Polystyrene plastic offers excellent rigidity and is lightweight, making it ideal for disposable containers and craft applications, while acrylic plastic provides superior transparency and impact resistance, often used in display cases and optical devices. Polystyrene is more affordable but prone to scratching and less resistant to UV degradation compared to acrylic, which maintains clarity over time and withstands outdoor conditions better. Choosing between polystyrene and acrylic depends on requirements for durability, visual clarity, and cost-efficiency in specific PET applications.
Table of Comparison
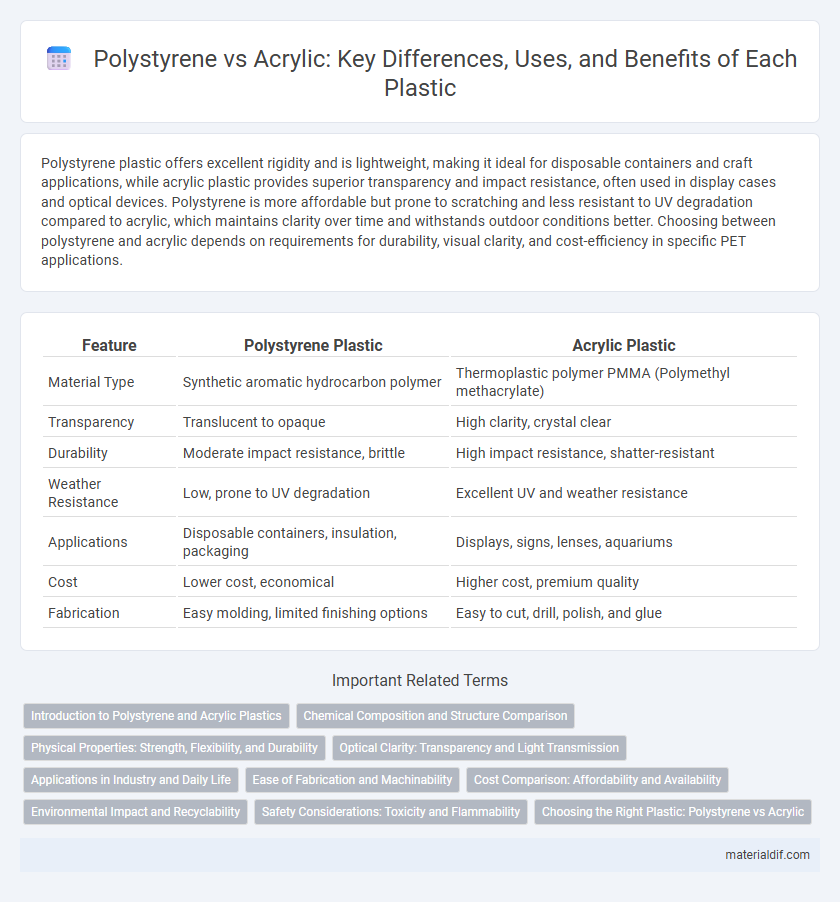
| Feature | Polystyrene Plastic | Acrylic Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer | Thermoplastic polymer PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) |
| Transparency | Translucent to opaque | High clarity, crystal clear |
| Durability | Moderate impact resistance, brittle | High impact resistance, shatter-resistant |
| Weather Resistance | Low, prone to UV degradation | Excellent UV and weather resistance |
| Applications | Disposable containers, insulation, packaging | Displays, signs, lenses, aquariums |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost, premium quality |
| Fabrication | Easy molding, limited finishing options | Easy to cut, drill, polish, and glue |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Acrylic Plastics
Polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer styrene, known for its rigidity, clarity, and ease of molding, commonly used in packaging, insulation, and disposable cutlery. Acrylic plastic, also called polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is a transparent thermoplastic noted for its superior UV resistance, clarity, and impact strength, often utilized in optical lenses, outdoor signs, and glazing. Both materials serve distinct applications based on their mechanical properties and durability, with polystyrene favored for lightweight and cost-effective solutions, while acrylic is chosen for optical clarity and weather resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polystyrene plastic is a synthetic aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, featuring a linear hydrocarbon chain with phenyl groups attached to every other carbon atom, which contributes to its rigidity and brittleness. Acrylic plastic, or polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), is composed of methyl methacrylate monomers, forming a polymer chain with ester functional groups that provide transparency and enhanced UV resistance. The chemical structure difference, where polystyrene has aromatic rings and acrylic contains ester groups, directly influences their mechanical properties, with acrylic being more durable and weather-resistant compared to the more brittle and less UV-stable polystyrene.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Polystyrene plastic exhibits moderate strength with good rigidity but is relatively brittle compared to acrylic plastic, which offers higher impact resistance and better flexibility. Acrylic plastic surpasses polystyrene in durability, maintaining clarity and structural integrity under prolonged UV exposure and varying temperatures. Both materials serve distinct applications, with polystyrene favored for lightweight, disposable products and acrylic preferred for more durable, transparent uses such as signage and displays.
Optical Clarity: Transparency and Light Transmission
Polystyrene plastic offers moderate optical clarity with a light transmission rate around 88%, making it suitable for applications requiring decent transparency but not high precision. Acrylic plastic exhibits superior optical clarity with a light transmission rate close to 92%, providing exceptional transparency and minimal distortion, ideal for lenses, displays, and light fixtures. The difference in light transmission and optical purity makes acrylic the preferred choice for high-clarity and light-sensitive uses.
Applications in Industry and Daily Life
Polystyrene plastic is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation due to its lightweight and cost-effective properties, while acrylic plastic is favored in applications requiring optical clarity and weather resistance, such as signage, aquariums, and protective barriers. Industrial uses of polystyrene include foam products and model making, whereas acrylic finds frequent use in automotive parts, lighting fixtures, and display cases. Both materials serve distinct roles in daily life and industry, with polystyrene excelling in insulation and disposable goods, and acrylic prized for durability and transparency.
Ease of Fabrication and Machinability
Polystyrene plastic offers easy fabrication with simple cutting, thermoforming, and gluing, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and hobby projects. Acrylic plastic provides superior machinability with higher precision, allowing for milling, drilling, and polishing to achieve clear, smooth surfaces for display and optical applications. Both materials accommodate various fabrication techniques, but acrylic's enhanced workability suits detailed and high-quality finishes.
Cost Comparison: Affordability and Availability
Polystyrene plastic offers a more affordable option compared to acrylic plastic, with lower raw material and manufacturing costs driving its widespread availability in packaging and disposable products. Acrylic plastic, while pricier, provides superior optical clarity and weather resistance, making it common in applications like signage and lenses despite its higher price point. Polystyrene's cost-effectiveness and ease of production make it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects requiring large volumes of plastic materials.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene plastic, commonly used in packaging and insulation, poses significant environmental challenges due to its slow degradation rate and limited recycling infrastructure, often ending up in landfills or as ocean pollutant. Acrylic plastic, although more durable and clearer, has a more complex recycling process but tends to have a lower environmental footprint in terms of long-term pollution compared to polystyrene. Both materials require improved recycling technologies and waste management strategies to mitigate their ecological impact and enhance sustainability.
Safety Considerations: Toxicity and Flammability
Polystyrene plastic releases styrene vapors, which are potentially harmful and classified as a possible carcinogen, raising toxicity concerns during manufacturing and combustion. Acrylic plastic, composed of polymethyl methacrylate, exhibits lower toxicity and releases fewer hazardous fumes when exposed to heat or flames. Both materials are flammable, but polystyrene ignites more easily and burns with a black, sooty smoke, whereas acrylic tends to melt and drip, presenting different safety hazards in fire scenarios.
Choosing the Right Plastic: Polystyrene vs Acrylic
Polystyrene plastic offers cost-effective, lightweight properties with good dimensional stability, making it ideal for disposable packaging and model prototypes. Acrylic plastic provides superior optical clarity, weather resistance, and impact strength, suitable for applications like signage, aquariums, and lenses. Choosing the right plastic depends on balancing budget constraints, durability requirements, and visual quality to meet specific project needs.
Polystyrene Plastic vs Acrylic Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com