Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) incorporates specialized additives that significantly enhance its resistance to ignition and slow down the spread of fire compared to standard PS. This modification makes flame-retardant PS ideal for applications requiring strict fire safety standards, such as in construction and electronics. In contrast, standard PS lacks these properties and poses a higher risk of rapid combustion and toxic smoke production under fire conditions.
Table of Comparison
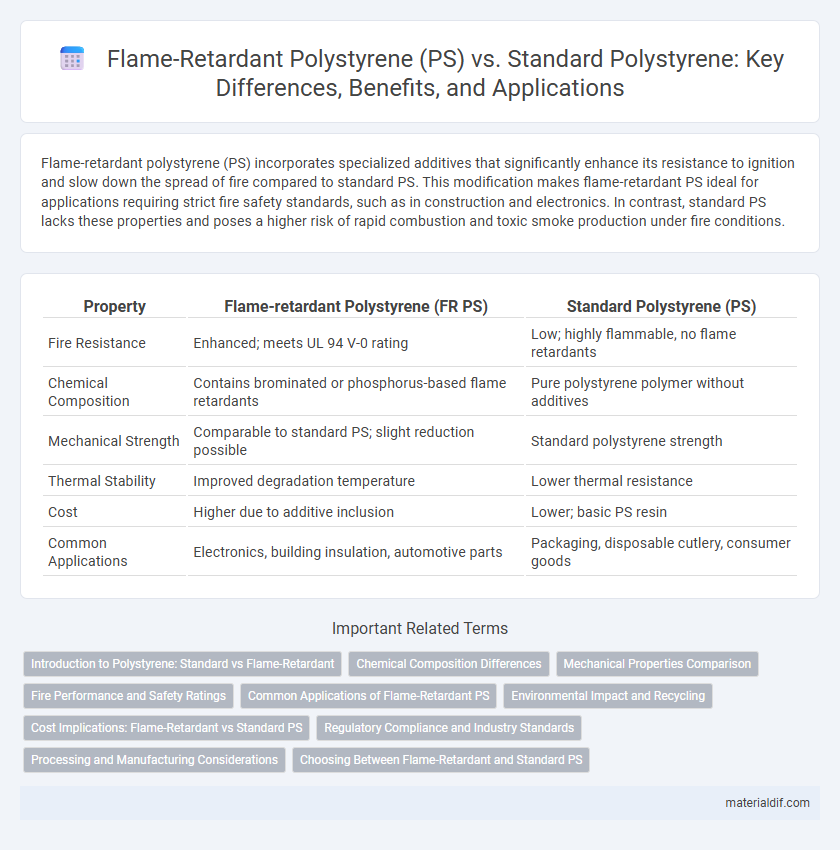
| Property | Flame-retardant Polystyrene (FR PS) | Standard Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Enhanced; meets UL 94 V-0 rating | Low; highly flammable, no flame retardants |
| Chemical Composition | Contains brominated or phosphorus-based flame retardants | Pure polystyrene polymer without additives |
| Mechanical Strength | Comparable to standard PS; slight reduction possible | Standard polystyrene strength |
| Thermal Stability | Improved degradation temperature | Lower thermal resistance |
| Cost | Higher due to additive inclusion | Lower; basic PS resin |
| Common Applications | Electronics, building insulation, automotive parts | Packaging, disposable cutlery, consumer goods |
Introduction to Polystyrene: Standard vs Flame-Retardant
Polystyrene (PS) exists in standard and flame-retardant variants, each designed for specific applications. Standard PS offers excellent clarity and insulation properties but has limited fire resistance, making it suitable for packaging and disposable containers. Flame-retardant PS incorporates additive compounds like brominated flame retardants or phosphorus-based agents to enhance fire resistance, ensuring compliance with safety regulations in electronics, construction, and automotive industries.
Chemical Composition Differences
Flame-retardant polystyrene (FR-PS) contains halogenated or phosphorus-based additives that chemically inhibit combustion by interrupting the radical chain reactions during burning, unlike standard polystyrene which lacks these flame-retardant compounds. The inclusion of these flame-retardant agents alters the polymer matrix, often incorporating compounds such as decabromodiphenyl ether or ammonium polyphosphate to enhance thermal stability and reduce flammability. Standard polystyrene primarily consists of linear hydrocarbon chains, making it more susceptible to ignition and rapid flame propagation.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) typically exhibits reduced mechanical strength and impact resistance compared to standard PS due to the incorporation of flame retardant additives that can alter the polymer matrix. Standard PS maintains higher tensile strength, flexural modulus, and elongation at break, making it preferable for applications demanding mechanical durability. The trade-off between flame retardancy and mechanical performance necessitates careful material selection based on the specific requirements of use cases such as electrical housings or consumer products.
Fire Performance and Safety Ratings
Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) significantly enhances fire performance compared to standard PS by incorporating fire-resistant additives that reduce flammability and slow combustion. Fire safety ratings for flame-retardant PS typically meet or exceed UL 94 V-0 standards, indicating rapid self-extinguishing properties and minimal drip flammability. In contrast, standard PS usually has lower fire resistance, classified as UL 94 HB or no rating, posing greater risks in fire safety-critical applications.
Common Applications of Flame-Retardant PS
Flame-retardant polystyrene is frequently used in electrical and electronic housings, where enhanced fire safety standards are critical to prevent ignition and propagation of flames. It is also common in building and construction materials such as insulation panels and decorative moldings, offering improved fire resistance compared to standard polystyrene. These applications benefit from flame-retardant additives that help meet rigorous fire codes and safety regulations in commercial and residential environments.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) typically contains additives that enhance fire resistance but can complicate recycling processes and increase environmental toxicity compared to standard PS. Standard polystyrene is more widely recyclable and generally has a lower environmental impact due to fewer chemical additives, facilitating easier mechanical recycling. The presence of flame retardants in PS often results in challenges during waste management, causing potential release of harmful compounds during incineration or landfill degradation.
Cost Implications: Flame-Retardant vs Standard PS
Flame-retardant polystyrene incurs higher production costs due to the incorporation of specialized additives that enhance fire resistance. Standard polystyrene remains more economical, making it preferable for applications where flame resistance is not critical. Budget considerations often drive the choice between these materials, balancing safety requirements against overall project expenses.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) is formulated to meet stringent regulatory compliance such as UL 94 V-0 flammability standards and REACH regulations, ensuring enhanced fire safety in consumer and industrial applications. Standard PS does not typically comply with these rigorous fire resistance requirements, limiting its use in environments with strict fire safety codes. Industry standards like ASTM E84 also differentiate flame-retardant PS for superior performance in fire test ratings, making it the preferred choice for construction and electronics sectors.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Flame-retardant polystyrene (FR-PS) requires modified processing parameters due to the incorporation of flame-retardant additives which can affect melt flow and viscosity, necessitating adjustments in extrusion and injection molding conditions. The presence of these additives may also influence thermal stability and compound homogeneity, requiring thorough mixing and potential changes in processing temperatures to prevent degradation. Manufacturing considerations for FR-PS include selecting compatible flame retardants that maintain mechanical properties while ensuring compliance with fire safety standards, potentially increasing production complexity compared to standard polystyrene.
Choosing Between Flame-Retardant and Standard PS
Flame-retardant polystyrene (PS) incorporates chemical additives that significantly reduce its flammability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced fire safety such as electronics housings and building insulation. Standard PS, while offering excellent clarity and rigidity at a lower cost, lacks these fire-resistant properties and is more suitable for packaging and disposable products where flame resistance is not critical. Choosing between flame-retardant and standard PS depends on balancing safety regulations, fire hazard risk, and budget constraints in the intended application.
Flame-retardant PS vs Standard PS Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com