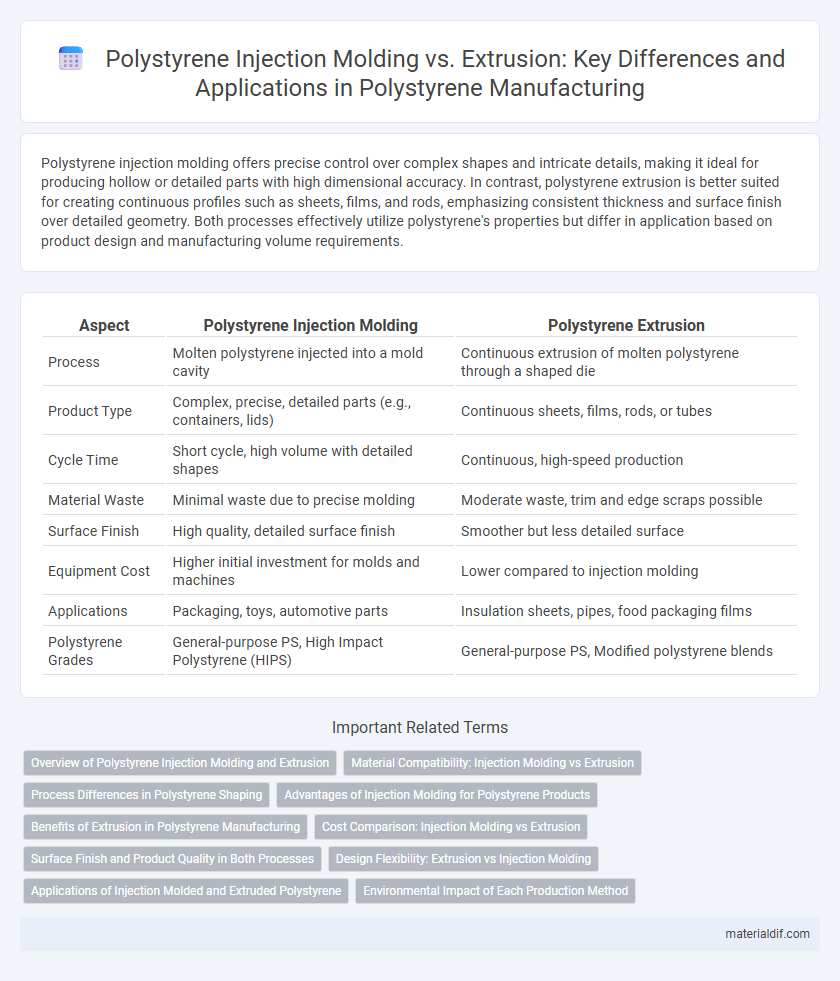
Polystyrene injection molding offers precise control over complex shapes and intricate details, making it ideal for producing hollow or detailed parts with high dimensional accuracy. In contrast, polystyrene extrusion is better suited for creating continuous profiles such as sheets, films, and rods, emphasizing consistent thickness and surface finish over detailed geometry. Both processes effectively utilize polystyrene's properties but differ in application based on product design and manufacturing volume requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Polystyrene Injection Molding | Polystyrene Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molten polystyrene injected into a mold cavity | Continuous extrusion of molten polystyrene through a shaped die |
| Product Type | Complex, precise, detailed parts (e.g., containers, lids) | Continuous sheets, films, rods, or tubes |
| Cycle Time | Short cycle, high volume with detailed shapes | Continuous, high-speed production |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to precise molding | Moderate waste, trim and edge scraps possible |
| Surface Finish | High quality, detailed surface finish | Smoother but less detailed surface |
| Equipment Cost | Higher initial investment for molds and machines | Lower compared to injection molding |
| Applications | Packaging, toys, automotive parts | Insulation sheets, pipes, food packaging films |
| Polystyrene Grades | General-purpose PS, High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) | General-purpose PS, Modified polystyrene blends |
Overview of Polystyrene Injection Molding and Extrusion
Polystyrene injection molding involves injecting molten polystyrene into a mold cavity to create precise, complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy, commonly used for producing detailed components like containers and casings. Polystyrene extrusion, by contrast, forces melted polystyrene through a die to form continuous profiles such as sheets, films, or tubes, suited for large-scale production with consistent cross-sectional geometry. Both processes leverage polystyrene's thermoplastic properties but differ fundamentally in output form, production speed, and application versatility.
Material Compatibility: Injection Molding vs Extrusion
Polystyrene injection molding offers precise control over complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for detailed components, while extrusion is better suited for continuous profiles and sheets with consistent cross-sections. Injection molding requires polystyrene grades with higher flow properties for intricate mold filling, whereas extrusion benefits from polystyrene resins with thermal stability to withstand continuous heat exposure. Material compatibility in injection molding emphasizes uniform melt flow and rapid cooling, whereas extrusion demands responsiveness to shear stress and sustained thermal processing.
Process Differences in Polystyrene Shaping
Polystyrene injection molding involves heating the polymer until molten and injecting it into a mold cavity under high pressure, allowing for complex and precise shapes with fine details. In contrast, polystyrene extrusion forces molten polymer through a die to create continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, suitable for producing sheets, films, or rods. Injection molding offers rapid cooling and solidification within molds, while extrusion relies on downstream cooling methods such as air or water baths to stabilize shaped polystyrene products.
Advantages of Injection Molding for Polystyrene Products
Injection molding offers superior precision and consistency in producing complex polystyrene parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances. The process enables high production rates and efficient material use, leading to reduced waste and lower overall costs compared to extrusion. This method also allows for enhanced surface finish and the integration of detailed features, making it ideal for manufacturing durable, high-quality polystyrene components.
Benefits of Extrusion in Polystyrene Manufacturing
Polystyrene extrusion offers continuous production, enabling high-volume manufacturing with consistent material properties and uniform thickness. This process enhances design flexibility for creating complex profiles and sheets used in packaging, insulation, and consumer products. Moreover, extrusion reduces material waste and operational costs compared to injection molding by minimizing cycle times and simplifying tooling requirements.
Cost Comparison: Injection Molding vs Extrusion
Polystyrene injection molding typically incurs higher initial tooling costs due to the complexity of molds, but offers lower per-unit costs for high-volume production runs. Extrusion requires less expensive equipment and tooling, making it cost-effective for continuous profiles and simpler shapes, especially in medium to low volumes. Evaluating production volume and part complexity is essential for optimizing overall cost-effectiveness between polystyrene injection molding and extrusion processes.
Surface Finish and Product Quality in Both Processes
Polystyrene injection molding delivers superior surface finish with high gloss and intricate detailing due to controlled mold temperature and pressure, producing products with excellent dimensional accuracy and consistent quality. In contrast, polystyrene extrusion tends to produce products with lower surface smoothness and less detailed features, as the process involves continuous shaping with cooling that may cause surface roughness or flow lines. Injection molding is preferred for high-quality, aesthetically demanding items, while extrusion suits large-scale production of simple shapes with moderate surface finish requirements.
Design Flexibility: Extrusion vs Injection Molding
Polystyrene injection molding offers superior design flexibility, enabling the creation of intricate, complex shapes with high precision and detailed surface finishes. In contrast, polystyrene extrusion is limited to producing continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, making it less suitable for complex geometries. This makes injection molding the preferred choice for applications requiring detailed and customized polystyrene components.
Applications of Injection Molded and Extruded Polystyrene
Injection molded polystyrene is widely used for producing complex, high-precision parts such as disposable cutlery, cosmetic containers, and electronic housings due to its ability to create detailed shapes and fine surface finishes. Extruded polystyrene, typically available as foam boards, excels in insulation applications for building construction, packaging, and cushioning materials because of its uniform density and thermal resistance. The distinct manufacturing processes result in variations in mechanical properties and cost-efficiency tailored to specific industrial and consumer needs.
Environmental Impact of Each Production Method
Polystyrene injection molding and extrusion differ significantly in their environmental impact due to energy consumption and material waste. Injection molding typically produces less waste through precise material usage and allows for better recycling of scrap, while extrusion often results in continuous operation but more potential material loss during start-up and shutdown phases. Both processes emit greenhouse gases, but injection molding's energy-intensive machinery may lead to higher carbon emissions compared to the generally lower-energy extrusion process.
Polystyrene injection molding vs Polystyrene extrusion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com