Heat shrink Teflon offers a flexible, conforming fit ideal for insulating irregular shapes, while extruded Teflon provides consistent thickness and superior mechanical strength for demanding applications. The heat shrink variant simplifies installation by shrinking to tightly fit the substrate when heated, whereas extruded Teflon maintains its original dimensions and resists abrasion and chemicals over time. Choosing between heat shrink and extruded Teflon depends on the specific requirements for flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance in your project.
Table of Comparison
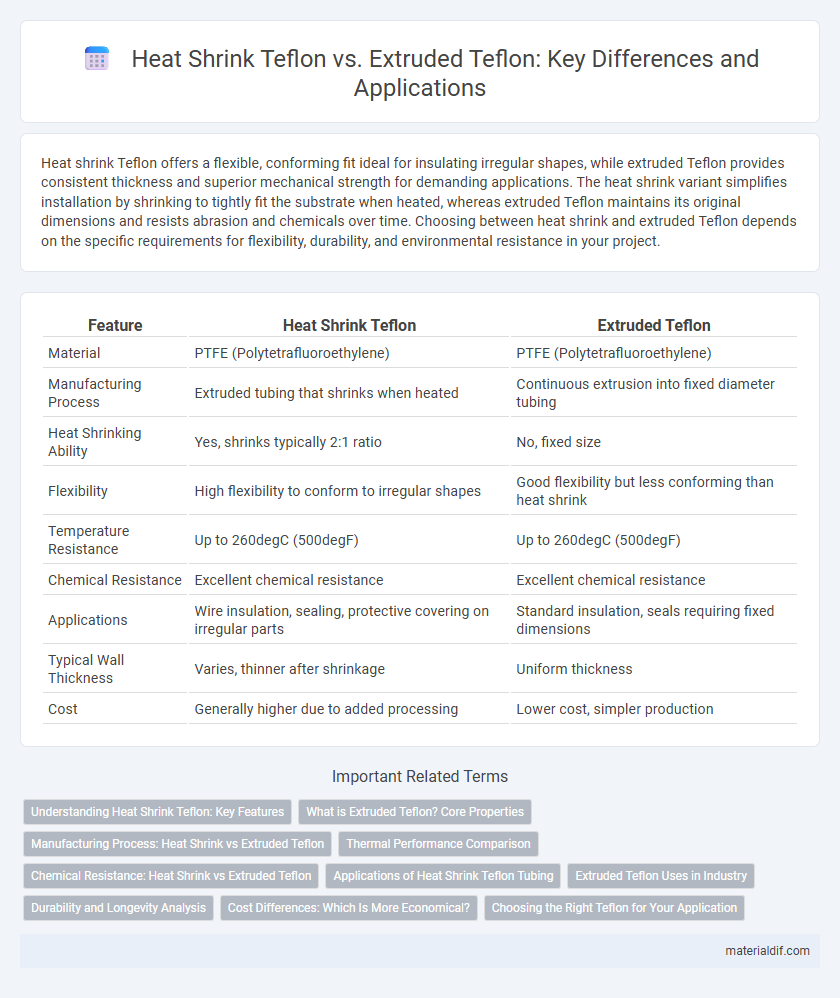
| Feature | Heat Shrink Teflon | Extruded Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Material | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) |
| Manufacturing Process | Extruded tubing that shrinks when heated | Continuous extrusion into fixed diameter tubing |
| Heat Shrinking Ability | Yes, shrinks typically 2:1 ratio | No, fixed size |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to conform to irregular shapes | Good flexibility but less conforming than heat shrink |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260degC (500degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical resistance | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Applications | Wire insulation, sealing, protective covering on irregular parts | Standard insulation, seals requiring fixed dimensions |
| Typical Wall Thickness | Varies, thinner after shrinkage | Uniform thickness |
| Cost | Generally higher due to added processing | Lower cost, simpler production |
Understanding Heat Shrink Teflon: Key Features
Heat Shrink Teflon offers a unique ability to contract when exposed to heat, providing tight, secure insulation and protection for wiring and components. This material features exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance up to 260degC, and excellent electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and electronics applications. Compared to Extruded Teflon, Heat Shrink Teflon conforms precisely to irregular shapes, ensuring a reliable seal and superior durability in harsh environments.
What is Extruded Teflon? Core Properties
Extruded Teflon is a type of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) formed by forcing the material through a shaped die, resulting in a dense, homogenous structure with excellent chemical resistance and a high melting point of around 327degC. Core properties include exceptional non-stick characteristics, low friction coefficient, superior electrical insulation, and outstanding thermal stability, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. Compared to heat shrink Teflon, extruded Teflon offers greater dimensional stability and mechanical strength without the ability to shrink when heated.
Manufacturing Process: Heat Shrink vs Extruded Teflon
Heat Shrink Teflon is manufactured through a process where extruded Teflon tubing is expanded at high temperature and rapidly cooled, allowing it to shrink back to its original size when reheated, making it ideal for tight-fitting insulation. Extruded Teflon tubing is produced by forcing molten Teflon through a die to form consistent, seamless tubes that offer excellent chemical resistance and structural integrity. The key manufacturing distinction lies in heat shrink tubing's ability to recover its shape upon heating, contrasting with the stable, pre-formed dimensions of extruded Teflon tubing.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat shrink Teflon tubing offers superior thermal resistance, maintaining integrity at continuous operating temperatures up to 204degC (400degF) and short-term exposures reaching 260degC (500degF). Extruded Teflon provides excellent thermal stability with a maximum continuous use temperature around 260degC (500degF) but lacks the shrinkage property, limiting its application in tight-fitting insulation scenarios. The choice between heat shrink and extruded Teflon depends on specific thermal management needs and physical fit requirements in high-temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance: Heat Shrink vs Extruded Teflon
Heat shrink Teflon offers enhanced chemical resistance due to its tighter molecular structure formed during the shrinking process, which reduces permeability to aggressive solvents and acids. Extruded Teflon provides reliable chemical resistance but may exhibit slightly higher permeability compared to heat shrink variants, making it less ideal for environments exposed to highly corrosive chemicals. Both forms resist most chemicals, but heat shrink Teflon's denser composition gives it a superior barrier against harsh chemical exposure.
Applications of Heat Shrink Teflon Tubing
Heat shrink Teflon tubing is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and electrical industries for its excellent insulation and chemical resistance properties. It provides a reliable seal over irregular shapes and connections, protecting wiring and components from moisture, abrasion, and extreme temperatures. Its ability to conform tightly upon heating makes it ideal for cable bundling, strain relief, and environmental protection in harsh operating conditions.
Extruded Teflon Uses in Industry
Extruded Teflon is widely used in the aerospace, chemical processing, and automotive industries due to its excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature durability. Its consistent density and smooth surface enhance performance in sealing applications, gaskets, and insulation. Industry sectors prioritize extruded Teflon for components requiring reliable thermal stability and low friction.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Heat Shrrink Teflon offers superior durability and longevity due to its ability to conform tightly to components, providing enhanced protection against abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Extruded Teflon, while resilient, typically has uniform thickness and can be less flexible, which may limit its lifespan under repetitive mechanical stress or thermal cycling. Evaluating heat resistance, chemical inertness, and mechanical flexibility, Heat Shrink Teflon generally outperforms Extruded Teflon in applications demanding extended service life and robust environmental protection.
Cost Differences: Which Is More Economical?
Heat shrink Teflon offers cost-efficiency primarily due to its ability to conform tightly to irregular shapes, reducing material waste and installation time compared to extruded Teflon, which involves a more complex manufacturing process and higher material costs. Extruded Teflon provides uniform thickness and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent mechanical properties but often at a higher price point. Evaluating overall project requirements and volume needs determines which option is more economical, with heat shrink Teflon typically favored in flexible, cost-sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Teflon for Your Application
Heat shrink Teflon offers precise insulation and protection for irregularly shaped components, making it ideal for electronic wiring and delicate assemblies. Extruded Teflon provides uniform thickness and excellent chemical resistance, suitable for tubing and sheets in harsh industrial environments. Selecting the right Teflon type depends on the application's mechanical needs, temperature exposure, and chemical resistance requirements.
Heat Shrink Teflon vs Extruded Teflon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com