Polystyrene insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance, making it a popular choice for pet housing and refrigerated environments. Polyurethane insulation typically provides higher R-values per inch, resulting in superior energy efficiency and better soundproofing properties. Choosing between polystyrene and polyurethane insulation depends on specific application needs, budget constraints, and environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
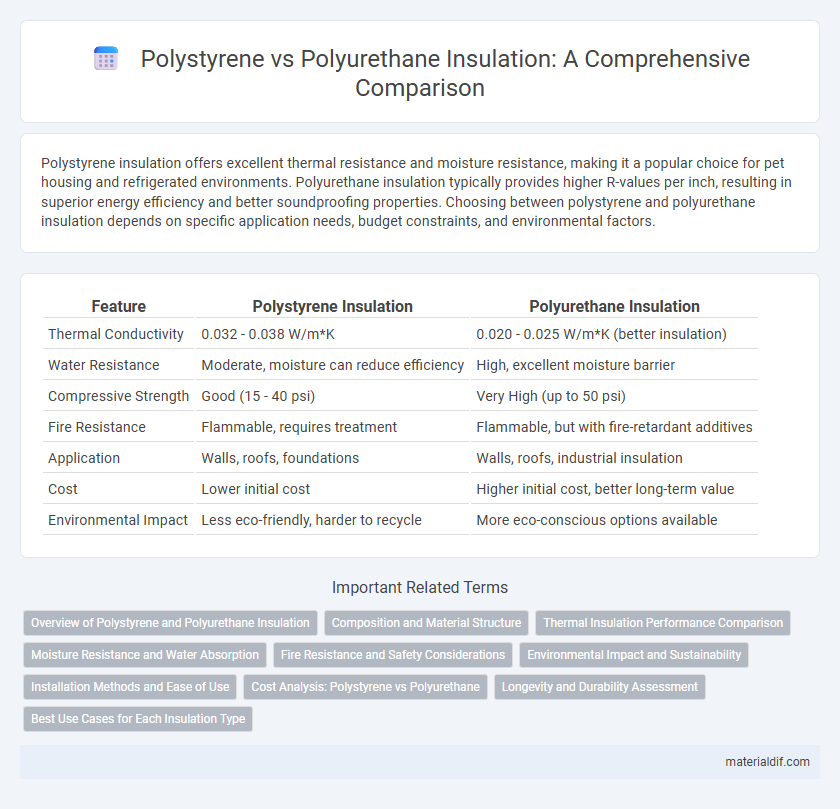
| Feature | Polystyrene Insulation | Polyurethane Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.032 - 0.038 W/m*K | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (better insulation) |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, moisture can reduce efficiency | High, excellent moisture barrier |
| Compressive Strength | Good (15 - 40 psi) | Very High (up to 50 psi) |
| Fire Resistance | Flammable, requires treatment | Flammable, but with fire-retardant additives |
| Application | Walls, roofs, foundations | Walls, roofs, industrial insulation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, better long-term value |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly, harder to recycle | More eco-conscious options available |
Overview of Polystyrene and Polyurethane Insulation
Polystyrene insulation, available as expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, offers excellent moisture resistance and moderate thermal performance with R-values typically ranging from 3.6 to 5 per inch. Polyurethane insulation provides superior thermal resistance with R-values between 6 and 7 per inch, making it more efficient for thermal insulation in building applications. Both materials are widely used for their durability and insulating properties, with polystyrene favored for its cost-effectiveness and moisture resistance, while polyurethane excels in thermal efficiency and adhesive qualities.
Composition and Material Structure
Polystyrene insulation is made from a rigid, closed-cell foam primarily consisting of styrene monomers, offering moderate thermal resistance and moisture resistance through its dense structure. Polyurethane insulation comprises a polymer matrix formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates, resulting in a highly cellular, open or closed-cell material with superior thermal insulating properties due to its low thermal conductivity. The molecular arrangement in polyurethane creates a more efficient barrier against heat transfer compared to the more uniform, solid structure of polystyrene.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polystyrene insulation exhibits a thermal conductivity typically ranging from 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, making it effective for standard insulation needs, while polyurethane insulation offers superior thermal performance with conductivity values as low as 0.022 to 0.028 W/m*K. This significant difference results in polyurethane providing better energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer more effectively, leading to enhanced thermal resistance (R-value) per inch of thickness. The higher R-value of polyurethane insulation makes it the preferred choice for environments demanding stringent thermal control and energy conservation.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polystyrene insulation exhibits low water absorption rates, ranging from 0.1% to 0.5%, making it highly resistant to moisture intrusion and ideal for damp environments. In contrast, polyurethane insulation, while boasting superior thermal resistance, tends to absorb slightly more moisture, generally between 0.5% and 2%, which can affect its insulating performance over time. The closed-cell structure of polystyrene significantly limits water permeability, enhancing durability and maintaining insulation efficacy in wet conditions.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Polystyrene insulation exhibits lower fire resistance compared to polyurethane insulation, as it tends to ignite more easily and produces toxic smoke when burned. Polyurethane insulation offers superior fire retardant properties and releases fewer harmful fumes, making it a safer choice in applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Safety considerations often prioritize polyurethane in building projects due to its enhanced performance in fire resistance tests and compliance with fire safety regulations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene insulation offers moderate thermal performance with lower embodied energy compared to polyurethane insulation, which provides superior thermal resistance but with higher environmental costs due to its petrochemical base and blowing agents. Polystyrene is more recyclable and generates less greenhouse gas emissions during production, while polyurethane's durability and energy-saving benefits can offset its initial environmental impact over time. Choosing between them requires balancing immediate sustainability metrics against long-term energy efficiency and lifecycle carbon footprint.
Installation Methods and Ease of Use
Polystyrene insulation typically comes in rigid foam boards that are easy to cut and install using adhesive or mechanical fasteners, making it suitable for both walls and floors. Polyurethane insulation often requires spraying or foaming in place, demanding professional application for optimal results and precise coverage. The ease of installation favors polystyrene for DIY projects, while polyurethane provides superior air-sealing but involves more complex installation techniques.
Cost Analysis: Polystyrene vs Polyurethane
Polystyrene insulation typically costs between $0.30 and $0.50 per square foot, making it a more affordable option compared to polyurethane insulation, which ranges from $0.50 to $0.90 per square foot. Polystyrene offers lower upfront material costs but has a lower R-value per inch, around 3.6 to 4.2, whereas polyurethane insulation boasts a higher R-value of approximately 6 to 7, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, initial investment in polystyrene is budget-friendly, while polyurethane may provide greater savings through enhanced thermal efficiency over time.
Longevity and Durability Assessment
Polystyrene insulation offers moderate longevity and durability, maintaining structural integrity for 20-30 years under typical conditions. Polyurethane insulation outperforms polystyrene with a longer lifespan, often exceeding 30 years, due to its superior resistance to moisture, compression, and thermal degradation. The enhanced durability of polyurethane results in sustained insulation performance and reduced maintenance costs over time.
Best Use Cases for Each Insulation Type
Polystyrene insulation offers excellent moisture resistance and is ideal for below-grade applications such as foundation walls and basements, where durability and water resistance are critical. Polyurethane insulation provides superior thermal resistance with higher R-values per inch, making it best suited for tight spaces and areas requiring maximum energy efficiency, such as roofs and walls in cold climates. Each insulation type maximizes performance by addressing specific environmental challenges and structural needs unique to residential and commercial construction projects.
Polystyrene Insulation vs Polyurethane Insulation Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com