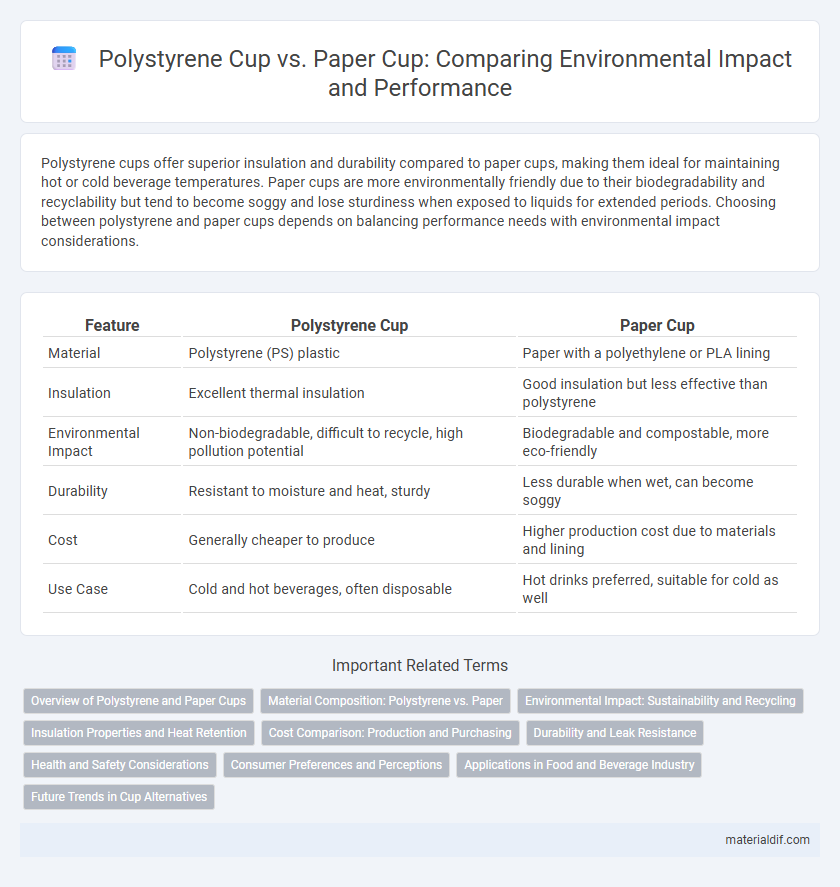
Polystyrene cups offer superior insulation and durability compared to paper cups, making them ideal for maintaining hot or cold beverage temperatures. Paper cups are more environmentally friendly due to their biodegradability and recyclability but tend to become soggy and lose sturdiness when exposed to liquids for extended periods. Choosing between polystyrene and paper cups depends on balancing performance needs with environmental impact considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polystyrene Cup | Paper Cup |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polystyrene (PS) plastic | Paper with a polyethylene or PLA lining |
| Insulation | Excellent thermal insulation | Good insulation but less effective than polystyrene |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, difficult to recycle, high pollution potential | Biodegradable and compostable, more eco-friendly |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture and heat, sturdy | Less durable when wet, can become soggy |
| Cost | Generally cheaper to produce | Higher production cost due to materials and lining |
| Use Case | Cold and hot beverages, often disposable | Hot drinks preferred, suitable for cold as well |
Overview of Polystyrene and Paper Cups
Polystyrene cups are made from a synthetic aromatic polymer, offering excellent insulation and durability for hot and cold beverages, while paper cups consist of cellulose fibers layered with a thin plastic lining to prevent leaks. Polystyrene provides superior thermal retention and rigidity but presents environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature. Paper cups are more eco-friendly, biodegradable, and widely recyclable, though they often lack the same heat retention properties as polystyrene cups.
Material Composition: Polystyrene vs. Paper
Polystyrene cups are composed of synthetic polymer derived from the polymerization of styrene monomers, offering lightweight and insulating properties but with limited biodegradability. Paper cups are primarily made from cellulose fibers sourced from wood pulp, often lined with polyethylene or biodegradable coatings to prevent leakage while enhancing durability. The material composition significantly impacts environmental footprint, with paper cups generally favored for recyclability and compostability compared to the plastic-based polystyrene.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Recycling
Polystyrene cups, made from non-biodegradable plastic, pose significant environmental challenges due to their persistence in landfills and difficulty in recycling, leading to increased pollution and resource depletion. Paper cups, often lined with polyethylene for waterproofing, complicate recycling efforts and require substantial water and energy during production, but they generally decompose faster than polystyrene. Sustainable alternatives include compostable paper cups certified for industrial composting and increased adoption of reusable beverage containers to minimize waste and reduce environmental footprints.
Insulation Properties and Heat Retention
Polystyrene cups offer superior insulation properties due to their closed-cell foam structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer, effectively maintaining beverage temperature longer than paper cups. Paper cups, often lined with polyethylene, provide moderate heat retention but dissipate heat faster because their cellulose fibers conduct heat more readily. For hot beverages requiring extended warmth, polystyrene cups outperform paper cups in minimizing heat loss and enhancing user comfort.
Cost Comparison: Production and Purchasing
Polystyrene cups generally have a lower production cost due to inexpensive raw materials and efficient manufacturing processes, making them more affordable for large-scale purchase. Paper cups involve higher material costs and more complex production steps, increasing their overall price. Bulk buying of polystyrene cups often results in better cost savings compared to paper cups, despite environmental considerations.
Durability and Leak Resistance
Polystyrene cups offer superior durability due to their rigid, non-porous structure, making them resistant to cracking and deformation under pressure. Their inherent waterproof properties ensure excellent leak resistance compared to paper cups, which can weaken and absorb moisture over time. This makes polystyrene cups ideal for hot and cold beverages where spill prevention is critical.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polystyrene cups contain styrene, a chemical linked to potential health risks such as respiratory issues and skin irritation, especially when exposed to high temperatures or acidic beverages. In contrast, paper cups, often lined with polyethylene, pose fewer chemical hazards but may leach chemicals if coated with harmful additives. Both cup types present environmental concerns; however, from a health and safety perspective, paper cups generally offer a safer option for hot or acidic drinks.
Consumer Preferences and Perceptions
Polystyrene cups are favored for their superior insulation and durability, appealing to consumers seeking to keep beverages hot or cold longer. Paper cups are perceived as more environmentally friendly, attracting eco-conscious buyers despite sometimes lacking the thermal retention of polystyrene. Consumer preferences increasingly hinge on balancing performance benefits with sustainability concerns, influencing purchasing decisions in both commercial and residential settings.
Applications in Food and Beverage Industry
Polystyrene cups provide excellent insulation and durability for hot and cold beverages, making them a popular choice in fast-food chains and coffee shops. Paper cups offer better environmental benefits due to their biodegradability, often favored by eco-conscious cafes and event organizers. Both materials serve distinct roles in the food and beverage industry, balancing consumer convenience with sustainability goals.
Future Trends in Cup Alternatives
Polystyrene cups, widely used for their insulation properties, face increasing restrictions due to environmental concerns and poor biodegradability. Future trends favor paper cups enhanced with biodegradable coatings and plant-based polymers to improve sustainability while maintaining durability and thermal insulation. Innovations in compostable materials and advances in recycling technologies are driving a shift towards eco-friendly cup alternatives that reduce plastic waste and carbon footprint.
Polystyrene Cup vs Paper Cup Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com