Polystyrene (PS) offers excellent clarity and rigidity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable containers, but it lacks impact resistance. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) incorporates rubber additives, providing enhanced toughness and durability while maintaining good processing ease and surface finish. Choosing between PS and HIPS depends on the application's need for strength versus transparency and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
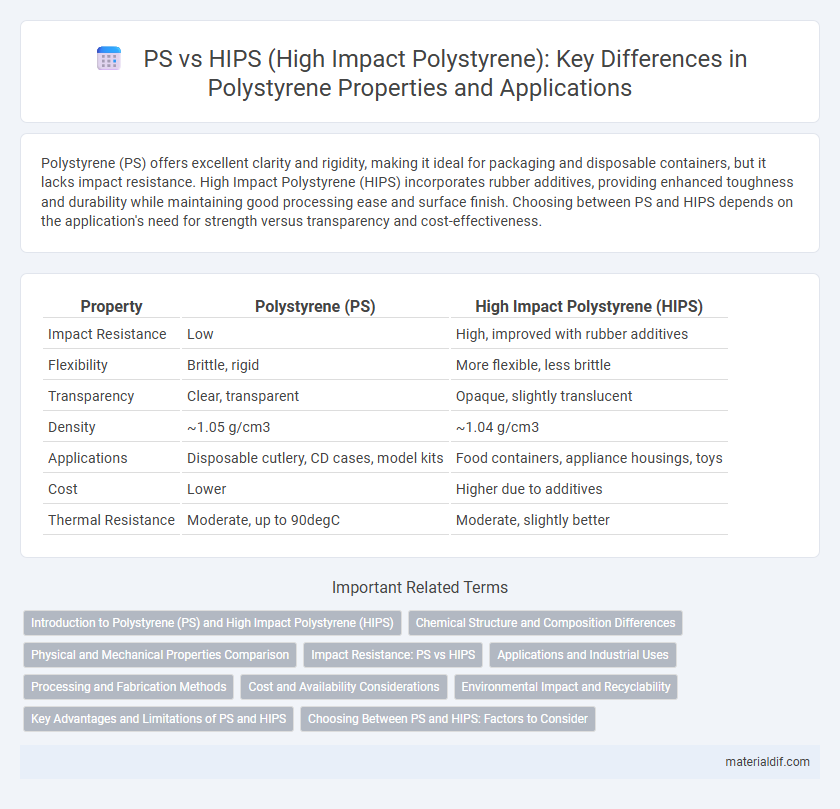
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | Low | High, improved with rubber additives |
| Flexibility | Brittle, rigid | More flexible, less brittle |
| Transparency | Clear, transparent | Opaque, slightly translucent |
| Density | ~1.05 g/cm3 | ~1.04 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Disposable cutlery, CD cases, model kits | Food containers, appliance housings, toys |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to additives |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, up to 90degC | Moderate, slightly better |
Introduction to Polystyrene (PS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
Polystyrene (PS) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used for packaging, insulation, and consumer products due to its rigidity and clarity. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a modified form of PS, incorporating rubber additives to enhance impact resistance and toughness without compromising processability. While PS is brittle and suited for applications requiring stiffness and transparency, HIPS offers improved durability and is commonly employed in automotive parts, appliance housings, and protective packaging.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polystyrene (PS) is a polymer composed solely of styrene monomers forming a rigid, transparent thermoplastic, whereas High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) incorporates rubbery polybutadiene particles dispersed within the polystyrene matrix to enhance toughness. The chemical structure of PS consists of linear chains of styrene units, while HIPS is a graft copolymer where polybutadiene rubber is grafted to styrene chains, creating a multiphase morphology. This compositional difference results in HIPS exhibiting improved impact resistance and flexibility compared to the more brittle, pure PS.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid, transparent thermoplastic with low impact resistance and moderate tensile strength, commonly used in packaging and disposable items. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) incorporates rubber particles, significantly enhancing its impact resistance and toughness while maintaining good machinability and dimensional stability. Compared to PS, HIPS exhibits higher elongation at break and improved impact strength, making it suitable for applications requiring greater durability and resistance to mechanical stress.
Impact Resistance: PS vs HIPS
Polystyrene (PS) is a rigid and brittle thermoplastic with low impact resistance, making it prone to cracking under stress. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) incorporates rubber particles, significantly enhancing its toughness and impact strength compared to standard PS. This makes HIPS ideal for applications requiring higher durability and resistance to mechanical shocks.
Applications and Industrial Uses
Polystyrene (PS) is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation due to its rigidity and clarity, while High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) offers enhanced durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for automotive parts, appliance housings, and protective packaging. HIPS combines the lightweight and cost-effectiveness of standard PS with improved toughness, expanding its applications in consumer electronics and toys. Industrial uses of PS focus on thermal insulation and food containers, whereas HIPS is preferred in environments requiring tougher mechanical performance and dimensional stability.
Processing and Fabrication Methods
Polystyrene (PS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) differ significantly in processing and fabrication methods due to their molecular structures; PS is typically processed via injection molding and extrusion with ease in producing rigid, clear parts, while HIPS incorporates rubber particles enhancing impact resistance, making it suitable for thermoforming and blow molding with improved toughness. The addition of polybutadiene in HIPS allows for better elongation and impact strength during fabrication, enabling the production of durable consumer goods and packaging materials. Processing parameters such as temperature and cooling rates are carefully controlled in both polymers to optimize mechanical performance and surface finish tailored to their end-use applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polystyrene (PS) is generally more cost-effective than High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) due to its simpler formulation and wider availability in raw materials. HIPS commands a higher price point because of its enhanced impact resistance, achieved by the incorporation of rubber additives, which increases production complexity. Both materials are readily available in global markets, but PS is often preferred for budget-sensitive projects while HIPS suits applications requiring improved durability.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene (PS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) differ significantly in environmental impact and recyclability, with standard PS being more brittle and less versatile in reuse streams, whereas HIPS incorporates rubber additives enhancing durability but complicating recycling processes. HIPS's composite nature often leads to lower recycling rates due to difficulties separating the added elastomer, resulting in increased landfill contribution compared to pure PS. Both materials pose environmental challenges as they degrade slowly, but advanced recycling technologies are focusing on mechanical and chemical recycling methods to improve sustainability for both PS and HIPS waste.
Key Advantages and Limitations of PS and HIPS
Polystyrene (PS) offers excellent clarity, rigidity, and ease of processing, making it ideal for packaging and disposable items, but its brittleness limits impact resistance. High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) combines PS with rubber to enhance toughness and durability, providing superior impact strength suitable for automotive parts and appliances, though it sacrifices some clarity and stiffness. PS excels in cost-effectiveness and aesthetic appeal, whereas HIPS is preferred for applications demanding higher mechanical performance and impact resilience.
Choosing Between PS and HIPS: Factors to Consider
When choosing between PS (Polystyrene) and HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene), consider the mechanical strength and impact resistance required for your application. HIPS offers improved toughness and flexibility compared to standard PS, making it ideal for products exposed to physical stress or requiring durability. Cost efficiency and ease of processing also influence selection, with PS favored for rigid, lightweight packaging and HIPS for more robust, impact-resistant items.
PS vs HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com