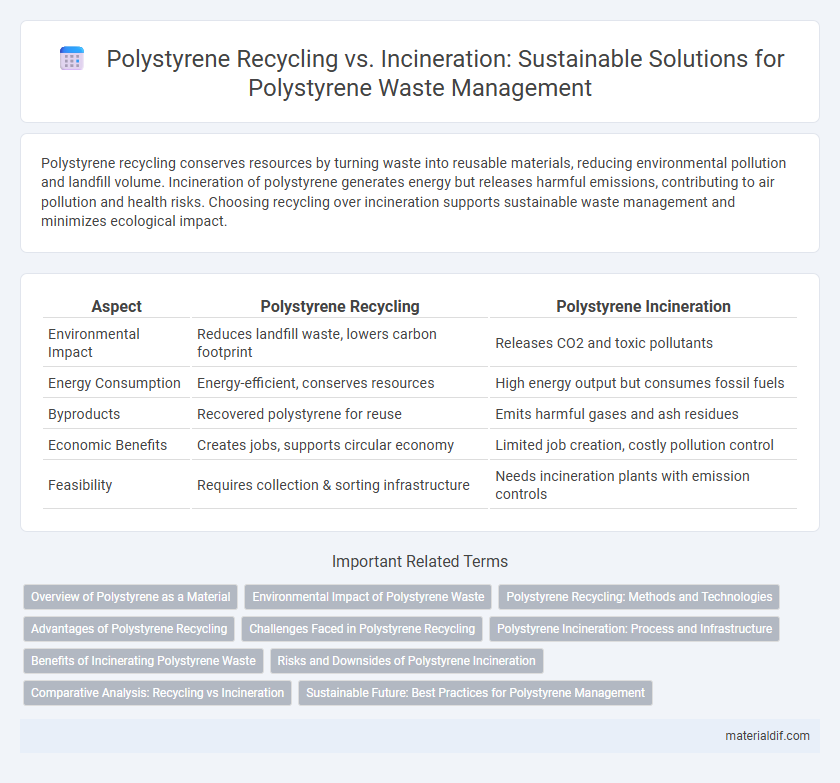
Polystyrene recycling conserves resources by turning waste into reusable materials, reducing environmental pollution and landfill volume. Incineration of polystyrene generates energy but releases harmful emissions, contributing to air pollution and health risks. Choosing recycling over incineration supports sustainable waste management and minimizes ecological impact.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Polystyrene Recycling | Polystyrene Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers carbon footprint | Releases CO2 and toxic pollutants |
| Energy Consumption | Energy-efficient, conserves resources | High energy output but consumes fossil fuels |
| Byproducts | Recovered polystyrene for reuse | Emits harmful gases and ash residues |
| Economic Benefits | Creates jobs, supports circular economy | Limited job creation, costly pollution control |
| Feasibility | Requires collection & sorting infrastructure | Needs incineration plants with emission controls |
Overview of Polystyrene as a Material
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, insulation, and disposable food containers due to its lightweight and insulating properties. Recycling polystyrene involves melting and reforming it into new products, which conserves resources and reduces environmental impact compared to incineration. Incineration of polystyrene generates energy but emits harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases, making recycling a more sustainable option for managing this material.
Environmental Impact of Polystyrene Waste
Polystyrene recycling significantly reduces environmental pollution by diverting non-biodegradable waste from landfills and decreasing the demand for virgin petroleum-based resources. In contrast, polystyrene incineration releases toxic emissions such as styrene gas and dioxins, contributing to air pollution and posing health risks to surrounding communities. Implementing widespread recycling programs can mitigate the ecological footprint of polystyrene waste more effectively than incineration methods.
Polystyrene Recycling: Methods and Technologies
Polystyrene recycling primarily involves mechanical recycling, where clean polystyrene waste is shredded, melted, and reformed into new products, and chemical recycling methods such as depolymerization, which breaks polystyrene back into its monomer, styrene, for repolymerization. Advanced technologies include solvent-based recycling, which uses selective solvents to dissolve polystyrene selectively, enabling the recovery of high-purity polymers. Compared to incineration, recycling methods reduce environmental pollution and conserve petroleum resources by enabling closed-loop reuse of polystyrene materials.
Advantages of Polystyrene Recycling
Polystyrene recycling reduces environmental pollution by diverting waste from landfills and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to incineration. It enables the recovery of valuable materials that can be reused in manufacturing, conserving resources and energy. Recycling polystyrene also minimizes the release of toxic compounds, such as styrene monomers and dioxins, typically associated with incineration processes.
Challenges Faced in Polystyrene Recycling
Polystyrene recycling faces significant challenges due to its low density and contamination risks, which increase collection and processing costs. The material's lightweight nature makes transportation economically inefficient, while contamination from food residues reduces the quality of recycled output. These obstacles contribute to low recycling rates, often leading to polystyrene waste being diverted to incineration or landfills.
Polystyrene Incineration: Process and Infrastructure
Polystyrene incineration involves the controlled combustion of polystyrene waste to reduce volume and generate energy, requiring specialized high-temperature furnaces equipped with advanced emission control systems to mitigate the release of toxic pollutants like styrene and dioxins. Incineration infrastructure typically includes gas scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and continuous emission monitoring systems to comply with environmental regulations and ensure air quality standards. This process offers rapid waste reduction but demands significant investment in technology and strict operational protocols to minimize environmental impact compared to recycling methods.
Benefits of Incinerating Polystyrene Waste
Incinerating polystyrene waste significantly reduces landfill volume, converting material into energy through waste-to-energy technology and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional disposal. This process also mitigates long-term environmental pollution by eliminating persistent plastic residues that are challenging to recycle due to contamination and low economic value. Furthermore, incineration recovers thermal energy, contributing to renewable energy production and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Risks and Downsides of Polystyrene Incineration
Polystyrene incineration releases hazardous pollutants such as styrene gas, benzene, and dioxins, which pose serious health risks including respiratory issues and increased cancer risk. The process contributes to air pollution and environmental contamination due to the emission of toxic substances and persistent organic pollutants. Unlike recycling, incineration wastes valuable resources and results in the loss of material that could otherwise be processed into new products.
Comparative Analysis: Recycling vs Incineration
Polystyrene recycling conserves resources by transforming waste into reusable materials, significantly reducing landfill volume and lowering carbon emissions compared to incineration, which generates harmful pollutants such as dioxins and heavy metals. Recycling processes, including mechanical and chemical recycling, enable recovery of polystyrene's polymer chains, maintaining material quality and supporting circular economy initiatives. In contrast, incineration yields energy recovery but poses environmental risks from toxic byproducts and requires advanced emission controls, making recycling the more sustainable option for managing polystyrene waste.
Sustainable Future: Best Practices for Polystyrene Management
Polystyrene recycling conserves resources by transforming waste into reusable materials, significantly reducing landfill volumes and environmental pollution. Incineration, while effective in energy recovery, generates harmful emissions and toxic residues that challenge sustainable waste management goals. Prioritizing advanced recycling technologies and developing circular economy strategies ensure a sustainable future for polystyrene management by minimizing ecological impact and maximizing material recovery.
Polystyrene Recycling vs Polystyrene Incineration Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com