Food-grade Teflon is specially formulated to meet strict safety standards, ensuring it is non-toxic and safe for contact with food, making it ideal for cookware and kitchen utensils. Industrial Teflon, on the other hand, is designed for high durability and chemical resistance in manufacturing and mechanical applications, but it may contain additives unsuitable for food use. Understanding the distinction between food-grade and industrial Teflon helps consumers choose safe, appropriate products for cooking and avoid harmful contamination.
Table of Comparison
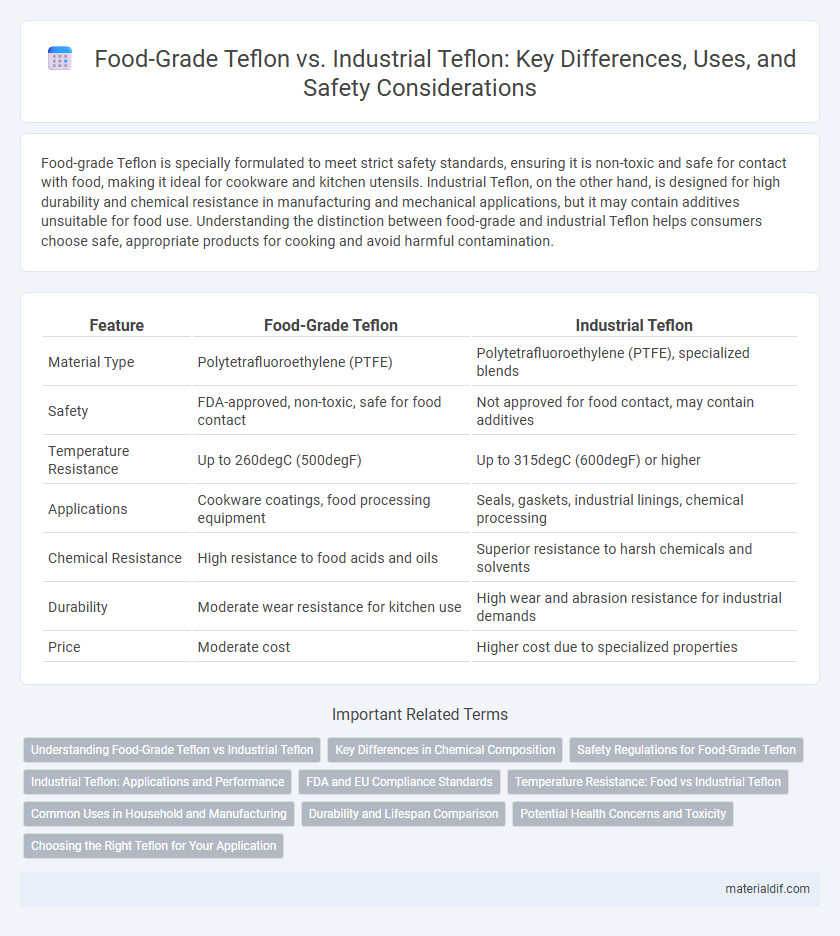
| Feature | Food-Grade Teflon | Industrial Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), specialized blends |
| Safety | FDA-approved, non-toxic, safe for food contact | Not approved for food contact, may contain additives |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 315degC (600degF) or higher |
| Applications | Cookware coatings, food processing equipment | Seals, gaskets, industrial linings, chemical processing |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to food acids and oils | Superior resistance to harsh chemicals and solvents |
| Durability | Moderate wear resistance for kitchen use | High wear and abrasion resistance for industrial demands |
| Price | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to specialized properties |
Understanding Food-Grade Teflon vs Industrial Teflon
Food-grade Teflon, specifically polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) approved for kitchen use, is designed to withstand high cooking temperatures without releasing harmful fumes, making it safe for cookware and food contact applications. Industrial Teflon variants often contain additives or fillers to enhance chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability, tailored for non-food environments such as chemical processing or automotive parts. Understanding the distinction is critical for ensuring appropriate safety standards and functionality in both culinary and industrial contexts.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Food-grade Teflon typically contains a higher purity of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with fewer fillers and additives, ensuring non-toxicity and safety at cooking temperatures. Industrial Teflon often includes additional compounds like glass fibers or other reinforcing agents to enhance mechanical strength and chemical resistance under extreme conditions. These compositional differences directly impact the performance, safety, and application scope of each Teflon type.
Safety Regulations for Food-Grade Teflon
Food-grade Teflon is manufactured under strict safety regulations set by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA to ensure non-toxicity and suitability for direct contact with food. These regulations limit the presence of harmful compounds like PFOA and require extensive testing to confirm chemical stability during cooking processes. Industrial Teflon, in contrast, may contain additives and impurities not approved for food contact, making it unsuitable and potentially hazardous for culinary uses.
Industrial Teflon: Applications and Performance
Industrial Teflon, known for its exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, is widely used in manufacturing sectors such as chemical processing, automotive, and electronics. Its superior non-stick and anti-corrosive properties make it ideal for seals, gaskets, and linings exposed to harsh environments. Performance reliability in extreme conditions ensures Industrial Teflon's critical role in enhancing equipment durability and operational efficiency.
FDA and EU Compliance Standards
Food-grade Teflon meets stringent FDA and EU compliance standards, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with food and resistant to high temperatures without releasing harmful substances. Industrial Teflon, while offering higher chemical and thermal resistance, often lacks the certifications required for food applications due to potential contamination risks. Manufacturers must verify FDA 21 CFR 177.1550 and EU Regulation No 10/2011 compliance when selecting Teflon materials for food-processing equipment.
Temperature Resistance: Food vs Industrial Teflon
Food-grade Teflon is designed to withstand temperatures up to 260degC (500degF) without degrading or releasing harmful fumes, making it safe for everyday cooking applications. Industrial Teflon, by contrast, can tolerate much higher temperatures, often exceeding 300degC (572degF), to endure harsh manufacturing environments and chemical exposure. The superior thermal stability of industrial Teflon allows it to maintain its non-stick and chemical-resistant properties under extreme heat, unlike food-grade variants which prioritize safety within typical culinary temperature ranges.
Common Uses in Household and Manufacturing
Food-grade Teflon is primarily used in non-stick cookware, bakeware, and kitchen utensils to ensure safety and prevent food contamination, while industrial Teflon is utilized in applications such as chemical processing equipment, gaskets, and seals due to its high resistance to heat, chemicals, and wear. Household products prioritize food safety certifications and easy cleaning properties, whereas industrial-grade Teflon emphasizes durability and chemical inertness for harsh manufacturing environments. Both types require different formulations tailored to their specific performance requirements in domestic and industrial settings.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Food-grade Teflon is engineered with a non-toxic composition ensuring safety for cooking applications, offering moderate durability suited for household use with an average lifespan of 3 to 5 years under regular conditions. Industrial Teflon boasts enhanced chemical resistance and higher thermal stability, making it significantly more durable and capable of lasting 10 to 15 years or more in demanding environments such as chemical processing or manufacturing. The difference in formulation directly impacts longevity, with industrial-grade Teflon designed to withstand harsher conditions and prolonged mechanical stress compared to its food-grade counterpart.
Potential Health Concerns and Toxicity
Food-grade Teflon is formulated to meet strict FDA regulations ensuring minimal toxic chemical release at typical cooking temperatures, making it safe for culinary use. Industrial Teflon, often containing higher levels of PFOA and other hazardous substances, poses increased health risks, including potential carcinogenicity and respiratory issues upon exposure during manufacturing or high-heat applications. Prolonged or improper use of industrial-grade Teflon in food preparation can lead to toxic fumes and chemical contamination, highlighting the importance of selecting food-grade non-stick coatings for safety.
Choosing the Right Teflon for Your Application
Food-grade Teflon coatings are engineered to meet strict FDA and NSF standards, ensuring non-toxicity and resistance to food contamination, making them ideal for cookware and food processing equipment. Industrial Teflon variants, such as PTFE with enhanced thermal and chemical resistance, are designed for demanding environments including chemical plants and mechanical parts exposed to extreme conditions. Selecting the right Teflon depends on application requirements like temperature tolerance, chemical exposure, and regulatory compliance to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Food-grade Teflon vs Industrial Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com