seals excel in chemical resistance and high-temperature endurance, making them ideal for applications in the chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food industries where exposure to harsh chemicals and sterilization processes is common. Rubber seals offer superior elasticity and cost-effectiveness, often used in automotive, HVAC, and water management systems requiring flexibility and vibration dampening. Selecting between Teflon and rubber seals depends on the operational environment, with Teflon seals favored for corrosive or high-temperature conditions and rubber seals preferred for dynamic sealing and lower temperature applications.
Performance in Extreme Environments
Teflon seals exhibit superior chemical resistance and maintain structural integrity at temperatures ranging from -200degC to 260degC, outperforming rubber seals that typically degrade in extreme heat or cold. Their low friction coefficient and non-stick properties reduce wear and enhance durability in harsh chemical or abrasive conditions where rubber seals may swell or crack. This makes Teflon seals ideal for applications in aerospace, chemical processing, and cryogenics where consistent performance under extreme environmental stress is critical.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Teflon seals offer superior chemical resistance and durability, leading to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs compared to rubber seals. Although Teflon seals generally entail higher initial investment due to material and manufacturing expenses, their low friction and thermal stability minimize replacement frequency and operational downtime, enhancing overall cost efficiency. Economic considerations favor Teflon seals in applications requiring high performance and longevity, while rubber seals may be more cost-effective for low-stress, budget-sensitive environments.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Teflon seals offer superior chemical resistance and low friction, resulting in easier installation and longer maintenance intervals compared to rubber seals. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments reduces the need for frequent replacements and maintenance checks. Rubber seals, while flexible and cost-effective, often require more precise installation and regular inspection to prevent wear and degradation.
Choosing the Right Seal: Key Decision Factors
Teflon seals offer superior chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction properties compared to rubber seals, making them ideal for aggressive environments and applications requiring durability. Rubber seals provide better flexibility, elasticity, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for dynamic applications with moderate temperature and chemical exposure. Consider factors such as operating temperature, chemical compatibility, pressure conditions, and budget constraints when selecting between Teflon and rubber seals for optimal performance.
Teflon Seals vs Rubber Seals Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com